Section: Verbal Ability
Question 1
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option.
If they want to succeed, they ______ have to work very hard.
If they want to succeed, they ______ have to work very hard.
C will
The appropriate form of the verb is the simple future tense ‘will have’ as it describes a future action.
Question 2
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option.
She stood ______ Amit, but could not utter a single word for quite some time.
She stood ______ Amit, but could not utter a single word for quite some time.
D before
The preposition “before” is appropriate here. To ‘stand before’ someone means to ‘stand in front of someone’.
Question 3
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option.
Kanak is endowed _______ many great qualities.
Kanak is endowed _______ many great qualities.
B with
The preposition “with” is appropriate when used with the verb ‘endowed’.
Question 4
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option.
The doctor advised him to go ______ several medical tests.
The doctor advised him to go ______ several medical tests.
B through
The correct preposition with the verb ‘go’ here is “through”. To ‘go through’ something is to ‘experience or do’ something.
Question 5
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option.
You have played a great role, for _______ your help I possibly would have landed myself into a problem.
You have played a great role, for _______ your help I possibly would have landed myself into a problem.
A without
The correct conjunction to be used here is ‘without’. It correctly expresses the fact that in the absence of something things would not have been the same.
Question 6
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option.
The passengers were very happy _______ the friendly and warm treatment.
The passengers were very happy _______ the friendly and warm treatment.
C about
The correct preposition here is ‘about’. Generally people are happy ‘about’ something.
Question 7
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option.
We shall fail _______ we are industrious.
We shall fail _______ we are industrious.
A unless
The correct conjunction here is ‘unless’ which conveys the meaning that “if we are not industrious, we will fail”.
Question 8
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option.
Sunita decided to set ______ some time every day for prayers.
Sunita decided to set ______ some time every day for prayers.
B aside
The correct preposition here is ‘aside’. It is usually common to ‘set aside’ time for some task, which means that ‘time has been allocated/apportioned for that task’.
Question 9
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option.
The minister flew ______ the flooded areas in a helicopter.
The minister flew ______ the flooded areas in a helicopter.
D over
When flying in a helicopter, one ‘flies over’ an area. Hence the appropriate preposition here would be ‘over’.
Question 10
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option.
Would anybody ______ a mother have risked her life for the baby?
Would anybody ______ a mother have risked her life for the baby?
A but
The correct conjunction here would be ‘but’. The sentence questions whether ‘anyone besides a mother would have risked here life for the baby’?
Question 11
The most likely reason for the acceptance of the WTO package by nations was that:
A They recognized the need for a rule-based environment to protect the benefits of increased trade.
Choices 1 and 3 and close choices. In paragraph two the author states that “Finally, and perhaps most important, many countries at the Uruguay Round came to put a higher priority on the export gains than on the import losses that the negotiation would produce, and they came to associate the WTO and a rule based system with those gains” this would make “3” as correct answer. However in the same paragraph the author further states – “This reasoning – replicated in many countries – was contained in U. S. Ambassador Kantor’s defence of the WTO, and it announced to a recognition that international trade and its benefits cannot be enjoyed unless trading nations accept the discipline of a negotiated rule based environment”. This summarizes the rationale behind WTO and makes “1” a better choice.
Question 12
In the method of interpretation of the European Court of Justice:
A Actions against member states needed to be evaluated against the said community goals.
Paragraph 4 “One means the Court used to expand integration was the ‘teleological method of interpretation’, whereby the actions of member states were evaluated against ‘the accomplishment of the most elementary goals set forth in the Preamble to the (Rome) treaty. The teleological method represents an effort to keep current policies consistent with slated goals” – this makes “1” the correct answer.
Question 13
According to the passage, WTO promoted the technical legal values partly through.
D Integrating under one roof the agreements signed under GATT.
In the last para the author states “The WTO codified the GATT institutional practice that had developed by custom over three decades, and it incorporated a new dispute settlement system that was necessary to keep both old and new rules from becoming a sham” – this makes choice “4” the correct answer.
Question 14
What would be the closest reason why WTO was not formed in 1970s?
B Important players did not find it in their best interest to do so.
The author does mention that WTO could have been negotiated as part of the Tokyo Round of the 1970s. So what could be the reason for WTO’s not getting formed in 1970s? The author further states the reason that helped its creation in the 1990s’. So it would be a safe assumption that the benefits anticipated in the 1990s’ were not anticipated in the 1970s’. One of the benefits citied by the author is that important players found WTO to be in their own interests in 1990s’. So it’s quite possible they did not find WTOs’ formation in their own interest in the 1970s’.
Question 15
In the statement ‘... it amounted to a recognition that international trade and its benefits cannot be enjoyed unless trading nations accept the discipline of a negotiated rule-based environment’, it refers to:
C The export gains many countries came to associate with a rule-based system.
In paragraph two the benefit anticipated are the export gains.
Question 16
In each of the following sentences, some part of the sentence or the entire sentence is underlined. Beneath each sentence, you will find four ways of phrasing the underlined part. Choose the most appropriate option given in each of the sentences given below that is the best version than the underlined part of the sentence
During her lecture, the speaker tried to clarify directional terms, for not everyone in attendance was knowledgeable that winds are designed by the direction from which they come.
During her lecture, the speaker tried to clarify directional terms, for not everyone in attendance was knowledgeable that winds are designed by the direction from which they come.
D For not everyone attending knew.
The phrase ‘not everyone in attendance was knowledgeable’ means that while some did know about this, not everyone knew. This meaning is best conveyed by option d.
Question 17
In each of the following sentences, some part of the sentence or the entire sentence is underlined. Beneath each sentence, you will find four ways of phrasing the underlined part. Choose the most appropriate option given in each of the sentences given below that is the best version than the underlined part of the sentence
Two valence states of uranium, one with a deficit of four electrons and the other one with a deficit of six occurs in nature and contributes to the diversity of uranium’s behaviour.
Two valence states of uranium, one with a deficit of four electrons and the other one with a deficit of six occurs in nature and contributes to the diversity of uranium’s behaviour.
A the other with a deficit of six, occur in Nature and contribute
The subject of this sentence ‘Two valence states of uranium’ is a plural one and hence the verbs should also be plural to agree with it. Hence options c and d can be ruled out. Also, in option b the preposition ‘with’ is missing.
Question 18
In each of the following sentences, some part of the sentence or the entire sentence is underlined. Beneath each sentence, you will find four ways of phrasing the underlined part. Choose the most appropriate option given in each of the sentences given below that is the best version than the underlined part of the sentence
Plausible though it sounds, the weakness of the hypothesis is that it does not incorporate all relevant facts.
Plausible though it sounds, the weakness of the hypothesis is that it does not incorporate all relevant facts.
A though the hypothesis sounds plausible, its weakness
There are two ideas being expressed in this sentence:
- Firstly that the hypothesis sounds plausible and
- Secondly it tell us what the weakness of the hypothesis is
Question 19
In each of the following sentences, some part of the sentence or the entire sentence is underlined. Beneath each sentence, you will find four ways of phrasing the underlined part. Choose the most appropriate option given in each of the sentences given below that is the best version than the underlined part of the sentence
Many of them chiselled from solid rock centuries ago the mountainous regions are dotted with hundreds of monasteries:
Many of them chiselled from solid rock centuries ago the mountainous regions are dotted with hundreds of monasteries:
A The mountainous regions are dotted with hundreds of monasteries, many of them chiselled from solid rock centuries ago.
The phrase ‘many of them chiselled from solid rock centuries ago’ is a modifier that describes the noun “monasteries”. Hence it should be placed right next to this noun.
In option b, the verb tense is incorrect as ‘are dotting’ in the present continuous refers to an action that is currently happening.
In option c, the verb tense is incorrect as ‘are chisseled’ in the simple present refers to this action as a habitual or regular one.
In option d, the phrase ‘chiselled from solid rock centuries ago’ modifies or describes the noun ‘mountainous regions’.
In option b, the verb tense is incorrect as ‘are dotting’ in the present continuous refers to an action that is currently happening.
In option c, the verb tense is incorrect as ‘are chisseled’ in the simple present refers to this action as a habitual or regular one.
In option d, the phrase ‘chiselled from solid rock centuries ago’ modifies or describes the noun ‘mountainous regions’.
Question 20
In each of the following sentences, some part of the sentence or the entire sentence is underlined. Beneath each sentence, you will find four ways of phrasing the underlined part. Choose the most appropriate option given in each of the sentences given below that is the best version than the underlined part of the sentence
Initiative and referendum, is a procedure that allows voters to propose and pass laws as well as to repeal them.
Initiative and referendum, is a procedure that allows voters to propose and pass laws as well as to repeal them.
D allows voters to propose, pass and to repeal laws
Here option a, the preposition ‘on’ has been incorrectly used with ‘law’.
In option b, the meaning is changed due to the expression ‘to propose to pass’.
In option c, the singular countable noun “voter” is unaccompanied by an article so this option is incorrect.
Hence the best choice is option d.
In option b, the meaning is changed due to the expression ‘to propose to pass’.
In option c, the singular countable noun “voter” is unaccompanied by an article so this option is incorrect.
Hence the best choice is option d.
Question 21
Choose the correct spellings in options given below.
D Gallows
Gallows
Question 22
Choose the correct spellings in options given below.
B Remuneration
Remuneration
Question 23
Choose the correct spellings in options given below.
D Blasphemy
Blasphemy
Question 24
Choose the correct spellings in options given below.
C Accommodation
Accommodation
Question 25
Choose the correct spellings in options given below.
C Annulment
Annulment
Question 26
Choose the correct spellings in options given below.
C Hypothecation
Hypothecation
Question 27
Choose the correct spellings in options given below.
D Gratuitous
Gratuitous
Question 28
Choose the correct spellings in options given below.
D Interrogation
Interrogation
Question 29
Choose the correct spellings in options given below.
A Moratorium
Moratorium
Question 30
Choose the correct spellings in options given below.
C Abeyance
Abeyance
Question 31
In each of the following sentences four words or phrases are underlined. If there is any mistake with regard to grammar or usage, it is in the underlined part only. Identify the incorrect part.
After being finished (A) the (B) last chapter of the book, return it (C) to me. (D)
After being finished (A) the (B) last chapter of the book, return it (C) to me. (D)
A A
The verb here is expressed in the passive form ‘being finished’. Instead it should be in the active form and the present continuous tense i.e. ‘finishing’.
Question 32
In each of the following sentences four words or phrases are underlined. If there is any mistake with regard to grammar or usage, it is in the underlined part only. Identify the incorrect part.
Five gallons of (A) petrol are (B) not enough (C) to cover the distance. (D)
Five gallons of (A) petrol are (B) not enough (C) to cover the distance. (D)
C B
Here the subject is ‘Five gallons of petrol’ which is a verb phrase. Hence it is treated as a singular subject and the verb should also be singular i.e. ‘is’ instead of ‘are’.
Question 33
In each of the following sentences four words or phrases are underlined. If there is any mistake with regard to grammar or usage, it is in the underlined part only. Identify the incorrect part.
Evidently (A) our product is the most (B) unique in (C) the market. (D)
Evidently (A) our product is the most (B) unique in (C) the market. (D)
A B
This is a case of redundancy – the adjective ‘unique’ means ‘one of a kind’, so it cannot be used in the superlative form ‘the most’.
Question 34
In each of the following sentences four words or phrases are underlined. If there is any mistake with regard to grammar or usage, it is in the underlined part only. Identify the incorrect part.
On listening (A) to the confession of love (B) she blushed until (C) she was purple. (D)
On listening (A) to the confession of love (B) she blushed until (C) she was purple. (D)
D C
The correct expression is ‘blushed until she was red’.
Question 35
In each of the following sentences four words or phrases are underlined. If there is any mistake with regard to grammar or usage, it is in the underlined part only. Identify the incorrect part.
Since (A) I have forgotten (B) all the equations I will have (C) to start from the scratch. (D)
Since (A) I have forgotten (B) all the equations I will have (C) to start from the scratch. (D)
D D
The correct expression is ‘to start from scratch’.
Question 36
In each of the following sentences four words or phrases are underlined. If there is any mistake with regard to grammar or usage, it is in the underlined part only. Identify the incorrect part.
The officer asked that (A) the report (B) be submitted (C) immediately. (D)
The officer asked that (A) the report (B) be submitted (C) immediately. (D)
D D
The sentence is grammatically correct. Note that the verb ‘be submitted’ is used in the subjunctive form to go along with the order given by the verb ‘asked’.
Question 37
In each of the following sentences four words or phrases are underlined. If there is any mistake with regard to grammar or usage, it is in the underlined part only. Identify the incorrect part.
He gave me (A) a ticket so that (B) I may visit (C) the (D) book fair.
He gave me (A) a ticket so that (B) I may visit (C) the (D) book fair.
C A
The sentence has two verbs ‘gave’ and ‘may visit’. While the former is in the simple past tense, the second verb is in the simple present tense. In order to correct this sentence the second verb can also be expressed in the simple past tense as ‘might visit’ or even better as ‘could visit’.
Question 38
In each of the following sentences four words or phrases are underlined. If there is any mistake with regard to grammar or usage, it is in the underlined part only. Identify the incorrect part.
The most (A) difficult job is to bend (B) and then lifting (C) the weight. (D)
The most (A) difficult job is to bend (B) and then lifting (C) the weight. (D)
B C
There is parallelism error here. The parallel structure in this sentence is “A and then B”. Since the first part in the parallel structure is a verb in the simple present tense, the second verb in B should also be in the same form. Hence correct the second verb as ‘lift’.
Question 39
In each of the following sentences four words or phrases are underlined. If there is any mistake with regard to grammar or usage, it is in the underlined part only. Identify the incorrect part.
The hope (A) to go through (B) the book today I have (C) almost read (D) half of it.
The hope (A) to go through (B) the book today I have (C) almost read (D) half of it.
C A
There are two clauses in this sentence “The hope to go through the book today” and “I have almost read half of it”. The first clause here is the dependent clause and hence should be “Hoping to go through the book today”.
Question 40
In each of the following sentences four words or phrases are underlined. If there is any mistake with regard to grammar or usage, it is in the underlined part only. Identify the incorrect part.
Our boss always (A) asks us to pay (B) full (C) attention to the work at hand. (D)
Our boss always (A) asks us to pay (B) full (C) attention to the work at hand. (D)
C C
The meaning of the phrase ‘at hand’ is ‘close by’ and is inappropriate in this sentence. We can correct this sentence by using the phrase ‘in hand”. When something is ‘in hand’, we are referring to the job or matter that is important at the present moment.
Section: Quantitative Aptitude
Question 1
Keerthi’s father gave him some money to buy books. He spent half of the money equally to buy books and entertaining his friends. Whatever amount left with him, he deposited half in his savings account and gave ₹5 to a poor person as charity. Finally, Keerthi was left with ₹20 which he returned to his father. What amount did his father give him initially?
C ₹100
Method-1:
Simply check the options one-by-one.
Option a: ₹160
Books & entertaining = 160/2 = ₹80
To savings account = ½ (160 – 80) = ₹40
To charity = ₹5
Then amount left = 160 – 125 = ₹35. Incorrect choice!
Option b: ₹200
Books & entertaining = 200/2 = ₹100
To savings account = ½ (200 – 100) = ₹50
To charity = ₹5
Then amount left = 200 – 155 = ₹45. Incorrect choice!
Option c: ₹100
Books & entertaining = 100/2 = ₹50
To savings account = ½ (100 – 50) = ₹25
To charity = ₹5
Then amount left = 100 – 80 = ₹20. Correct choice!
Option d: ₹120
Books & entertaining = 120/2 = ₹60
To savings account = ½ (120 – 60) = ₹30
To charity = ₹5
Then amount left = 120 – 95 = ₹25. Incorrect choice!
Method-2:
Let initial sum given to Keerthi be ₹N.
Books & entertaining = N/2
To savings account = ½ (N – N/2) = N/4
To charity = ₹5
Then amount left = N – (N/2 + N/4 + 5) = 20
i.e. N – 3N/4 – 5 = 20
i.e. N/4 = 20 + 5 or N = 4 x 25 = ₹100
Simply check the options one-by-one.
Option a: ₹160
Books & entertaining = 160/2 = ₹80
To savings account = ½ (160 – 80) = ₹40
To charity = ₹5
Then amount left = 160 – 125 = ₹35. Incorrect choice!
Option b: ₹200
Books & entertaining = 200/2 = ₹100
To savings account = ½ (200 – 100) = ₹50
To charity = ₹5
Then amount left = 200 – 155 = ₹45. Incorrect choice!
Option c: ₹100
Books & entertaining = 100/2 = ₹50
To savings account = ½ (100 – 50) = ₹25
To charity = ₹5
Then amount left = 100 – 80 = ₹20. Correct choice!
Option d: ₹120
Books & entertaining = 120/2 = ₹60
To savings account = ½ (120 – 60) = ₹30
To charity = ₹5
Then amount left = 120 – 95 = ₹25. Incorrect choice!
Method-2:
Let initial sum given to Keerthi be ₹N.
Books & entertaining = N/2
To savings account = ½ (N – N/2) = N/4
To charity = ₹5
Then amount left = N – (N/2 + N/4 + 5) = 20
i.e. N – 3N/4 – 5 = 20
i.e. N/4 = 20 + 5 or N = 4 x 25 = ₹100
Question 2
The difference between simple interest and compound interest at the same rate for rupees 5,000 for two years is rupees 98. The rate of interest is:
B 14%
Formula for CI – SI for 2 years on same principal at same rate = R% of SI/CI in year-1 or R% of R% of P
So, 98 = R% of R% of 5000
i.e. (R/100)2 = 98/5000 = 49/2500
Taking square root:
R/100 = 7/50
i.e. R = 7/50 x 100 = 14%
So, 98 = R% of R% of 5000
i.e. (R/100)2 = 98/5000 = 49/2500
Taking square root:
R/100 = 7/50
i.e. R = 7/50 x 100 = 14%
Question 3
There are two urns. One contains two white balls and four red balls, the other contains three white and nine red balls. All balls are of the same shape and size. From each urn, one ball is drawn. What is the probability of getting both the balls of the same colour?
C 7/12
First urn has 2W and 4R, while second urn has 3W and 9R
Total ways of drawing 1 ball each from the two urns = 6C1 x 12C1 = 6 x 12 = 72
Now, the favourable cases will be drawing 2 white balls or 2 red balls.
Ways of drawing 2 white balls = 2C1 x 3C1 = 2 x 3 = 6 ways
Ways of drawing 2 red balls 4C1 x 9C1 = 4 x 9 = 36 ways
By the ‘Or’ rule, the total favourable ways = 6 + 36 = 42
Hence required probability = 42/72 = 7/12
Total ways of drawing 1 ball each from the two urns = 6C1 x 12C1 = 6 x 12 = 72
Now, the favourable cases will be drawing 2 white balls or 2 red balls.
Ways of drawing 2 white balls = 2C1 x 3C1 = 2 x 3 = 6 ways
Ways of drawing 2 red balls 4C1 x 9C1 = 4 x 9 = 36 ways
By the ‘Or’ rule, the total favourable ways = 6 + 36 = 42
Hence required probability = 42/72 = 7/12
Question 4
A clock was set correct at 12 O’ clock. It loses 10 minutes per hour. What will be the angle between the hour and minute hands of the clock after one hour?
A 75˚
The faulty clock loses 10 mins every hour, so it will show the time as 12:50 after an hour.
Hence we want angle between hands at 12:50
Speed of minute hand = 6˚ per minute (it covers 360˚ in 60 minutes)
Speed of hour hand = ½˚ per minute (it covers 360˚ in 12 hours)
Relative speed of minute hand w.r.t. hour hand = 6 – ½ = 5½˚ or 11/2˚ per minute
Now, Angle at 12:50 = 50 x 11/2˚ = 275˚
But this is the reflex angle between the hands.
The correct angle will be 360˚ – 275˚ = 75˚
Hence we want angle between hands at 12:50
Speed of minute hand = 6˚ per minute (it covers 360˚ in 60 minutes)
Speed of hour hand = ½˚ per minute (it covers 360˚ in 12 hours)
Relative speed of minute hand w.r.t. hour hand = 6 – ½ = 5½˚ or 11/2˚ per minute
Now, Angle at 12:50 = 50 x 11/2˚ = 275˚
But this is the reflex angle between the hands.
The correct angle will be 360˚ – 275˚ = 75˚
Question 5
A vessel contains a mixture of milk and water in the ratio of 5:3 respectively. How much of the mixture must be siphoned off and replaced with water, so that the mixture may be half milk and half water?
C 1/5
There are two stages in this problem:

