Section: Verbal Ability
Question 1
Fill in the blanks by choosing the most appropriate option:
I like reading journals _______ novels.
I like reading journals _______ novels.
B More than
When comparing two things, we should use the comparative degree ‘more than’.
Question 2
Fill in the blanks by choosing the most appropriate option:
There isn't _______ water in the overhead tank.
There isn't _______ water in the overhead tank.
B Any
The negative used in the first part of the sentence rules out the positive quantifier ‘lot of’. Also ‘little’ and ‘something’ are incorrect with water in this context. So the correct word is ‘any’.
Question 3
Fill in the blanks by choosing the most appropriate option:
They always give the available seats to _______ comes first.
They always give the available seats to _______ comes first.
D Whoever
We need an indefinite pronoun here in the subjective form. Hence the correct word is ‘whoever’.
Question 4
Fill in the blanks by choosing the most appropriate option:
A fire broke _____ in the neighbourhood.
A fire broke _____ in the neighbourhood.
B Out
The correct preposition that agrees with the verb ‘broke’ in this sentence is ‘out’. To ‘break out’ means ‘to start suddenly’.
Question 5
Fill in the blanks by choosing the most appropriate option:
If you promise _______ angry with me, I'll tell you what I broke.
If you promise _______ angry with me, I'll tell you what I broke.
A Not to get
We need an infinitive after the verb ‘promise’. Hence the infinitive ‘to get’ should be used with the negation ‘not’ to agree with the context of the sentence.
Question 6
Fill in the blanks by choosing the most appropriate option:
A thief does not ______ the door.
A thief does not ______ the door.
B Knock on
The correct choice here is ‘knock at’. “Knock on” would be used to convey that “a sound is produced by repeatedly hitting something”. In this sentence, we are not talking about the sound; rather the implication is that the expectation that a thief would ‘knock at the door’ is misplaced.
Question 7
Fill in the blanks by choosing the most appropriate option:
There is a lot of work ______ hand. Let's cancel ______ picnic.
There is a lot of work ______ hand. Let's cancel ______ picnic.
C In, the
When work is ‘in hand’ it means that the work demand immediate attention. Also picnic should be preceded by the definite article ‘the’, as it must have been planned beforehand and hence is a specific thing being discussed.
Question 8
Fill in the blanks by choosing the most appropriate option:
It's unfortunate that he died _____ cancer.
It's unfortunate that he died _____ cancer.
B Of
It is correct to say that somebody ‘died of’ cancer or something else.
Question 9
Fill in the blanks by choosing the most appropriate option:
Professor Ahmed _____ teaching us _____ August, 2012.
Professor Ahmed _____ teaching us _____ August, 2012.
C Has been, since
Clearly we need to use the perfect continuous tense, so option a can be ruled out. Also note that ‘for’ is used for a particular duration of time, while ‘since’ is used along with a particular time (i.e. date, month, year etc.). Finally, the present perfect continuous is apt as the past perfect tense must be accompanied by another verb in the simple past tense.
Question 10
Fill in the blanks by choosing the most appropriate option:
The method and practice of teaching is called ______.
The method and practice of teaching is called ______.
B Pedagogy
The meaning of pedagogy is ‘teaching’.
Paediatrics refers to ‘the branch of medicine that deals with children and their diseases’.
Training is a general term used to refer to ‘teaching a particular skill’.
Philately is ‘the collection and study of stamps’.
Paediatrics refers to ‘the branch of medicine that deals with children and their diseases’.
Training is a general term used to refer to ‘teaching a particular skill’.
Philately is ‘the collection and study of stamps’.
Question 11
Complete the sentences with the correct options:
Her parents have arrived _____ the airport.
Her parents have arrived _____ the airport.
B At
The preposition of location here should be ‘at’ as it is a specific place i.e. the airport.
Question 12
Complete the sentences with the correct options:
They returned home _____ a taxi.
They returned home _____ a taxi.
A In
The correct preposition here should be ‘in’.
Question 13
Complete the sentences with the correct options:
I have never come _______ anyone as rude as him.
I have never come _______ anyone as rude as him.
A Across
The correct preposition that is used along with the verb ‘come’ is ‘across’.
Question 14
Complete the sentences with the correct options:
I can't bear ____ late.
I can't bear ____ late.
D Being
After the verb ‘bear’ we need a noun. Hence the correct word is the gerund ‘being’, a noun form of the verb ‘to be’.
Question 15
Complete the sentences with the correct options:
Mani, along with his friends, _____ for basketball practice every morning.
Mani, along with his friends, _____ for basketball practice every morning.
C Goes
Since the action is something that Mani does ‘every morning’ i.e. habitually, we must use the simple present tense i.e. ‘goes’.
Question 16
Choose the correct spellings in questions given below:
Choose the correct spellings
.
Choose the correct spellings
.
C Sacrilegious
Sacrilegious
Question 17
Choose the correct spellings in questions given below:
A Deceive
Deceive
Question 18
Choose the correct spellings in questions given below:
A Collaborate
Collaborate
Note: The correct word has been repeated in option (c) as well.
Note: The correct word has been repeated in option (c) as well.
Question 19
Choose the correct spellings in questions given below:
B barrister
barrister
Question 20
Choose the correct spellings in questions given below:
A Integrity
Integrity
Question 21
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions:
"Faux pas" means:
"Faux pas" means:
C Social blunder
A ‘faux pas’ is a ‘an embarrassing or tactless act or remark in a social situation’.
Question 22
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions:
"Ab initio" means:
"Ab initio" means:
B from the beginning
The meaning of the legal phrase ‘ab initio’