As shown above, let the initial volume of the solution be A litres and B litres of it be removed.
Important note: The ratio of milk and water will remain the same when some quantity is removed from it.
Hence Solution-2 will now have a volume of (A – B) litres with milk : water being unchanged as 5 : 3
So, water in solution-2 = 3/8th of (A – B) = 3(A – B)/8 litres
Now, B litres of water is added to this solution.
As a result, solution-2 has volume of A litres and milk : water now becomes 1 : 1.
Hence water in solution-3 = ½ of A = A/2 litres
Clearly, Water in solution-2 + Water added = Water in solution-3
i.e. 3(A – B)/8 + B = A/2
i.e. (3A – 3B + 8B)/8 = A/2
i.e. 3A + 5B = 4A
i.e. A = 5B
Hence the fraction of volume of solution-1 that was originally removed = B/A = 1/5
Alternatively:
We can apply alligation to the replacement part of this problem.
Milk concentration in solution-2 = 5/8 x 100 = 62.5%
Milk concentration in water (that was added to solution-2) = 0%
Milk concentration in solution-3 = ½ x 100 = 50%
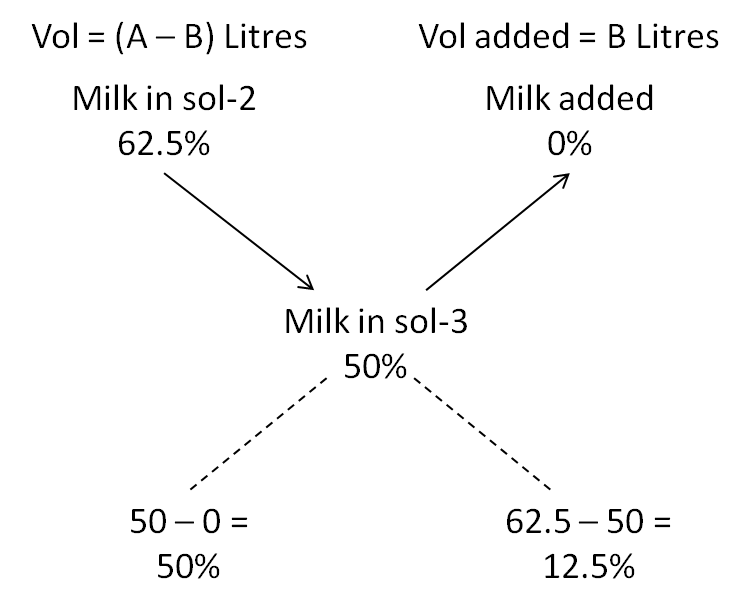
Hence, by the rule of alligation:
50/12.5 = (A – B)/B
i.e. 4/1 = (A – B)/B
i.e. A – B = 4B or A = 5B
Hence, B/A = 1/5
- Removal of a part of the solution
- Replacement with an equal volume of water

As shown above, let the initial volume of the solution be A litres and B litres of it be removed.
Important note: The ratio of milk and water will remain the same when some quantity is removed from it.
Hence Solution-2 will now have a volume of (A – B) litres with milk : water being unchanged as 5 : 3
So, water in solution-2 = 3/8th of (A – B) = 3(A – B)/8 litres
Now, B litres of water is added to this solution.
As a result, solution-2 has volume of A litres and milk : water now becomes 1 : 1.
Hence water in solution-3 = ½ of A = A/2 litres
Clearly, Water in solution-2 + Water added = Water in solution-3
i.e. 3(A – B)/8 + B = A/2
i.e. (3A – 3B + 8B)/8 = A/2
i.e. 3A + 5B = 4A
i.e. A = 5B
Hence the fraction of volume of solution-1 that was originally removed = B/A = 1/5
Alternatively:
We can apply alligation to the replacement part of this problem.
Milk concentration in solution-2 = 5/8 x 100 = 62.5%
Milk concentration in water (that was added to solution-2) = 0%
Milk concentration in solution-3 = ½ x 100 = 50%

Hence, by the rule of alligation:
50/12.5 = (A – B)/B
i.e. 4/1 = (A – B)/B
i.e. A – B = 4B or A = 5B
Hence, B/A = 1/5
Question 6
A boat travels upstream from A to B and back from B to A in 5 hours. The speed of the boat in still water is 8 km/hour and the speed of the current is 4 km/hour. Then, the distance from A to B is:
D 15 kms
Speed of boat = B = 8 km/hr
Speed of current = S = 4 km/hr
Effective speed going upstream = B – S = 4 km/hr
Effective speed going downstream = B + S = 12 km/hr
Let distance travelled in either direction be D kms.
Using Time = Distance/Speed we get:
Time to go upstream = D/4
Time to go downstream = D/12
But we are given, total time = 5 hours
i.e. D/4 + D/12 = 5
i.e. (3D + D)/12 = 5
i.e. D = 5 x 12/4 = 15 kms
Speed of current = S = 4 km/hr
Effective speed going upstream = B – S = 4 km/hr
Effective speed going downstream = B + S = 12 km/hr
Let distance travelled in either direction be D kms.
Using Time = Distance/Speed we get:
Time to go upstream = D/4
Time to go downstream = D/12
But we are given, total time = 5 hours
i.e. D/4 + D/12 = 5
i.e. (3D + D)/12 = 5
i.e. D = 5 x 12/4 = 15 kms
Question 7
A man rows to a place 45 kms distant and back in 12 hours. He realises that he can row 5 kms downstream in the same time as 3 kms against the stream. The velocity of the stream is:
A 2 kms/hr
Let the speeds of the boat and current be B km/hr and S km/hr respectively.
Then speed upstream = B – S
And speed downstream = B + S
So, Time to go 5 km downstream = 5/(B + S)
And, Time to go 3 km upstream = 3/(B – S)
Hence, 5/(B + S) = 3/(B – S)
i.e. 5B – 5S = 3B + 3S
i.e. 2B = 8S or B = 4S ... (1)
Also, time to travel 45 km upstream and 45 km downstream = 12 hours
i.e. Time upstream (for 45 kms) + Time downstream (45 kms) = 12
i.e. 45/(B – S) + 45/(B + S) = 12
Using equation (1):
45/(4S – S) + 45/(4S + S) = 12
i.e. 45/3S + 45/5S = 12
i.e. 15/S + 9/S = 12
i.e. 24/S = 12 or S = 24/12 = 2 km/hr
Then speed upstream = B – S
And speed downstream = B + S
So, Time to go 5 km downstream = 5/(B + S)
And, Time to go 3 km upstream = 3/(B – S)
Hence, 5/(B + S) = 3/(B – S)
i.e. 5B – 5S = 3B + 3S
i.e. 2B = 8S or B = 4S ... (1)
Also, time to travel 45 km upstream and 45 km downstream = 12 hours
i.e. Time upstream (for 45 kms) + Time downstream (45 kms) = 12
i.e. 45/(B – S) + 45/(B + S) = 12
Using equation (1):
45/(4S – S) + 45/(4S + S) = 12
i.e. 45/3S + 45/5S = 12
i.e. 15/S + 9/S = 12
i.e. 24/S = 12 or S = 24/12 = 2 km/hr
Question 8
The average weight of three men ‘X’, ‘Y’ and ‘Z’ is 75 kgs. Another man ‘A’ joins the group and the average weight now becomes 80 kgs. If another person ‘B’ whose weight is 5 kgs more than ‘A’ replaces ‘X’, then the average weight of ‘Y’, ‘Z’, ‘A’ and ‘B’ will be 85 kgs. What is the weight of ‘X’?
C 80 kgs.
Let X, Y, Z, A and B be the ages of the five persons.
Then, (X + Y + Z)/3 = 75
i.e. X + Y + Z = 225 ... (1)
Also (A + X + Y + Z)/4 = 80
i.e. A + X + Y + Z = 320
Using (1): A + 225 = 320
i.e. A = 95 kg
Given, B = 5 + A = 100 kgs
Then, (A + B + Y + Z)/4 = 85
i.e. 95 + 100 + Y + Z = 340
i.e. Y + Z = 340 – 195 = 145
Using this in (1): X + 145 = 225
i.e. X = 225 – 145 = 80 kgs
Then, (X + Y + Z)/3 = 75
i.e. X + Y + Z = 225 ... (1)
Also (A + X + Y + Z)/4 = 80
i.e. A + X + Y + Z = 320
Using (1): A + 225 = 320
i.e. A = 95 kg
Given, B = 5 + A = 100 kgs
Then, (A + B + Y + Z)/4 = 85
i.e. 95 + 100 + Y + Z = 340
i.e. Y + Z = 340 – 195 = 145
Using this in (1): X + 145 = 225
i.e. X = 225 – 145 = 80 kgs
Question 9
Gold and copper are as heavy as water by 19 and 9 times respectively. The ratio in which these two metals be mixed so that the mixture is 17 times as heavy as water is:
A 4:1
Note that here the word ‘heavy’ is used to describe the density i.e. weight per unit volume.
Hence we must understand the first statement as “Gold is 19 times as dense as water, and copper is 9 times as dense as water”.
Method-1:
Let A litres of gold be mixed with B litres of copper.
Now weight of gold = Volume x Density = A x 19w = 19Aw
And weight of copper = Volume x Density = B x 9w = 9Bw
Now the resultant mixture has a volume of (A + B) litres
And the resultant is 17 times as dense as water.
Hence, weight of the resultant mixture = (A + B) x 17w
But weight of gold + weight of copper = weight of the mixture
i.e. 19Aw + 9Bw = 17Aw + 17Bw
i.e. 2Aw = 8Bw
or A/B = 8/2 = 4/1
Method-2:
In this problem the density of the mixture will be a weighted average of the densities of the constituent metals. Hence, we can also use the rule of alligation here.
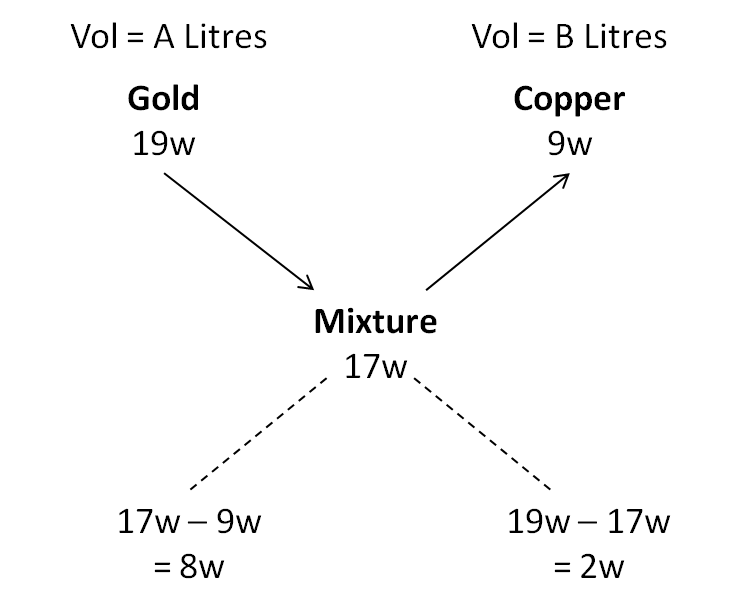
Hence, the ratio in which the two metals are mixed i.e. A : B = 8w : 2w or 4 : 1
Hence we must understand the first statement as “Gold is 19 times as dense as water, and copper is 9 times as dense as water”.
Method-1:
Let A litres of gold be mixed with B litres of copper.
Now weight of gold = Volume x Density = A x 19w = 19Aw
And weight of copper = Volume x Density = B x 9w = 9Bw
Now the resultant mixture has a volume of (A + B) litres
And the resultant is 17 times as dense as water.
Hence, weight of the resultant mixture = (A + B) x 17w
But weight of gold + weight of copper = weight of the mixture
i.e. 19Aw + 9Bw = 17Aw + 17Bw
i.e. 2Aw = 8Bw
or A/B = 8/2 = 4/1
Method-2:
In this problem the density of the mixture will be a weighted average of the densities of the constituent metals. Hence, we can also use the rule of alligation here.

Hence, the ratio in which the two metals are mixed i.e. A : B = 8w : 2w or 4 : 1
Question 10
Two men and seven boys can do a work in 14 days. Three men and eight boys can do the same work in 11 days. Further eight men and six boys can do three times the amount of this work in:
D 21 days
Let M and B be the work done by a man and a boy respectively in a day i.e. their rates.
Then, work done by 2 men and 7 boys in 14 days = 2M x 14 + 7B x 14 = 14(2M + 7B)
Also, work done by 3 men and 8 boys in 11 days = 3M x 11 + 8B x 11 = 11(3M + 8B)
Since the work done by both groups is the same we can equate these:
Work = 14(2M + 7B) = 11(3M + 8B)
i.e. 98B – 88B = 33M – 28M
i.e. 10B = 5M or M = 2B
Then initial work = 14(2 x 2B + 7B) = 14 x 11B
Now, work done by 8 men and 6 boys in a day = 8M + 6B = 16B + 6B = 22B
If this group takes D days to finish three times the previous work:
Work = 22B x D = 3 x 14 x 11B
i.e. D = 42 x 11/22 = 21 days
Then, work done by 2 men and 7 boys in 14 days = 2M x 14 + 7B x 14 = 14(2M + 7B)
Also, work done by 3 men and 8 boys in 11 days = 3M x 11 + 8B x 11 = 11(3M + 8B)
Since the work done by both groups is the same we can equate these:
Work = 14(2M + 7B) = 11(3M + 8B)
i.e. 98B – 88B = 33M – 28M
i.e. 10B = 5M or M = 2B
Then initial work = 14(2 x 2B + 7B) = 14 x 11B
Now, work done by 8 men and 6 boys in a day = 8M + 6B = 16B + 6B = 22B
If this group takes D days to finish three times the previous work:
Work = 22B x D = 3 x 14 x 11B
i.e. D = 42 x 11/22 = 21 days
Question 11
Age of father 10 years ago was three times the age of his son. After 10 years, father’s age is twice that of his son. The ratio of their present ages is:
B 7:3
Let present ages of father and son be F and S years respectively.
Then, ages 10 years ago were (F – 10) and (S – 10) years
So, F – 10 = 3(S – 10) ... (1)
Also, ages 10 years later would be (F + 10) and (S + 10) years
So, F + 10 = 2(S + 10) ... (2)
On subtracting (1) from (2) we get:
F + 10 – (F – 10) = 2S + 20 – (3S – 30)
i.e. 20 = 50 – S
i.e. S = 50 – 20 = 30 years
And F = 10 + 3(30 – 10) = 10 + 3 x 20 = 70 years
So ratio of their present ages = 70 : 30 = 7 : 3
Then, ages 10 years ago were (F – 10) and (S – 10) years
So, F – 10 = 3(S – 10) ... (1)
Also, ages 10 years later would be (F + 10) and (S + 10) years
So, F + 10 = 2(S + 10) ... (2)
On subtracting (1) from (2) we get:
F + 10 – (F – 10) = 2S + 20 – (3S – 30)
i.e. 20 = 50 – S
i.e. S = 50 – 20 = 30 years
And F = 10 + 3(30 – 10) = 10 + 3 x 20 = 70 years
So ratio of their present ages = 70 : 30 = 7 : 3
Question 12
The Banker’s discount on a sum of money for 18 months is ₹600 and the true discount on the same sum for 3 years is ₹750/-. The rate percentage is:
C 20%
Given, True discount = ₹750 for 3 years
Bankers discount = ₹600 for 18 months = ₹1200 for 3 years
Now we know: TD = BD x 100/(100 + RT)
So, 750 = 1200 x 100/(100 + 3R)
i.e. 100 + 3R = 120000/750 = 160
So R = 60/3 = 20%
Bankers discount = ₹600 for 18 months = ₹1200 for 3 years
Now we know: TD = BD x 100/(100 + RT)
So, 750 = 1200 x 100/(100 + 3R)
i.e. 100 + 3R = 120000/750 = 160
So R = 60/3 = 20%
Question 13
A train ‘X’ leaves station ‘A’ at 3 p.m and reaches station ‘B’ at 4.30 p.m., while another train ‘Y’ leaves station ‘B’ at 3.00 p.m and reaches station ‘A’ at 4.00 p.m. These two trains cross each other at:
D 3.36 p.m.
Train X takes 1.5 hours to cover the distance AB.
Train Y takes 1 hour to cover the same distance AB.
Let the distance AB be 3 kms.
Then, speed of X = 3/1.5 = 2 km/hr
And speed of Y = 3/1 = 3 km/hr
Now, relative speed = 3 + 2 = 5 km/hr
Hence time taken for them to cross each other = D/SR = 3/5 hours or 3/5 x 60 = 36 minutes
Hence, time when they cross will be 3:36 p.m.
Train Y takes 1 hour to cover the same distance AB.
Let the distance AB be 3 kms.
Then, speed of X = 3/1.5 = 2 km/hr
And speed of Y = 3/1 = 3 km/hr
Now, relative speed = 3 + 2 = 5 km/hr
Hence time taken for them to cross each other = D/SR = 3/5 hours or 3/5 x 60 = 36 minutes
Hence, time when they cross will be 3:36 p.m.
Question 14
In an office, 1/3 of the workers are Men, ½ of the men are married and 1/3 of the married men have children. If ¾ of the women are married and 2/3 of the 2/3 of the married women have children, then the part of workers without children are:
D 4/9
All the information can be expressed in the diagram shown below:
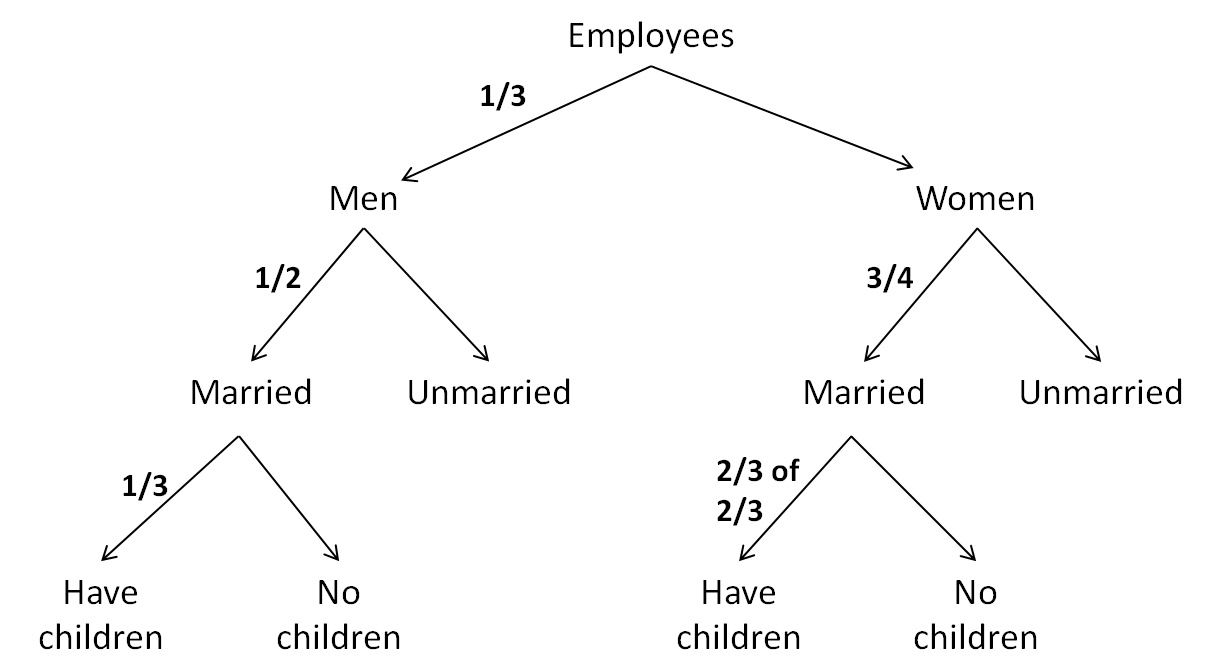
Let there be 900 employees in total.
Then, Number of men = 1/3 x 900 = 300
And, Number of women = 900 – 300 = 600
Now, Men who are married = ½ of 300 = 150
Married men who have children = 1/3 x 150 = 50
Similarly, Women who are married = ¾ x 600 = 450
Married women who have children = 2/3 x 2/3 x 450 = 200
So total employees who have children = 50 + 250 = 250
Hence the others (without children) = 900 – 250 = 650
i.e. these form 650/900 = 13/18th part of employees

Let there be 900 employees in total.
Then, Number of men = 1/3 x 900 = 300
And, Number of women = 900 – 300 = 600
Now, Men who are married = ½ of 300 = 150
Married men who have children = 1/3 x 150 = 50
Similarly, Women who are married = ¾ x 600 = 450
Married women who have children = 2/3 x 2/3 x 450 = 200
So total employees who have children = 50 + 250 = 250
Hence the others (without children) = 900 – 250 = 650
i.e. these form 650/900 = 13/18th part of employees
Question 15
A can do a piece of work in 8 days and B alone can do the same work in 10 days. A and B agreed to do the work together for ₹720. With the help of C, they finished the work in 4 days. How much C is to be paid?
B ₹72
Let the work be 40 units.
Using Rate = Work/Time:
Rate of A = 40/8 = 5 units/day
Rate of B = 40/10 = 4 units/day
Also combined rate of A, B and C = 40/4 = 10
Hence rate of C = 10 – 5 – 4 = 1 unit/day
Now they will receive money in proportion to their rates i.e. 5 : 4 : 1
So C will be paid 1/10th of 720 = ₹72
Using Rate = Work/Time:
Rate of A = 40/8 = 5 units/day
Rate of B = 40/10 = 4 units/day
Also combined rate of A, B and C = 40/4 = 10
Hence rate of C = 10 – 5 – 4 = 1 unit/day
Now they will receive money in proportion to their rates i.e. 5 : 4 : 1
So C will be paid 1/10th of 720 = ₹72
Question 16
A piece of cloth costs rupees 75. If the piece is four meters longer and each meter costs rupees 5 less, the cost remains unchanged. What is the length of the piece?
B 6 meters
Method-1:
We can quickly check the options one-by-one:
Option a: 10 metres
Each metre costs 75/10 = ₹7.5
Check: (7.5 – 5) x (4 + 10) = 2.5 x 14 = ₹35 which is not the same as actual cost.
Option b: 6 metres
Each metre costs 75/6 = ₹12.5
Check: (12.5 – 5) x (6 + 4) = 7.5 x 10 = ₹75 which is the same as actual cost!
Option c: 8 metres
Each metre costs 75/8 = ₹9.375
Check: (9.375 – 5) x (8 + 4) = 4.375 x 12 = ₹52.5 which is not the same as actual cost.
Option d: 12 metres
Each metre costs 75/12 = ₹6.25
Check: (6.25 – 5) x (12 + 4) = 1.25 x 16 = ₹20 which is not the same as actual cost.
Method-2:
Let the length of the piece be N metres.
Then cost per metre = 75/N
New cost per metre = 75/N – 5
New length = N + 4
Then, (75/N – 5)(N + 4) = 75
i.e. (75 – 5N)(N + 4) = 75N
i.e. 75N + 300 – 5N2 – 20N = 75N
i.e. 5N2 + 20N – 300 = 0
i.e. N2 + 4N – 60 = 0
i.e. N2 + 10N – 6N – 60 = 0
i.e. (N + 10)(N – 6) = 0
Since N cannot be negative, N must be 6.
We can quickly check the options one-by-one:
Option a: 10 metres
Each metre costs 75/10 = ₹7.5
Check: (7.5 – 5) x (4 + 10) = 2.5 x 14 = ₹35 which is not the same as actual cost.
Option b: 6 metres
Each metre costs 75/6 = ₹12.5
Check: (12.5 – 5) x (6 + 4) = 7.5 x 10 = ₹75 which is the same as actual cost!
Option c: 8 metres
Each metre costs 75/8 = ₹9.375
Check: (9.375 – 5) x (8 + 4) = 4.375 x 12 = ₹52.5 which is not the same as actual cost.
Option d: 12 metres
Each metre costs 75/12 = ₹6.25
Check: (6.25 – 5) x (12 + 4) = 1.25 x 16 = ₹20 which is not the same as actual cost.
Method-2:
Let the length of the piece be N metres.
Then cost per metre = 75/N
New cost per metre = 75/N – 5
New length = N + 4
Then, (75/N – 5)(N + 4) = 75
i.e. (75 – 5N)(N + 4) = 75N
i.e. 75N + 300 – 5N2 – 20N = 75N
i.e. 5N2 + 20N – 300 = 0
i.e. N2 + 4N – 60 = 0
i.e. N2 + 10N – 6N – 60 = 0
i.e. (N + 10)(N – 6) = 0
Since N cannot be negative, N must be 6.
Question 17
Praveen has Rs. 4,662 in the form of 2, 5 and 10 rupee notes. If these notes are in the ratio of 3:5:8, the number of five rupees notes with him is:
B 210
Let the number of notes of ₹2, ₹5 and ₹10 be 3n, 5n and 8n respectively.
Then, Value of ₹2 notes = 2 x 3n = 6n
Value of ₹5 notes = 5 x 5n = 25n
Value of ₹10 notes = 10 x 8n = 80n
Hence total value of all notes = 6n + 25n + 80n = 4662
i.e. 111n = 4662 or n = 4662/111 = 42
Hence number of ₹5 notes = 5 x 42 = 210
Then, Value of ₹2 notes = 2 x 3n = 6n
Value of ₹5 notes = 5 x 5n = 25n
Value of ₹10 notes = 10 x 8n = 80n
Hence total value of all notes = 6n + 25n + 80n = 4662
i.e. 111n = 4662 or n = 4662/111 = 42
Hence number of ₹5 notes = 5 x 42 = 210
Question 18
Taps ‘A’ and ‘B’ can fill a tank in 37½ minutes and 45 minutes respectively. Both taps are opened and after some time tap ‘B’ is turned off.
The tank is filled completely in exactly 30 minutes, if tap ‘B’ is turned off after:
The tank is filled completely in exactly 30 minutes, if tap ‘B’ is turned off after:
D 9 minutes
Let the capacity of the tank be 225 litres.
Using Rate = (Work or capacity)/Time we get:
Rate of A = 225/37.5 = 6 litres/minute
Rate of B = 225/45 = 5 litres/minute
Let tap B be turned off after N minutes.
Then, A & B will together fill for first N mins and then A alone will fill for remaining (30 – N) mins.
So, Work done by A and B together + Work done by A alone = Capacity of the tank
i.e. (6 + 5) x N + 6 x (30 – N) = 225
i.e. 11N + 180 – 6N = 225
i.e. N = 45/5 = 9 minutes
Hence tap B is turned off after 9 minutes.
Using Rate = (Work or capacity)/Time we get:
Rate of A = 225/37.5 = 6 litres/minute
Rate of B = 225/45 = 5 litres/minute
Let tap B be turned off after N minutes.
Then, A & B will together fill for first N mins and then A alone will fill for remaining (30 – N) mins.
So, Work done by A and B together + Work done by A alone = Capacity of the tank
i.e. (6 + 5) x N + 6 x (30 – N) = 225
i.e. 11N + 180 – 6N = 225
i.e. N = 45/5 = 9 minutes
Hence tap B is turned off after 9 minutes.
Question 19
‘A’ and ‘B’ complete a work in 12 days, ‘B’ and ‘C’ in 8 days and ‘C’ and ‘A’ in 16 days. ‘A’ left after working for 3 days. In how many days more will ‘B’ and ‘C’ finish the remaining work?
D 4 ¾
Note that in this question it is not clear who begins the task. Does A alone start working or do all three start the work for the initial three days?
Let the work be 48 units. Also let A, B and C be the rates of the three persons respectively.
Using Rate = Work/Time we get:
A + B = 48/12 = 4 units/day ... (1)
B + C = 48/8 = 6 units/day ... (2)
C + A = 48/16 = 3 units/day ... (3)
Adding these: 2(A + B + C) = 13
or A + B + C = 6.5
Using (1): 4 + C = 6.5 or C = 2.5 units/day
Using (2): A + 6 = 6.5 or A = 0.5 units/day
Using (3): B + 3 = 6.5 or B = 3.5 units/day
Now, initially A, B and C work together for 3 days.
So work done = (A + B + C) x 3 = 6.5 x 3 = 19.5 units
Hence, work left = 48 – 19.5 = 28.5 units
Now using Time = Work/Rate,
Time taken by B and C to finish remaining work = 28.5/6 = 4.75 days
Let the work be 48 units. Also let A, B and C be the rates of the three persons respectively.
Using Rate = Work/Time we get:
A + B = 48/12 = 4 units/day ... (1)
B + C = 48/8 = 6 units/day ... (2)
C + A = 48/16 = 3 units/day ... (3)
Adding these: 2(A + B + C) = 13
or A + B + C = 6.5
Using (1): 4 + C = 6.5 or C = 2.5 units/day
Using (2): A + 6 = 6.5 or A = 0.5 units/day
Using (3): B + 3 = 6.5 or B = 3.5 units/day
Now, initially A, B and C work together for 3 days.
So work done = (A + B + C) x 3 = 6.5 x 3 = 19.5 units
Hence, work left = 48 – 19.5 = 28.5 units
Now using Time = Work/Rate,
Time taken by B and C to finish remaining work = 28.5/6 = 4.75 days
Question 20
A trader sells rice at a profit of 20% and uses weights which are 10% less than the correct weight. The total gain earned by him is:
A 33<sup>1</sup>/<sub>3</sub>%
Let the trader’s cost price of 1000 gms be ₹1000
Using the faulty weight he actually gives 1000 – 10% of 1000 = 900 gm
Also, profit = 20% means that the trader sells at SP = CP + profit
i.e. SP = 1000 + 20/100 x 1000 = ₹1200
So the trader charges ₹1200 for 900 gms
Hence, for 1000 gms he will charge 1200/900 x 1000 = 4000/3
So total gain% = (4000/3 – 1000)/1000 x 100 = 100/3 = 331/3%
Using the faulty weight he actually gives 1000 – 10% of 1000 = 900 gm
Also, profit = 20% means that the trader sells at SP = CP + profit
i.e. SP = 1000 + 20/100 x 1000 = ₹1200
So the trader charges ₹1200 for 900 gms
Hence, for 1000 gms he will charge 1200/900 x 1000 = 4000/3
So total gain% = (4000/3 – 1000)/1000 x 100 = 100/3 = 331/3%
Section: General Knowledge
Question 1
Volvo has launched the world’s largest bus that can carry up to:
D 300 passengers
300 passengers
Question 2
Immediately before Antonio Guterres was appointed the U.N Secretary General in October 2016, he was:
D United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees
Question 3
India emerged as ___________ largest holder of the U.S Government Securities at the end of 2016:
A Twelfth
Twelfth
Question 4
Juno is the name of a:
A Solar powered space craft
Solar powered space craft
Question 5
Among the following M.L.As, who was disqualified by the Governor during January 2017 under Article 192 of the Constitution for undertaking government contracts?
A Uma Shankar Singh of Bihar
Uma Shankar Singh of Bihar
Question 6
Who called the immigration the ‘Trojan horse of Terrorism’?
C Viktor Orban, Prime Minister of Hungary
Viktor Orban, Prime Minister of Hungary
Question 7
Solar Impulse – 2 is:
A Solar powered airplane that completed the first around the world
Solar powered airplane that completed the first around the world
Question 8
The world’s first artificial intelligence lawyer, a robot, is named as:
A Ross
Ross
Question 9
Which of the following individuals was called a ‘deceptive actor’ by China’s foreign ministry during March 2017?
D Dalai Lama
Dalai Lama
Question 10
The bowler who has claimed the fastest 250 wickets in Cricket test matches is:
C Ravichandran Ashwin
Ravichandran Ashwin
Question 11
India’s third largest trading partner during 2016 is
C U.A.E
U.A.E
Question 12
Highest number of open prisons in India as on 2015 are in
D Rajasthan
Rajasthan
Question 13
The Union Cabinet has recently approved the setting up of a Permanent Tribunal for resolving:
A Interstate water disputes
Interstate water disputes
Question 14
India’s voting rights at the International Monetary Fund increased from 2.3 % to
D 2.6%
2.6%
Question 15
Prithvi Defence Vehicle is
A The name of India’s Nuclear Intercepter Missile
The name of India’s Nuclear Intercepter Missile
Question 16
Which of the following country enacted a law during August 2016 providing for the right to register the marriages of Hindus?
D Pakistan
Pakistan
Question 17
During 2017, which SAARC country has notified the Right to Information Act?
A Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Question 18
Who has been selected for 2016 BC Roy Award?
B Dr. P. Raghu Ram
Dr. P. Raghu Ram
Question 19
The Happiness Index Department or a Wing has been established in the states of:
C Andhra Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh
Question 20
Which country offered asylum seekers 1,200 Euros to leave by withdrawing their application for protection?
B Germany
Germany
Question 21
Among the following professors of Indian origin who has received Knighthood for the work as a co-inventor of next generation DNA Sequencing called Solexa Sequencing is?
C Shankar Balasubramanian
Shankar Balasubramanian
Question 22
The Japanese Prime Minister who offered ‘sincere and everlasting condolences’ to the people of the United States for killing more than 2,400 soldiers in the attack on Pearl harbour was:
A Shinzo Abe
Shinzo Abe
Question 23
Among the following, who has won the maximum number of titles?
A Saina Nehwal
Saina Nehwal
Question 24
How many billionaires India has lost since demonetization on November 8, 2016?
C Eleven
Eleven
Question 25
COIN, a software programme developed by J. P. Morgan supports:
C Interpreting commercial documents
Interpreting commercial documents
Question 26
Name the President elect of France who is likely to take the oath on 14 May 2017.
B Emmanuel Macron
Emmanuel Macron
Question 27
Which shoe company in the United States of America has won an IPR dispute against China recently for using their logo?
A New Balance
New Balance
Question 28
According to the Survey Report released by Transparency International during March 2017 on India, the most corrupt are
B Police
Police
Question 29
With the development of Terahertz (THz) transmitter, it is expected to be faster than 5G mobile networks by:
C Ten times
Ten times
Question 30
Which country 3D – Printed a home of 37 sq.mts?
D Russia
Russia
Question 31
As on 31st January 2016, the highest number of law colleges were present in:
B Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh
Question 32
The first country to have announced euthanasia of a child is:
B Belgium
Belgium
Question 33
The first country in the world to have begun shutting down the entire Frequency Modulation (FM) radio network to be replaced by Digital Audio Broadcasting is:
A Norway
Norway
Question 34
Which court has stayed the execution of death sentence of Kulbhushan Jadhav in May 2017?
A International Court of Justice
International Court of Justice
Question 35
The World Bank had cut India’s GDP growth for 2016 – 2017 to:
A 7%
7%
Question 36
World’s longest rail tunnel is about:
D 57 kms.
57 kms.
Question 37
The first elected civilian President in Myanmar is:
A Htin Kyaw
Htin Kyaw
Question 38
The first Commercial Court and Commercial Disputes Resolution Centre was inaugurated at
A Raipur, Chattisgarh
Raipur, Chattisgarh
Question 39
The Hubble telescope of NASA is located in
B Space
Space
Question 40
The 2016 Nobel Peace Prize was won by the President of:
A Columbia
Columbia
Question 41
Among the following who was crowned as ‘Miss Supernational’ during 2016?
A Srinidhi Shetty
Srinidhi Shetty
Question 42
‘Scorpion kick’ is a phrase used in
A Kabaddi
Kabaddi
Question 43
Donald Trump is _____________ President of the United States.
C 45th
45th
Question 44
Till the end of 2016, the total number of UNESCO’s World Heritage Sites in India is:
B 35
35
Question 45
NASA rediscovered India’s lunar spacecraft that was lost in the space during the past eight years known as:
D Chandrayan – I
Chandrayan – I
Question 46
Japan is threatening to drag India to W.T.O on issues relating to the export of its:
A Steel
Steel
Question 47
In terms of steel production in the world during 2015 – 2016, India stood at:
B Third
Third
Question 48
The first statue of a woman in Parliament Square in England is that of:
B Millicent Fawcett
Millicent Fawcett
Question 49
‘World’s longestall women Non-stop flight’ from New Delhi to San Francisco covering 14,500 kms was operated by:
C Air India
Air India
Question 50
The top destination for domestic tourists in India for the past three consecutive years has been:
D Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu
Section: Logical Reasoning
Question 1
Who is a Dancer?
A C
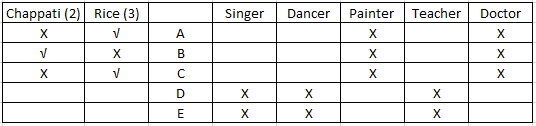
Using clue (iii) we can infer that A and C cannot be a doctor and that three people prefer rice while two people prefer chappatis. Also, that B is not a painter. Also, since B likes chappati B cannot be a doctor. Also, D and E can only be a doctor or a painter. The table will look as follows -
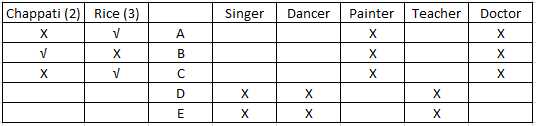
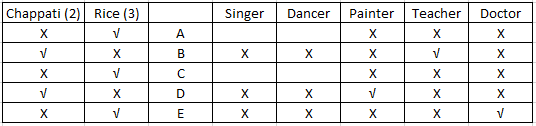
Using (iv) we can infer that D and A are not a teacher. Since A prefers rice, teacher and D will prefer chappatis. From (iii) we know that the doctor prefers rice. Since, now we know that D likes chappati D cannot be a doctor and will be a painter and so E will be a doctor. Since B prefers chappatis , B could be either a painter or a teacher. Since D is a painter B will be a teacher. The updated table will look as follows:-
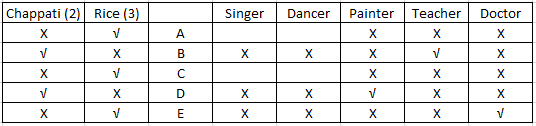
Using (v) we can conclude that C is not a singer. With this the table will be complete and will look as follows:-
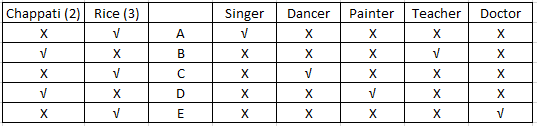
C is the dancer.

Using (iv) we can infer that D and A are not a teacher. Since A prefers rice, teacher and D will prefer chappatis. From (iii) we know that the doctor prefers rice. Since, now we know that D likes chappati D cannot be a doctor and will be a painter and so E will be a doctor. Since B prefers chappatis , B could be either a painter or a teacher. Since D is a painter B will be a teacher. The updated table will look as follows:-

Using (v) we can conclude that C is not a singer. With this the table will be complete and will look as follows:-

C is the dancer.
Question 2
Who is a Singer?
B A
Using clue (iii) we can infer that A and C cannot be a doctor and that three people prefer rice while two people prefer chappatis. Also, that B is not a painter. Also, since B likes chappati B cannot be a doctor. Also, D and E can only be a doctor or a painter. The table will look as follows -
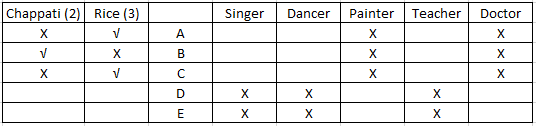
Using (iv) we can infer that D and A are not a teacher. Since A prefers rice, teacher and D will prefer chappatis. From (iii) we know that the doctor prefers rice. Since, now we know that D likes chappati D cannot be a doctor and will be a painter and so E will be a doctor. Since B prefers chappatis , B could be either a painter or a teacher. Since D is a painter B will be a teacher. The updated table will look as follows:-
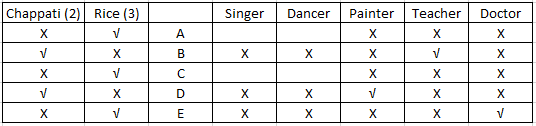
Using (v) we can conclude that C is not a singer. With this the table will be complete and will look as follows:-
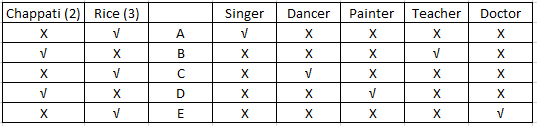
A is the singer.

Using (iv) we can infer that D and A are not a teacher. Since A prefers rice, teacher and D will prefer chappatis. From (iii) we know that the doctor prefers rice. Since, now we know that D likes chappati D cannot be a doctor and will be a painter and so E will be a doctor. Since B prefers chappatis , B could be either a painter or a teacher. Since D is a painter B will be a teacher. The updated table will look as follows:-

Using (v) we can conclude that C is not a singer. With this the table will be complete and will look as follows:-

A is the singer.
Question 3
Who is a Teacher?
C B
Using clue (iii) we can infer that A and C cannot be a doctor and that three people prefer rice while two people prefer chappatis. Also, that B is not a painter. Also, since B likes chappati B cannot be a doctor. Also, D and E can only be a doctor or a painter. The table will look as follows -
Using (iv) we can infer that D and A are not a teacher. Since A prefers rice, teacher and D will prefer chappatis. From (iii) we know that the doctor prefers rice. Since, now we know that D likes chappati D cannot be a doctor and will be a painter and so E will be a doctor. Since B prefers chappatis , B could be either a painter or a teacher. Since D is a painter B will be a teacher. The updated table will look as follows:-
Using (v) we can conclude that C is not a singer. With this the table will be complete and will look as follows:-
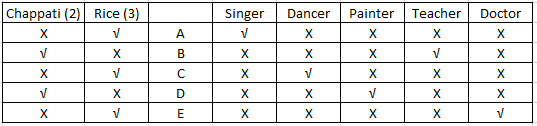
B is the teacher.

Using (iv) we can infer that D and A are not a teacher. Since A prefers rice, teacher and D will prefer chappatis. From (iii) we know that the doctor prefers rice. Since, now we know that D likes chappati D cannot be a doctor and will be a painter and so E will be a doctor. Since B prefers chappatis , B could be either a painter or a teacher. Since D is a painter B will be a teacher. The updated table will look as follows:-

Using (v) we can conclude that C is not a singer. With this the table will be complete and will look as follows:-

B is the teacher.
Question 4
Which of the following combination gets South-facing flats?
A U, R, P
From (iii) and (iv) we can conclude that S gets a north facing flat. From (ii) we get two possible scenarios. These are:-
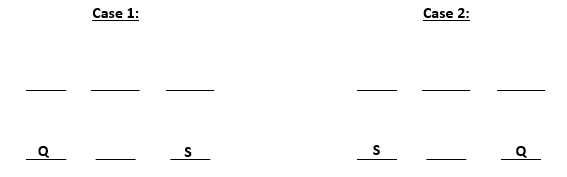
U gets diagonally opposite flat to S and R gets a flat next to U. Also, T gets a north facing flat, this means that the north facing flats are Q, T and S and south facing flats are U, R and P. The possible cases are: -
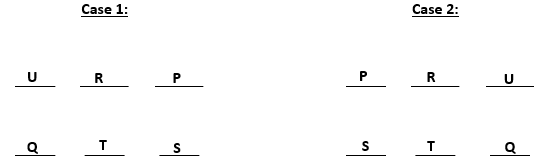
So, U, R and P are south – facing flats.
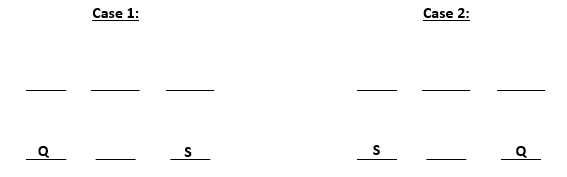
U gets diagonally opposite flat to S and R gets a flat next to U. Also, T gets a north facing flat, this means that the north facing flats are Q, T and S and south facing flats are U, R and P. The possible cases are: -
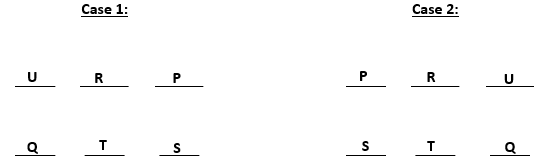
So, U, R and P are south – facing flats.
Question 5
Whose flat is between Q and S?
D T
From (iii) and (iv) we can conclude that S gets a north facing flat. From (ii) we get two possible scenarios. These are:-
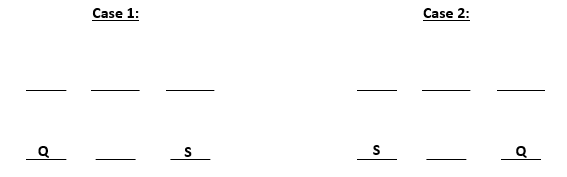
U gets diagonally opposite flat to S and R gets a flat next to U. Also, T gets a north facing flat, this means that the north facing flats are Q, T and S and south facing flats are U, R and P. The possible cases are: -
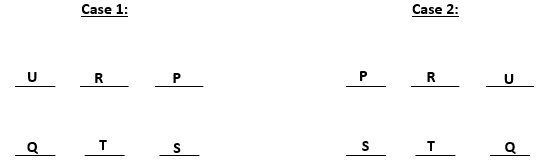
T is between Q and S.
From (iii) and (iv) we can conclude that S gets a north facing flat. From (ii) we get two possible scenarios. These are:-
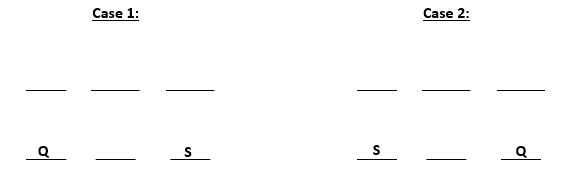
U gets diagonally opposite flat to S and R gets a flat next to U. Also, T gets a north facing flat, this means that the north facing flats are Q, T and S and south facing flats are U, R and P. The possible cases are: -
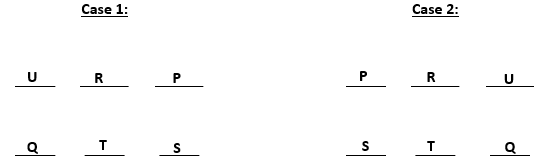
The information is irrelevant as the only flat next to U will be R.
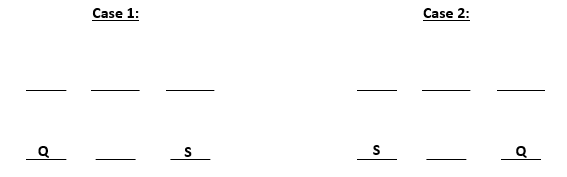
U gets diagonally opposite flat to S and R gets a flat next to U. Also, T gets a north facing flat, this means that the north facing flats are Q, T and S and south facing flats are U, R and P. The possible cases are: -
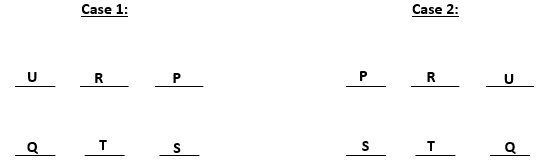
T is between Q and S.
From (iii) and (iv) we can conclude that S gets a north facing flat. From (ii) we get two possible scenarios. These are:-
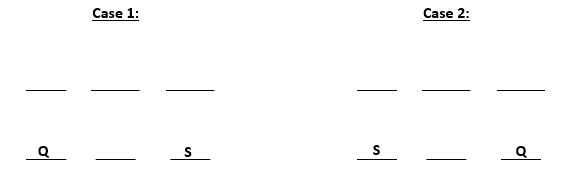
U gets diagonally opposite flat to S and R gets a flat next to U. Also, T gets a north facing flat, this means that the north facing flats are Q, T and S and south facing flats are U, R and P. The possible cases are: -
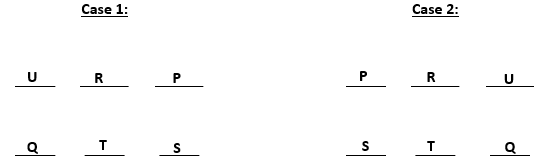
The information is irrelevant as the only flat next to U will be R.
Question 6
If the flats of T and P are interchanged, who’s flat will be next to that of U?
B R
From (iii) and (iv) we can conclude that S gets a north facing flat. From (ii) we get two possible scenarios. These are:-
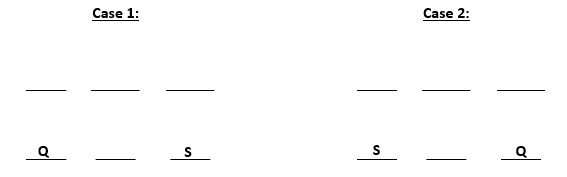
U gets diagonally opposite flat to S and R gets a flat next to U. Also, T gets a north facing flat, this means that the north facing flats are Q, T and S and south facing flats are U, R and P. The possible cases are: -
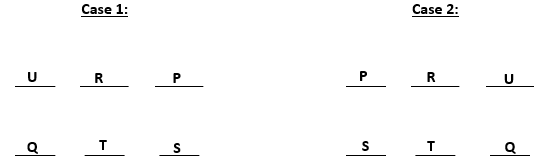
The information is irrelevant as the only flat next to U will be R.
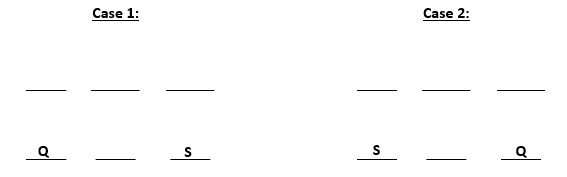
U gets diagonally opposite flat to S and R gets a flat next to U. Also, T gets a north facing flat, this means that the north facing flats are Q, T and S and south facing flats are U, R and P. The possible cases are: -
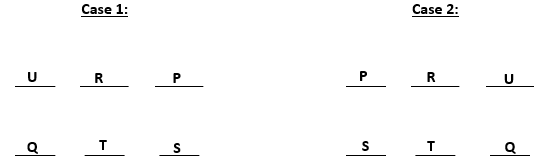
The information is irrelevant as the only flat next to U will be R.
Question 7
‘Only ignorant people believe in witchcraft’ is equivalent to:
C All persons who believe in witchcraft are ignorant.
As per the statement given - Can you have any other group of people other than ignorant people who could believe in witchcraft? No. Therefore, anybody who believes in witchcraft has to be ignorant. For detailed theory on deductive logic refer to our theory books or get in touch with us at the number given on the website.
Question 8
‘There is no man that is not naturally good’ is equivalent to the proposition:
B All men are naturally good.
There is not even a single man who is not naturally good is equivalent to All men are naturally good.
Question 9
Find the odd one out from the following:
B Cruise
Campaign means - a series of military operations intended to achieve a goal
Crusade means - a vigorous campaign for political, social, or religious change
Expedition means - an organized journey for a particular purpose
Cruise means - sail about in an area without a precise destination, especially for pleasure
As could be seen, cruise does not belong to the group.
Crusade means - a vigorous campaign for political, social, or religious change
Expedition means - an organized journey for a particular purpose
Cruise means - sail about in an area without a precise destination, especially for pleasure
As could be seen, cruise does not belong to the group.
Question 10
Find the odd one out from the following:
B Clearly visible
As per CLAT key the answer is 2.
Question 11
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
‘Some of the valuable books are seldom read’, means:
‘Some of the valuable books are seldom read’, means:
C Some of the valuable books are not read.
From some of the books are seldom read we can safely conclude that some valuable books are not read.
Question 12
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
A girl introduced a boy as the son of the daughter of the father of her uncle. The boy is girl's:
A girl introduced a boy as the son of the daughter of the father of her uncle. The boy is girl's:
A Brother
From the information provided there are two cases possible. In case 1 the son is the brother of the girl, in case 2 the son is the cousin of the girl. Since cousin and cannot be determined are not our choices we will go with brother as the correct choice.
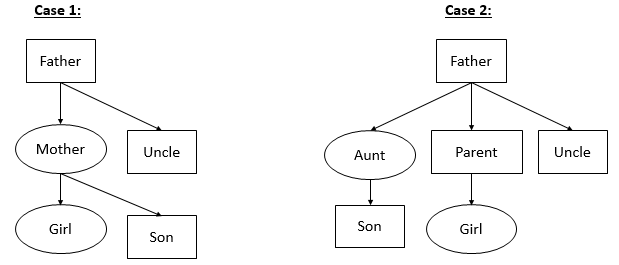

Question 13
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
Mare is to Horse as –
Mare is to Horse as –
D Sow is to Boar
The female of a horse is called a mare, similarly the female of a Boar is called Sow.
Question 14
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
If in a certain code, the word MILITARY is written as 12324567, then in the same code, the word TAIL will be written as:
If in a certain code, the word MILITARY is written as 12324567, then in the same code, the word TAIL will be written as:
D 4523
The pattern is M = 1, I = 2, L = 3, I = 2, T = 4 , A = 5, R = 6 and Y =7. The letters are already coded we just have to write their values. So TAIL will be written as 4523.
Question 15
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
If in a code language, ‘ABANDON’ is written as ‘aramoim’; ‘BORE’ iswritten as ‘rits’ and ‘BASIL’ is written as ‘rabut’, then what is the original word for the code: ‘bituo’?
If in a code language, ‘ABANDON’ is written as ‘aramoim’; ‘BORE’ iswritten as ‘rits’ and ‘BASIL’ is written as ‘rabut’, then what is the original word for the code: ‘bituo’?
A SOLID
If we observe this is a simple rearrangement of words in which the first term of the original is replaced by the first term of the replaced word. For example A of “ABANDON” becomes “a” of “aramoim” and d of “ABANDON” becomes “o” of “aramoim”. By this logic original word of ‘bituo’ will be ‘SOLID’.
Question 16
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
In the series of alphabets given below, which is the missing alphabet series?
AX, DU, GR, ____, ML
In the series of alphabets given below, which is the missing alphabet series?
AX, DU, GR, ____, ML
D JO
A of AX becomes D of DU, that is +3, and D of DU becomes D + 3 = G of GR. By this logic the first term of the missing word will be G + 3 = J.
X of AX becomes U of DU, that is -3, and U of DU becomes U – 3 = R of GR. By this logic the last term of the missing alphabet will become R – 3 = O. So the missing alphabets are JO.
X of AX becomes U of DU, that is -3, and U of DU becomes U – 3 = R of GR. By this logic the last term of the missing alphabet will become R – 3 = O. So the missing alphabets are JO.
Question 17
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
John wants to go the university. He starts from his house which is in the East and comes to a crossing. The road to his left ends in a theatre, straight ahead is the hospital. In which direction is the University?
John wants to go the university. He starts from his house which is in the East and comes to a crossing. The road to his left ends in a theatre, straight ahead is the hospital. In which direction is the University?
B North
It is given that John starts from East but it is not mentioned towards which direction he moves. For lack of this information the answer should have been cannot be determined. However since that is not an option choice we will assume that he moved towards West. Using the given information we can come up with the following diagram –
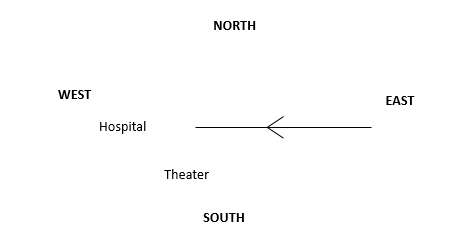
Now we cannot place University unless we assume that the hospital, theater and the University are all in different directions. After doing so we can place University in North. This was an extremely vague question.

Now we cannot place University unless we assume that the hospital, theater and the University are all in different directions. After doing so we can place University in North. This was an extremely vague question.
Question 18
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
A person who renounces religious or political belief or principle is called:
A person who renounces religious or political belief or principle is called:
D apostate
Apostle means - an important early Christian teacher or pioneering missionary, a vigorous and pioneering advocate or supporter of a particular policy, idea, or cause
Ascetic means - characterized by severe self-discipline and abstention from all forms of indulgence, typically for religious reasons
Antiquarian means - relating to or dealing in antiques or rare books
Apostate means - a person who renounces a religious or political belief or principle
Ascetic means - characterized by severe self-discipline and abstention from all forms of indulgence, typically for religious reasons
Antiquarian means - relating to or dealing in antiques or rare books
Apostate means - a person who renounces a religious or political belief or principle
Question 19
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
Identify the statement which cannot be accepted
Identify the statement which cannot be accepted
A Almost one third of the human body is made up of water
The average adult human body is more than 34% water.
Question 20
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
Two ladies and two men are playing bridge and seated at North, East, South and West of a table. No lady is facing East. Persons sitting opposite to each other are not of the same sex. One man is facing South. Which direction are the ladies facing to?
Two ladies and two men are playing bridge and seated at North, East, South and West of a table. No lady is facing East. Persons sitting opposite to each other are not of the same sex. One man is facing South. Which direction are the ladies facing to?
D North and West.
From the information we’ll get the diagram as follows:-
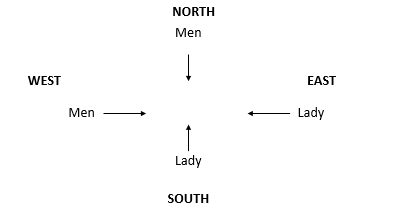
So the two ladies are facing North and West.

So the two ladies are facing North and West.
Question 21
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
Sunil’s school bus is facing North when it reaches his school. After starting from Sunil’s house, it turned right twice and then left before reaching the school. What direction the bus was facing when it left the bus stop in front of Sunil’s house?
Sunil’s school bus is facing North when it reaches his school. After starting from Sunil’s house, it turned right twice and then left before reaching the school. What direction the bus was facing when it left the bus stop in front of Sunil’s house?
B West
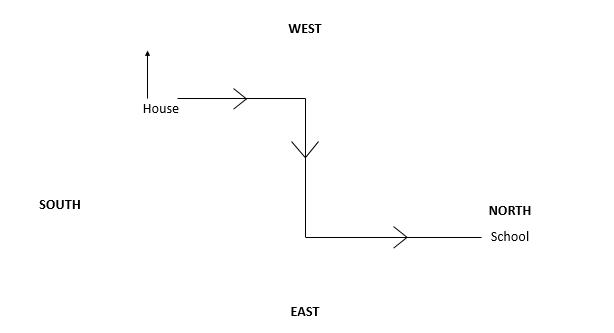
The bus was facing west before leaving his house.
Question 22
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
The birthday of Ms. Y was celebrated six days before Ms. X, who was born on 4th October 1999. The independence day of that year fell on Sunday. On which day did Ms. Y celebrate her birthday, if it was not a leap year?
The birthday of Ms. Y was celebrated six days before Ms. X, who was born on 4th October 1999. The independence day of that year fell on Sunday. On which day did Ms. Y celebrate her birthday, if it was not a leap year?
A Tuesday
Ms Y’s birthday is 6 days before 4th October, that is, on 28th September. 15th of August of this year was a Sunday. From 15th of August to 28th September we have a total of 44 days. 44/7 = 2 remainder or 2 odd days. So, 28th September will be Sunday plus 2 = Tuesday.
Question 23
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
When Ravi saw Ramesh, he recalled, ‘He is the son of the father of my daughter’. Who is Ramesh?
When Ravi saw Ramesh, he recalled, ‘He is the son of the father of my daughter’. Who is Ramesh?
B Brother-in-law
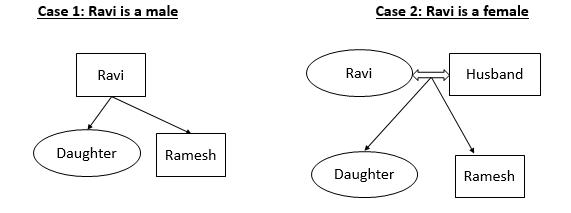
This is a question with all incorrect choices. As per the CLAT answer key the correct answer is 2.
The question “Who is Ramesh?” is vague. Even if we take the question as how is Ramesh related to Ravi the answer will be son which is not given in the option choices.
Question 24
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
What is meant by ‘Alliteration’?
What is meant by ‘Alliteration’?
D The occurrence of the same letter or sound at the beginning of adjacent or closely connected words.
Alliteration means - the occurrence of the same letter or sound at the beginning of adjacent or closely connected words
Question 25
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
A man walks 1 km. towards East and then he turns to South and walks 5 kms. Again he turns to East and walks 2 kms. After this he turns to North and walks 9 kms. Now, how far is he from his starting point?
A man walks 1 km. towards East and then he turns to South and walks 5 kms. Again he turns to East and walks 2 kms. After this he turns to North and walks 9 kms. Now, how far is he from his starting point?
A 5 kms.
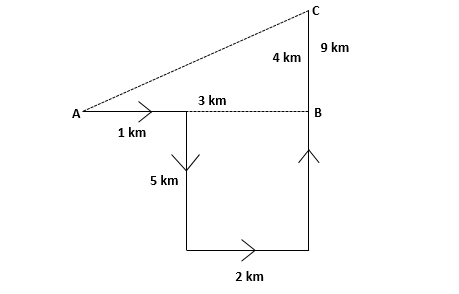
Distance = AC.
AC 2 = AB 2 + BC 2; 32 + 42 = 25. AC = 5
Question 26
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
No parrots are black.
All crows are black.
From the above premises which one of the following conclusions is true?
No parrots are black.
All crows are black.
From the above premises which one of the following conclusions is true?
C No crows are parrots.
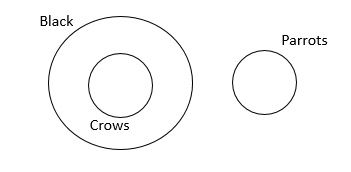
The option choices are weird in this question. Even 1 and 4 are correct. But since we can mark only one and 1 and 4 are basically making the same conclusion we will mark choice 3.
Question 27
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
In a company, 60 % workers are males. If the number of female workers in the company is 800, what is the number of male workers in the company?
In a company, 60 % workers are males. If the number of female workers in the company is 800, what is the number of male workers in the company?
B 1200
40% are females. This is equal to 800. So 60% will be equal to (800 x 60) / 40 = 1200.
Question 28
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
Pointing to a photograph, Prakash said, ‘She is the daughter of my grandfather’s only son’ How is Prakash related to the girl in the photograph?
Pointing to a photograph, Prakash said, ‘She is the daughter of my grandfather’s only son’ How is Prakash related to the girl in the photograph?
C Brother
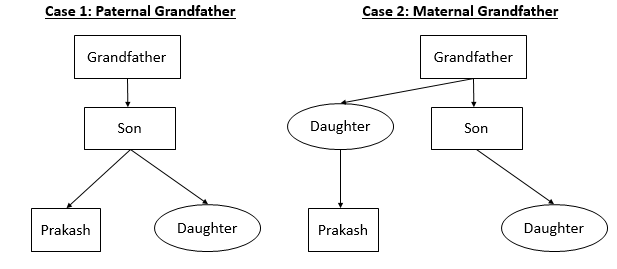
CLAT’s official key states 3 as the correct answer. The correct answer could be 3 or 4. In this year’s questions CLAT assumed only son to be the only child. Also, we had to assume Prakash to be a male.
Question 29
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
wave: crest as _________ : peak.
wave: crest as _________ : peak.
D Mountain
Crest is the top of a wave just like peak is the top of a mountain.
Question 30
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
Crumb : Bread is as
Crumb : Bread is as
D Splinter : Wood
Crumb is a small fragment of bread just like splinter is a small piece of wood.
Question 31
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
________ is a hater of knowledge and learning.
________ is a hater of knowledge and learning.
B Misologist
Misology is defined as the hatred of reasoning
Question 32
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
Ravi was showing a photograph to his friend, Gopi. Pointing at a boy in the photograph, Ravi said: ‘The boy sitting at the left is the son of the wife of the only son of the grandmother of my younger brother’. What is the relation between the boy in the photograph and Ravi?
Ravi was showing a photograph to his friend, Gopi. Pointing at a boy in the photograph, Ravi said: ‘The boy sitting at the left is the son of the wife of the only son of the grandmother of my younger brother’. What is the relation between the boy in the photograph and Ravi?
C Brothers
The question can be solved by using two interpretations:-
Interpretation 1 – only son of grandmother could imply she had only one child.
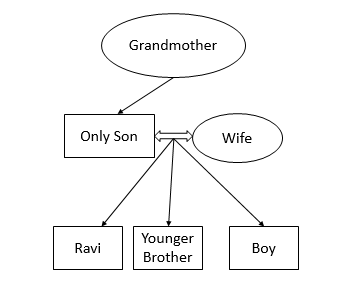
In this case the answer is they are brothers.
Interpretation 2 – only son of grandmother – she might have a daughter and Ravi could be the son of that daughter.
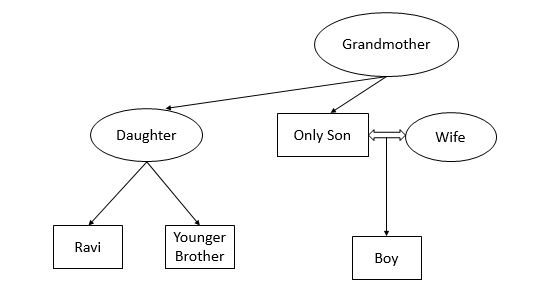
In this case they are cousins. Apparently CLAT marked the answers using first interpretation.
Interpretation 1 – only son of grandmother could imply she had only one child.

In this case the answer is they are brothers.
Interpretation 2 – only son of grandmother – she might have a daughter and Ravi could be the son of that daughter.

In this case they are cousins. Apparently CLAT marked the answers using first interpretation.
Question 33
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
Coding and decoding 9: 72 : : 8 : ?
Coding and decoding 9: 72 : : 8 : ?
A 64
9 x 8 = 72 , so 8 x 8 = 64.
Question 34
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
In a military secret service map, South-East is shown as North, North East as West and so on. What will West become?
In a military secret service map, South-East is shown as North, North East as West and so on. What will West become?
D South-East
If South East becomes North the other changes will be as follows:-
So West will become South East.

So West will become South East.
Question 35
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
How many times from 4 pm to 10 pm, the hands of a clock are at right angles?
How many times from 4 pm to 10 pm, the hands of a clock are at right angles?
B 11
In every hour the hands of a clock are at right angles twice. So in six hours, that is, from 4 to 10 they would be at right angles to each other 12 times. However, since 3 o clock is the common time in time range 2 to 3 and 3 to 4, thus we subtract this once due to repetition in counting. So 11 times the hands will be at right angle.
Question 36
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
If 27th March, 2011 was Sunday, what was the day on 27th June, 2011?
If 27th March, 2011 was Sunday, what was the day on 27th June, 2011?
D Monday
Between 27th March’2011 to 27th June 2011 there are 92 days. So 92 / 7 = 1 is the remainder or one odd day. So 27th June will be a Monday.
Question 37
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
Pointing to a girl in the photograph, Ram said, ‘Her mother`s brother is the only son of my mother's father’. How is the girl`s mother related to Ram?
Pointing to a girl in the photograph, Ram said, ‘Her mother`s brother is the only son of my mother's father’. How is the girl`s mother related to Ram?
D Aunt
Again there are two ways by which one can go about solving this question –
Case 1: My mother’s father had only one daughter.
In this case the girl’s mother is also Ram’s mother.
Case 2: My mother’s father had one more daughter and the girl is the daughter of this person.
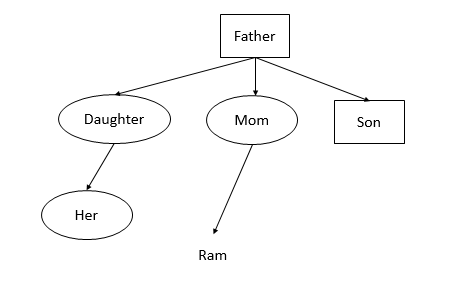
In this case the girl’s mother is the aunt of Ram.
Case 1: My mother’s father had only one daughter.

In this case the girl’s mother is also Ram’s mother.
Case 2: My mother’s father had one more daughter and the girl is the daughter of this person.

In this case the girl’s mother is the aunt of Ram.
Question 38
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
There were twelve dozens of chocolates with a shopkeeper. Ten chocolates were distributed by the shopkeeper to the children of his colony. The shopkeeper then added two more dozens of chocolates in his stock. If the shopkeeper divided the total chocolates equally in two different packets, then how many chocolates were there in each packet?
There were twelve dozens of chocolates with a shopkeeper. Ten chocolates were distributed by the shopkeeper to the children of his colony. The shopkeeper then added two more dozens of chocolates in his stock. If the shopkeeper divided the total chocolates equally in two different packets, then how many chocolates were there in each packet?
D 79
Initially the shopkeeper had twelve dozens of chocolates = 12 x 12 = 144.
He distributed 10 so he will be left with 134 chocolates. He added 2 dozens more, that is, 24. So now he has 134 + 24 = 158. He divided them equally in two packets, so each packet will have 158/2 = 79 chocolates.
He distributed 10 so he will be left with 134 chocolates. He added 2 dozens more, that is, 24. So now he has 134 + 24 = 158. He divided them equally in two packets, so each packet will have 158/2 = 79 chocolates.
Question 39
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
Vaishnavi prefers Economics to Maths, English to Social science, and Political Science to History. If she prefers Maths to History, and Social science to Maths, which is Vaishnavi’s least preferred subject?
Vaishnavi prefers Economics to Maths, English to Social science, and Political Science to History. If she prefers Maths to History, and Social science to Maths, which is Vaishnavi’s least preferred subject?
B History
In this case it is better to work with options. Maths is preferred to History, Social Science to Maths and also Economics to Maths.
Question 40
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions.
If South-East becomes North, North-East becomes West and so on, what will West become?
If South-East becomes North, North-East becomes West and so on, what will West become?
B South-East
If South East becomes North the other changes will be as follows:-
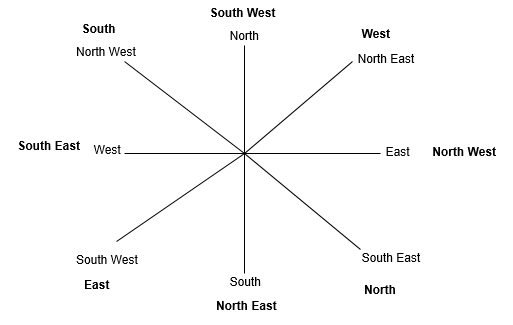
So West will become South East.

So West will become South East.
Section: Legal Aptitude
Question 1
Principle: A contract would be invalid and unlawful, if the contract is for an immoral or illegal purpose.
Facts: P, was a young and helpless widow, living on the pavement. R, a neighbour gave her a house, registered in her name, on the condition that she should allow R to keep his smuggled goods and drugs in her house. After the registration was done, according to the condition in the contract, R’s agents went to keep some packets in her house, she refused. R told her the condition under which the house was given to her. She still refused. Is P justified in her action?
Facts: P, was a young and helpless widow, living on the pavement. R, a neighbour gave her a house, registered in her name, on the condition that she should allow R to keep his smuggled goods and drugs in her house. After the registration was done, according to the condition in the contract, R’s agents went to keep some packets in her house, she refused. R told her the condition under which the house was given to her. She still refused. Is P justified in her action?
D As R was making the contract for illegal activities, P’s stand is valid in law.
Since as per the principle, any contract for immoral or illegal purpose would be invalid, hence P can refuse to keep smuggled goods and drugs in the house.
Question 2
Principle: Acceptance of a proposal must be absolute and unqualified.
Facts: ‘A’ made a proposal to sell his motorcycle to ‘B’ for rupees 25,000/.‘B’ agreed to buy it for rupees 24,000/.‘A’ sold his motorcycle to ‘C’ for 26,000/the next day. ‘B’ sues ‘A’ for damages.
Facts: ‘A’ made a proposal to sell his motorcycle to ‘B’ for rupees 25,000/.‘B’ agreed to buy it for rupees 24,000/.‘A’ sold his motorcycle to ‘C’ for 26,000/the next day. ‘B’ sues ‘A’ for damages.
C ‘B’ will not get any damages from ‘A’
B will not get any damages from A because acceptance must be absolute and unqualified as given in the principle.
Question 3
Principle: Negligence is actionable in law. In simple terms, negligence is the failure to take proper care over something.
Facts: A, a doctor, conducted a hysterectomy sincerely on B and left a small cotton swab inside the abdomen. As a consequence of which B developed some medical problems and had to undergo another surgery. Is A liable?
Facts: A, a doctor, conducted a hysterectomy sincerely on B and left a small cotton swab inside the abdomen. As a consequence of which B developed some medical problems and had to undergo another surgery. Is A liable?
D A is liable for the negligence as he failed to take proper care during the surgery.
A is liable for the negligence as he failed to take proper care during the surgery. The principle given is completely applicable over fact.
Question 4
Principle: When a person consented to an act to be done by another, he cannot claim any damages resulting from doing that act, provided the act done is the same for which consent is given.
Facts: 'P' submitted a written consent to a surgeon 'S' for undergoing a surgical operation for removal of appendicitis. The surgeon while doing surgery also removed the gall bladder of 'A':
Facts: 'P' submitted a written consent to a surgeon 'S' for undergoing a surgical operation for removal of appendicitis. The surgeon while doing surgery also removed the gall bladder of 'A':
C 'P' can claim damages from 'S'
P can claim damages from S because the consent was given for the removal of appendicitis and not for the gall bladder.
Question 5
Principle: Ownership in property consists of right to possess, right to use, right to alienate and right to exclude others. Sale is complete when property gets transferred from the seller to the buyer on sale.
Facts: ‘A’ sold his car to ‘B’. After this, ‘B’ requested ‘A’ to keep the car in his care on behalf ‘B’ for one month. ‘A’ agreed.
Facts: ‘A’ sold his car to ‘B’. After this, ‘B’ requested ‘A’ to keep the car in his care on behalf ‘B’ for one month. ‘A’ agreed.
B Sale of car is complete.
Sale of car is complete and it is absolutely immaterial that B asks A to keep the car on his behalf for a temporary period of time.
Question 6
Principle: Nothing is an offence which is done in the exercise of the right of private defence.
Facts: ‘A’, under the influence of madness, attempts to kill ‘B’. ‘B’ to save his life kills ‘A’.
Facts: ‘A’, under the influence of madness, attempts to kill ‘B’. ‘B’ to save his life kills ‘A’.
B ‘B’ has not committed any offence.
B has not committed any offence because it is immaterial that against whom the right of private defence is exercised.
Question 7
Principle: The Constitution of India guarantees certain fundamental rights to its citizens. The Constitution also provides that these rights cannot be taken away by state even by a law. For violation of this, the person adversely affected by the law may approach the High Court or the Supreme Court for the issuance of an appropriate writ. One of these rights includes the freedom to form association that implies the right to join an association or not to join such an association.
Facts: Owing to some industrial disturbances created by XATU, one of the several trade unions in AB Chemicals (Pvt) Ltd., the Company issued a circular to all its employees that as far as possible the employees may disassociate with XATU. Navin is an employee of AB Chemicals and the current General Secretary of XATU. Aggrieved by this circular, which affected the fundamental rights of his and other members of the Union, approaches the High Court of the state for a relief. Identify the most reasonable legal proposition.
Facts: Owing to some industrial disturbances created by XATU, one of the several trade unions in AB Chemicals (Pvt) Ltd., the Company issued a circular to all its employees that as far as possible the employees may disassociate with XATU. Navin is an employee of AB Chemicals and the current General Secretary of XATU. Aggrieved by this circular, which affected the fundamental rights of his and other members of the Union, approaches the High Court of the state for a relief. Identify the most reasonable legal proposition.
C The prohibition against any imposition of restriction against a fundamental right is not applicable to anybody other than the state and hence Navin will not get any relief from the High Court.
The prohibition against any imposition of restriction against a fundamental right is not applicable to anybody other than the state and hence Navin will not get any relief from the High Court since Navin does not fall within the category of state as given in the principle.
Question 8
Principle: In criminal law, misappropriation is the intentional, illegal use of the property or funds of another person for one's own use or other unauthorized purpose, particularly by a public official, a trustee of a trust, an executor or administrator of a dead person's estate or by any person with a responsibility to care for and protect another's assets. Embezzlement is misappropriation when the funds involved have been lawfully entrusted to the embezzler. On the contrary, theft is the illegal taking of another person's property or services without that person's permission or consent with the intent to deprive the rightful owner of it.
Facts: A went for swimming at the Municipal Swimming Pool. A handed over all his valuables, including some cash to X, the guard on duty for safe custody, as notified by the Municipality. After swimming for an hour, A came out and searched for X. He found another guard on duty and that guard informed A that X had gone home after completing his shift and did not hand over anything to be given to A. A registered a complaint with the police. X was traced but he told the police that he sold all the valuables and the entire cash was used for drinking liquor. What offence, if any, was/were committed by X?
Facts: A went for swimming at the Municipal Swimming Pool. A handed over all his valuables, including some cash to X, the guard on duty for safe custody, as notified by the Municipality. After swimming for an hour, A came out and searched for X. He found another guard on duty and that guard informed A that X had gone home after completing his shift and did not hand over anything to be given to A. A registered a complaint with the police. X was traced but he told the police that he sold all the valuables and the entire cash was used for drinking liquor. What offence, if any, was/were committed by X?
A X is liable for criminal misappropriation and embezzlement.
X is liable for criminal misappropriation because he illegally used the property of another person for one’s own purpose and is liable for embezzlement because he was entrusted the valuable by A.
Question 9
Principle: Contract is a written or spoken agreement, with specific terms between two or more persons or entities in which there is a promise to do something in return for a valuable benefit known as consideration. Such an agreement is intended to be enforceable by law. A unilateral contract is one in which there is a promise to pay or give other consideration in return for actual performance.
Facts: A Toilet Soap Manufacturing Company in India in order to promote the sale of their product, published an advertisement in all the Newspapers on January 1, 2017 that the Company has kept a model ignition key of an Audi A3 Car. The advertisement also stated that whoever gets the said key before December 31, 2017 from a soap bar will be gifted with the Audi A3 Car. Mr. Martin, a foreigner who came to India as a Tourist who was staying in a Hotel found a Key similar to same Car Ignition Key. Mr. Martin brought this matter to the notice of the Hotel Manager. The Manager informed Mr. Martin about the Company’s advertisement on January 1, 2017. Mr. Martin wants to claim the Car.
Will he succeed?
Facts: A Toilet Soap Manufacturing Company in India in order to promote the sale of their product, published an advertisement in all the Newspapers on January 1, 2017 that the Company has kept a model ignition key of an Audi A3 Car. The advertisement also stated that whoever gets the said key before December 31, 2017 from a soap bar will be gifted with the Audi A3 Car. Mr. Martin, a foreigner who came to India as a Tourist who was staying in a Hotel found a Key similar to same Car Ignition Key. Mr. Martin brought this matter to the notice of the Hotel Manager. The Manager informed Mr. Martin about the Company’s advertisement on January 1, 2017. Mr. Martin wants to claim the Car.
Will he succeed?
D Mr. Martin obtained the Key before the stipulated date from the Soap Bar. So he is covered by the offer of the Soap Company and can claim the car.
Mr. Martin obtained the Key before the stipulated date from the Soap Bar. So he is covered by the offer of the Soap Company and can claim the car.
Question 10
Principle: The concept of natural justice is against bias and for the right to a fair hearing. While the term natural justice is often retained as a general concept, and it has largely been replaced and extended by the general ‘duty to act fairly’.
Facts: ‘X’, a male employee of a company was dismissed by the employer just on the basis of a complaint by ‘Y’, a female employee of the company that ‘X’ was trying to be too friendly with her and often requested her to accompany him to the canteen. Is the dismissal of ‘X’ valid?
Facts: ‘X’, a male employee of a company was dismissed by the employer just on the basis of a complaint by ‘Y’, a female employee of the company that ‘X’ was trying to be too friendly with her and often requested her to accompany him to the canteen. Is the dismissal of ‘X’ valid?
C No, because the employer did not give a chance to ‘X’ to explain his side, thereby violated the principles of natural justice.
No, because the employer did not give a chance to ‘X’ to explain his side, thereby violated the principles of natural justice.
Question 11
Principle: A violation of a legal right of someone, whether results in a legal injury or not, gives rise to an action in tort for compensation. At the same time, an action by someone, which results in some loss or damage to somebody else is not actionable, if there is no violation of a right of that somebody.
Facts: AB Coaching Centre was a popular CLAT coaching academy with several good trainers. A lot of aspirants used to attend its coaching classes from all over and was making good profit. This was going on for the past several years. During a session, T, one of the very good and popular trainers of ABCC, had some difference of opinion with the owner of ABCC and left the coaching centre. In August 2016, T started another Entrance Coaching Centre closer to ABCC which resulted in a substantial drop in its students and huge financial loss. The owner of ABCC wants to file a case against T for the loss sustained by ABCC. What do you think is the right legal position?
Facts: AB Coaching Centre was a popular CLAT coaching academy with several good trainers. A lot of aspirants used to attend its coaching classes from all over and was making good profit. This was going on for the past several years. During a session, T, one of the very good and popular trainers of ABCC, had some difference of opinion with the owner of ABCC and left the coaching centre. In August 2016, T started another Entrance Coaching Centre closer to ABCC which resulted in a substantial drop in its students and huge financial loss. The owner of ABCC wants to file a case against T for the loss sustained by ABCC. What do you think is the right legal position?
B T has not violated any of ABCC’s legal right though they sustained some financial loss, and not legally bound to compensate ABCC.
T has not violated any of ABCC’s legal right though they sustained some financial loss, and not legally bound to compensate ABCC because as per the principle if there is no violation of a right even if some loss is caused it is not actionable.
Question 12
Principle: Where one of the parties to a contract was in a position to dominate the decision of the other party, the contract is enforceable only at the option of the party who was in a position to dominate the decision of the other party.
Facts: A doctor asked his patient to make a payment of rupees Ten Lakh for treatment of his fever. The patient paid an amount of rupees Five Lakh and promised to pay the remaining amount after the treatment. After treatment the patient recovered from fever. The doctor demanded the remaining amount from the patient. The patient refused to pay.
Facts: A doctor asked his patient to make a payment of rupees Ten Lakh for treatment of his fever. The patient paid an amount of rupees Five Lakh and promised to pay the remaining amount after the treatment. After treatment the patient recovered from fever. The doctor demanded the remaining amount from the patient. The patient refused to pay.
C The contract is enforceable against the patient by the doctor.
The contract is enforceable against the patient by the doctor since as per the principle doctor is in the position to dominate the decision of the other party.
Question 13
Principle: Every agreement, by which any party is restricted absolutely from enforcing his right in respect of any contract, by the usual legal proceedings in the ordinary Tribunals, is void to that extent. The law also provides that nobody can confer jurisdiction to a civil court by an agreement between parties.
Facts: A and B entered into a valid contract for rendering certain service. A clause in the contract was that in case of any dispute arose out of the contract; it shall be referred to for Arbitration only. Is the contract valid?
Facts: A and B entered into a valid contract for rendering certain service. A clause in the contract was that in case of any dispute arose out of the contract; it shall be referred to for Arbitration only. Is the contract valid?
B Arbitration is also a valid dispute settlement machinery recognized by law and hence the entire contract is valid.
Arbitration is also valid dispute settlement machinery recognized by law and hence the entire contract is valid. As given in the principle, the agreement does not absolutely restrict the parties from enforcing the right in respect of contract.
Question 14
Principle: It is a case of fraud where a party to a contract knows or believes a fact to be true, but conceals it actively from the other party with a view to induce that person to enter into the contract.
Facts: While taking a life insurance policy, in reply to questions by the insurance company during the inquiry into his proposal, Zameer deliberately concealed the fact of his medical treatment for a serious ailment, which he had undergone only a few weeks ago.
Facts: While taking a life insurance policy, in reply to questions by the insurance company during the inquiry into his proposal, Zameer deliberately concealed the fact of his medical treatment for a serious ailment, which he had undergone only a few weeks ago.
B The concealment of fact by Zameer amounted to fraud.
The concealment of fact by Zameer amounted to fraud because Zameer deliberately concealed the fact of his medical treatment for a serious ailment, which he had undergone only a few weeks ago.
Question 15
Principle: When a person falsifies something with the intent to deceive another person or entity is forgery and is a criminal act. Changing or adding the signature on a document, deleting it, using or possessing the false writing is also considered forgery. In the case of writing to fall under the definition, the material included must have been fabricated or altered significantly in order to represent something it is actually not.
Facts: John was a publisher of ancient books and papers. In one of his books on the World Wars, he gave photograph of some letters written by famous historic personalities. A researcher in history noted that in the pictures of some of the letters printed in the book, John had added some words or sentences in his own handwriting to give completeness to the sentences, so that the readers will get a clear picture of the writer’s intention. The researcher challenges the originality of those pictures and claims that the book containing the forged letters should be banned. Examine the validity of the researcher’s demand.
Facts: John was a publisher of ancient books and papers. In one of his books on the World Wars, he gave photograph of some letters written by famous historic personalities. A researcher in history noted that in the pictures of some of the letters printed in the book, John had added some words or sentences in his own handwriting to give completeness to the sentences, so that the readers will get a clear picture of the writer’s intention. The researcher challenges the originality of those pictures and claims that the book containing the forged letters should be banned. Examine the validity of the researcher’s demand.
C The additions were made to give clarity to the original document and did not in any sense change the contents of the documents and hence there is no forgery as alleged by the researcher.
The additions were made to give clarity to the original document and did not in any sense change the contents of the documents and hence there is no forgery as alleged by the researcher.
Question 16
Principle: Whoever takes away with him any minor less than sixteen years of age if a male, or less than eighteen years of age if a female, out of the custody of parents of such minor without the consent of such parents, is said to commit no offence.
Facts: ‘A’, a man, took away a girl below sixteen years to Mumbai without informing the parents of the girl.
Facts: ‘A’, a man, took away a girl below sixteen years to Mumbai without informing the parents of the girl.
C ‘A’ committed no offence against the girl as well as her parents.
Candidates are advised to be careful while reading such questions since the principle given here in is absolutely contrary to the general concept but since the act prescribed in the principle is no offence the candidate is suppose to mark accordingly. Therefore, ‘A’ committed no offence against the girl as well as her parents.
Question 17
Principle: There are legal provisions to give authority to a person to use necessary force against an assailant or wrongdoer for the purpose of protecting one’s own body and property as also another’s body and property when immediate aid from the state machinery is not readily available; and in so doing he is not answerable in law for his deeds.
Facts: X, a rich man was taking his morning walk. Due to the threat of robbers in the locality, he was carrying his pistol also. From the opposite direction, another person was coming with a ferocious looking dog. All of a sudden, the dog which was on a chain held by the owner, started barking at X. The owner of the dog called the dog to be calm. They crossed each other without any problem. But suddenly, the dog started barking again from a distance. X immediately took out his pistol. By seeing the pistol the dog stopped barking and started walking with the owner. However, X shot at the dog which died instantly. The owner of the dog files a complaint against X, which in due course reached the Magistrate Court. X pleads the right of private defence. Decide.
Facts: X, a rich man was taking his morning walk. Due to the threat of robbers in the locality, he was carrying his pistol also. From the opposite direction, another person was coming with a ferocious looking dog. All of a sudden, the dog which was on a chain held by the owner, started barking at X. The owner of the dog called the dog to be calm. They crossed each other without any problem. But suddenly, the dog started barking again from a distance. X immediately took out his pistol. By seeing the pistol the dog stopped barking and started walking with the owner. However, X shot at the dog which died instantly. The owner of the dog files a complaint against X, which in due course reached the Magistrate Court. X pleads the right of private defence. Decide.
A There was no imminent danger to X as the dog stopped barking and was walking with the owner. Hence, shooting it amounted to excessive use of the right of private defence and hence liable for killing the dog.
There was no imminent danger to X as the dog stopped barking and was walking with the owner. Hence, shooting it amounted to excessive use of the right of private defence and hence liable for killing the dog.
Question 18
Principle: A person is said to do a thing fraudulently, if he does that thing with intent to defraud, but not otherwise.
Facts: 'A' occasionally hands over his ATM card to 'B' to withdraw money for 'A'. On one occasion 'B' without the knowledge of 'A', uses 'A's ATM card to find out the balance in 'A's account, but does not withdraw any money.
Facts: 'A' occasionally hands over his ATM card to 'B' to withdraw money for 'A'. On one occasion 'B' without the knowledge of 'A', uses 'A's ATM card to find out the balance in 'A's account, but does not withdraw any money.
C 'B' has not committed the act fraudulently
'B' has not committed the act fraudulently because there was no intent to defraud, hence not liable.
Question 19
Principle: Section 34 of Indian Penal Code provides that ‘When a criminal act is done by several persons in furtherance of the common intention of all, each of such persons is liable for that act in the same manner as if it were done by him alone.’
Facts: Three vagabonds, Sanju, Dilbag and Sushil decided to commit burglary. In the night, Sushil opened the lock and they broke into a rich man’s house when the entire family was on a pilgrimage. Sanju had gone to that house earlier in connection with some cleaning job. There was only a servant lady in the house. Hearing some sounds from the master bed room, the servant switched on the lights and went up to the room from where she heard the sound. Noticing that the servant was going to cry for help, Sanju grabbed her and covered her mouth with his hands and dragged her into the nearby room. The other two were collecting whatever they could from the room. When they were ready to go out of the house, they looked for Sanju and found him committing rape on the servant. They all left the house and the servant reported the matter to the police and identified Sanju. Subsequently, all three were arrested in connection with the offences of house breaking, burglary and rape. Identify the legal liability of the three.
Facts: Three vagabonds, Sanju, Dilbag and Sushil decided to commit burglary. In the night, Sushil opened the lock and they broke into a rich man’s house when the entire family was on a pilgrimage. Sanju had gone to that house earlier in connection with some cleaning job. There was only a servant lady in the house. Hearing some sounds from the master bed room, the servant switched on the lights and went up to the room from where she heard the sound. Noticing that the servant was going to cry for help, Sanju grabbed her and covered her mouth with his hands and dragged her into the nearby room. The other two were collecting whatever they could from the room. When they were ready to go out of the house, they looked for Sanju and found him committing rape on the servant. They all left the house and the servant reported the matter to the police and identified Sanju. Subsequently, all three were arrested in connection with the offences of house breaking, burglary and rape. Identify the legal liability of the three.
C Only Sanju will be liable for rape as he was the one who actually committed the offence.
Only Sanju will be liable for rape as he was the one who actually committed the offence. There is no common intention between Sanju, Dilbag and Sushil to commit rape.
Question 20
Principle: Every agreement, of which the object or consideration is opposed to public policy, is void. An agreement which has the tendency to injure public interest or public welfare is one against public policy. What constitutes an injury to public interest or public welfare would depend upon the times and the circumstances.
Facts: ‘A’ promises to obtain for ‘B’ an employment in the public service, and ‘B’ promises to pay rupees 5,00,000/-to ‘A’.
Facts: ‘A’ promises to obtain for ‘B’ an employment in the public service, and ‘B’ promises to pay rupees 5,00,000/-to ‘A’.
D The agreement is void, as the object and consideration for it is opposed to public policy.
The agreement is void, as the object and consideration for it is opposed to public policy. Obtaining employment in public service for someone is unlawful as well as against public policy.
Question 21
Principle: If a party to a contract agrees to it under undue influence of any other party then the party under the undue influence may refuse to perform in accordance with the agreement.
Facts: A, a rich youngster became a member of a religious group and soon he was appointed by P the head of the group as his personal secretary. As per the rules of the group, all officials and staff of the group were supposed to stay in the group’s official premises itself. Some days later, A was asked by P to execute a Gift deed in favour of P, in which it was mentioned that all immovable properties in his name are being gifted to P. A was unwilling to execute the deed, but he was forcefully restrained by P and his body guards in P’s office and made A sign the gift deed. Soon after this A left the group and refused to hand over the property as agreed to in the gift deed. Is A’s action valid?
Facts: A, a rich youngster became a member of a religious group and soon he was appointed by P the head of the group as his personal secretary. As per the rules of the group, all officials and staff of the group were supposed to stay in the group’s official premises itself. Some days later, A was asked by P to execute a Gift deed in favour of P, in which it was mentioned that all immovable properties in his name are being gifted to P. A was unwilling to execute the deed, but he was forcefully restrained by P and his body guards in P’s office and made A sign the gift deed. Soon after this A left the group and refused to hand over the property as agreed to in the gift deed. Is A’s action valid?
B A executed the deed, under compulsion and undue influence, and was right in withdrawing from the contract.
A executed the deed, under compulsion and undue influence, and was right in withdrawing from the contract.
Question 22
Principle: Penal laws provide that whoever voluntarily has carnal intercourse against the order of nature with any man or woman, shall be punished for rape.
Facts: A Police Officer found a man engaged in carnal intercourse with an animal. The Police Officer arrested the man and produced him before the Court.
Facts: A Police Officer found a man engaged in carnal intercourse with an animal. The Police Officer arrested the man and produced him before the Court.
A Court will not punish the man for rape.
Court will not punish the man for rape because as per the given principle intercourse only with the man or woman constitutes rape but in the given case the man has committed intercourse with the anima, hence rape has not been committed.
Question 23
Principle: When a person makes such a statement which lowers other person's reputation in the estimation of other persons, is liable for committing defamation.
Facts: 'A' writes a letter to 'B' in which he uses abusive language against 'B' and also states that 'B' is a dishonest person. 'A' put the letter in a sealed envelope and delivered it to 'B'.
Facts: 'A' writes a letter to 'B' in which he uses abusive language against 'B' and also states that 'B' is a dishonest person. 'A' put the letter in a sealed envelope and delivered it to 'B'.
D 'A' has not committed defamation
'A' has not committed defamation because the letter in the sealed envelope has only been delivered, it has not been opened yet and hence the principle is not applicable.
Question 24
Principle: When a person falsifies something with the intent to deceive another person or entity is forgery and is a criminal act. Changing or adding the signature on a document, deleting it, using or possessing the false writing is also considered forgery. In the case of writing/painting to fall under the definition, the material included must have been fabricated or altered significantly in order to represent something it is actually not.
Facts: David made a living traveling from city to city, selling paintings that he claimed were done by great artists. Since the artists’ signatures were in place, many people fell for them and purchased the paintings. One of these artists saw three of his alleged paintings in a City gallery containing his name. He knew these were not his works and he complained to the police. Police traced David and initiated legal proceedings. Is David guilty of any offence?
Facts: David made a living traveling from city to city, selling paintings that he claimed were done by great artists. Since the artists’ signatures were in place, many people fell for them and purchased the paintings. One of these artists saw three of his alleged paintings in a City gallery containing his name. He knew these were not his works and he complained to the police. Police traced David and initiated legal proceedings. Is David guilty of any offence?
C David is guilty of forgery as the addition of the signature was with an intention to make people believe that those were the paintings of the great artists.
David is guilty of forgery as the addition of the signature was with an intention to make people believe that those were the paintings of the great artists.
Question 25
Principle: According to Sec. 2 of the Industrial Disputes Act, 1947, ‘Industrial dispute means any dispute or difference between employers and employers or between employers and workmen or between work men and workmen, which is connected with the employment or non-employment or the terms of employment or with the conditions of labour of any person’.
Facts: The employees of DK Enterprises met the management and requested half a day leave to allow them to celebrate a lunar eclipse, which was going to happen two days later. The management refused the request. Does this situation amount to an ‘industrial dispute’?
Facts: The employees of DK Enterprises met the management and requested half a day leave to allow them to celebrate a lunar eclipse, which was going to happen two days later. The management refused the request. Does this situation amount to an ‘industrial dispute’?
D As the difference of opinion between the employees and employer is on declaration of holiday it amounts to an issue connected with employment or with the terms of employment and hence, an industrial dispute.
As the difference of opinion between the employees and employer is on declaration of holiday it amounts to an issue connected with employment or with the terms of employment and hence, an industrial dispute.
Question 26
Principle: A master shall be liable for the fraudulent acts of his servants committed in the course of employment. However, the master and third parties must exercise reasonable care in this regard.
Facts: Rahul was a door to door salesman with United Manufacturing
Company (the Company). The Company was manufacturing Water Purifiers. Rahul, along with the Company’s products, used to carry Water Purifiers manufactured by his Cousin in a local Industrial Estate. He used to sell the local product at a lower rate giving the impression to the buyers that he is offering a discount on the Company’s product. The Company Management detected the fraudulent activity of Rahul and dismissed him from service. Rahul still continued to carry on with his activity of selling the local product pretending that he was still a salesman of the Company. Several customers got cheated in this process. The fraud was noticed by the Company when the customers began to complain about the product. The customers demanded the Company to compensate their loss.
Facts: Rahul was a door to door salesman with United Manufacturing
Company (the Company). The Company was manufacturing Water Purifiers. Rahul, along with the Company’s products, used to carry Water Purifiers manufactured by his Cousin in a local Industrial Estate. He used to sell the local product at a lower rate giving the impression to the buyers that he is offering a discount on the Company’s product. The Company Management detected the fraudulent activity of Rahul and dismissed him from service. Rahul still continued to carry on with his activity of selling the local product pretending that he was still a salesman of the Company. Several customers got cheated in this process. The fraud was noticed by the Company when the customers began to complain about the product. The customers demanded the Company to compensate their loss.
A The Company is liable to compensate all the customers as it did not inform the public about Rahul’s fraudulent conduct and the subsequent dismissal.
The Company is liable to compensate all the customers as it did not inform the public about Rahul’s fraudulent conduct and the subsequent dismissal.
Question 27
Principle: When a person who has made a promise to another person to do something does not fulfill his promise, the other person becomes entitled to receive, from the person who did not fulfill his promise, compensation in the form of money.
Facts: ‘X’ made a promise to ‘Y’ to repair his car engine. ‘Y’ made the payment for repair. After the repair, ‘Y’ went for a drive in the same car. While driving the car, ‘Y’ met with an accident due to bursting of a tyre.
Facts: ‘X’ made a promise to ‘Y’ to repair his car engine. ‘Y’ made the payment for repair. After the repair, ‘Y’ went for a drive in the same car. While driving the car, ‘Y’ met with an accident due to bursting of a tyre.
B ‘Y’ will not be entitled to receive compensation from ‘X’.
‘Y’ will not be entitled to receive compensation from ‘X’ because Y met with an accident due to bursting of tire which was absolutely different from X’s promise to repair the car engine.
Question 28
Principle: According to law, a person who find goods belonging to another and takes them into his custody, is subject to the same responsibility as a bailee. Bailee is a person or party to whom goods are delivered for a purpose, such as custody or repair, without transfer of ownership. The finder of the goods legally can sell the goods found by him under certain circumstances including the situation that the owner refuses to pay the lawful charges of the finder.
Facts: P, a college student, while coming out of a Cricket stadium found a necklace, studded with apparently precious diamonds. P kept it for two days thinking that the owner would notify it in a local newspaper. Since he did not notice any such notification, P published a small classified advertisement in a local newspaper. In two days’ time, P was contacted by a film actor claiming that it was her Necklace and requested P to return it to her. P told her that she should compensate him for the advertisement charges then only he would return it otherwise he will sell it and make good his expenses. The film star told P that she had advertised in a national newspaper about her lost Necklace which was lost somewhere in the Cricket Stadium. The advertisement was published for three consecutive days incurring a large expenditure for her. Mentioning all this she refuses to pay P and claims the Necklace back. Which among the following is the most appropriate answer to this?
Facts: P, a college student, while coming out of a Cricket stadium found a necklace, studded with apparently precious diamonds. P kept it for two days thinking that the owner would notify it in a local newspaper. Since he did not notice any such notification, P published a small classified advertisement in a local newspaper. In two days’ time, P was contacted by a film actor claiming that it was her Necklace and requested P to return it to her. P told her that she should compensate him for the advertisement charges then only he would return it otherwise he will sell it and make good his expenses. The film star told P that she had advertised in a national newspaper about her lost Necklace which was lost somewhere in the Cricket Stadium. The advertisement was published for three consecutive days incurring a large expenditure for her. Mentioning all this she refuses to pay P and claims the Necklace back. Which among the following is the most appropriate answer to this?
A P was requesting the film star for the actual expenditure incurred by him before returning the Necklace. This request is legally sustainable.
P was requesting the film star for the actual expenditure incurred by him before returning the Necklace. This request is legally sustainable.
Question 29
Principle: Assault is causing bodily injury to another person by use of physical force.
Facts: Rustum while entering into compartment of a train raised his fist in anger towards a person Sheetal, just in front of him in the row, to get way to enter into the train first, but did not hit him. Rustum has:
Facts: Rustum while entering into compartment of a train raised his fist in anger towards a person Sheetal, just in front of him in the row, to get way to enter into the train first, but did not hit him. Rustum has:
D not committed an assault on Sheetal
Rustom has not commited assault on Sheetal because no bodily injury has been caused to Sheetal by use of physical force.
Question 30
Principle: Under the Employees Compensation Act, 1923, an employer is liable to pay compensation to his workmen for injuries sustained by them by an accident arising out of and in the course of employment.
Facts: M, the Manager of SRK Industries asked his secretary S to submit a report at the Government Labour Office. ‘S’ submitted the report as directed. On his way back S met one of his class mates. He then decided to have a cup of tea together on a way side restaurant. Sometime later, ‘S’ got a message from his office to report back as it was long time since he left the office. ‘S’ rushed back on his Motor Cycle. On his way back a Truck which was coming from a side road hit ‘S’. He was admitted in a nearby hospital with multiple injuries. He claims compensation under the Employees Compensation Act from his employer.
Facts: M, the Manager of SRK Industries asked his secretary S to submit a report at the Government Labour Office. ‘S’ submitted the report as directed. On his way back S met one of his class mates. He then decided to have a cup of tea together on a way side restaurant. Sometime later, ‘S’ got a message from his office to report back as it was long time since he left the office. ‘S’ rushed back on his Motor Cycle. On his way back a Truck which was coming from a side road hit ‘S’. He was admitted in a nearby hospital with multiple injuries. He claims compensation under the Employees Compensation Act from his employer.
C The Employer is liable to pay compensation as the accident took place arising out of and in the course of employment.
The Employer is liable to pay compensation as the accident took place arising out of and in the course of employment.
Question 31
Principle: According to the law of trade unions in India, no suit or other legal proceeding shall be maintainable in any civil court against any registered trade union or any officer or member thereof in respect of any act done in contemplation or in furtherance of a trade dispute.
Facts: Soloman, the Secretary of a registered Trade Union took a loan from a Bank for the higher education of his daughter. Soon after completing the course she was married to an NRI Engineer. Solomon did not repay the loan. The Bank demanded the payments from Soloman and warned him that the Bank will take suitable legal action against him. Identify the legal position in this regard.
Facts: Soloman, the Secretary of a registered Trade Union took a loan from a Bank for the higher education of his daughter. Soon after completing the course she was married to an NRI Engineer. Solomon did not repay the loan. The Bank demanded the payments from Soloman and warned him that the Bank will take suitable legal action against him. Identify the legal position in this regard.
C The Bank can file a suit for recovery of the loan amount against Soloman as he took the loan for a personal purpose and in such case no immunity will work.
The Bank can file a suit for recovery of the loan amount against Soloman as he took the loan for a personal purpose and in such case no immunity will work.
Question 32
Principle: An agreement, the terms of which are not certain, or capable of being made certain, is void.
Facts: Sunder agreed to take Bhola’s penthouse on rent for three years at the rate of rupees 12, 00,000/per annum provided the house was put to thorough repairs and the living rooms were decorated according to contemporary style.
Facts: Sunder agreed to take Bhola’s penthouse on rent for three years at the rate of rupees 12, 00,000/per annum provided the house was put to thorough repairs and the living rooms were decorated according to contemporary style.
A There is no valid contract because it has vague and uncertain terms, as the term ‘present style’ may mean one thing to Sunder and another to Bhola.
There is no valid contract because it has vague and uncertain terms, as the term ‘present style’ may mean one thing to Sunder and another to Bhola.
Question 33
Principle: According to law, a person is deemed to have attained the age of majority when he completes the age of 18 years, except in the case of a person where a guardian of a minor’s person or property has been appointed under the Guardians and Wards Act, 1890 or where the superintendence of a minor’s property is assumed by a Court of Wards. Indian law expressly forbids a minor from entering into a contract. Hence, any contract entered into by a minor is void-ab-initio regardless of whether the other party was aware of his minority or not. Further, though a minor is not competent to contract, nothing in the Contract Act prevents him from making the other party bound to the minor.
Facts: Lal executed a promissory note in favour of Gurudutt, aged 16years stating that he would pay Gurudutt a sum of Rs. 2 Lakhs when he attains the age of majority. On attaining the age of 18, Gurudutt demanded the amount from Lal, who refused to pay. Gurudutt wants to take legal action against Lal. Identify the most appropriate legal position from the following:
Facts: Lal executed a promissory note in favour of Gurudutt, aged 16years stating that he would pay Gurudutt a sum of Rs. 2 Lakhs when he attains the age of majority. On attaining the age of 18, Gurudutt demanded the amount from Lal, who refused to pay. Gurudutt wants to take legal action against Lal. Identify the most appropriate legal position from the following:
A A promissory note duly executed in favour of a minor is not void and can be sued upon by him, because he though incompetent to contract, may yet accept a benefit.
A promissory note duly executed in favour of a minor is not void and can be sued upon by him, because he though incompetent to contract, may yet accept a benefit.
Question 34
Principle: When a person interferes with peaceful possession of another person without the permission of the person in possession of those premises, commits trespass to land.
Facts: 'T' just walked over the land of 'P' to reach his house as it was a short cut. 'P' had displayed a notice that it is not a thoroughfare. 'P' did not cause any damage to the land.
Facts: 'T' just walked over the land of 'P' to reach his house as it was a short cut. 'P' had displayed a notice that it is not a thoroughfare. 'P' did not cause any damage to the land.
A 'T' has committed trespass to land
'T' has committed trespass to land because he has interfered with peaceful possession of another person without the permission of the person in possession of those premises. It is immaterial that damage has been caused to the land or not.
Question 35
Principle: An offer made by one party when accepted by another makes it a contract.
Transactions:
1. P offered to sell his house for Rs. 20 lakhs to R; R told P that he was interested to buy a house for 15 lakhs only.
2. C was looking for a house for not more than 25 lakhs; P informed C that his house was available for 20 lakhs.
3. K wanted to buy some old furniture; L told K that he would sell his furniture for Rs. 10, 000.
4. R advertised to sell his old car for a price of Rs. Three lakhs; S found the advertisement and offered to buy it for Rs. 2 lakhs 50 thousand; R agrees to sell it to S.
Which among the above is actually a contract?
Transactions:
1. P offered to sell his house for Rs. 20 lakhs to R; R told P that he was interested to buy a house for 15 lakhs only.
2. C was looking for a house for not more than 25 lakhs; P informed C that his house was available for 20 lakhs.
3. K wanted to buy some old furniture; L told K that he would sell his furniture for Rs. 10, 000.
4. R advertised to sell his old car for a price of Rs. Three lakhs; S found the advertisement and offered to buy it for Rs. 2 lakhs 50 thousand; R agrees to sell it to S.
Which among the above is actually a contract?
A Situation 4 only is a contract
It is only in situation 4 that the principle given is being fulfilled as the offer given by S to buy car for Rs. 2 lakh 50 thousand has been accepted by R and he sells it to S consequently.
Question 36
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
Paripassu
Paripassu
A On equal footing
On equal footing
Question 37
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
Malus animus
Malus animus
D Bad intention
Bad intention
Question 38
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
In pari delicto
In pari delicto
A Where both parties to a dispute are equally at fault
Where both parties to a dispute are equally at fault
Question 39
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
Lispendens
Lispendens
A Pending suit
Pending suit
Question 40
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
Per incuriam
Per incuriam
D Mistaken decision
Mistaken decision
Question 41
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
Bona vacantia
Bona vacantia
D Goods that have no owner
Goods that have no owner
Question 42
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
‘PunctumTemporis’ means:
‘PunctumTemporis’ means:
A Point of time
Point of time
Question 43
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
Faux pas
Faux pas
A Tactless mistake
Tactless mistake
Question 44
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
Caveat venditor
Caveat venditor
D Seller beware
Seller beware
Question 45
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
Autrefois convict
Autrefois convict
B Formerly convicted
Formerly convicted
Question 46
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
Lex loci
Lex loci
B Law of a place
Law of a place
Question 47
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
Animus posssidendi’ means:
Animus posssidendi’ means:
C Intention to possess
Intention to possess
Question 48
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
‘JusGentium’ means:
‘JusGentium’ means:
A Law among Nations
Law among Nations
Question 49
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
‘Sine die’ means:
‘Sine die’ means:
B Adjourned without fixing any date for the next meeting.
Adjourned without fixing any date for the next meeting.
Question 50
Legal phrases are followed by four meanings. Choose the most appropriate option:
Turpis arbiter’ means:
Turpis arbiter’ means:
B Corrupt judge
Corrupt judge

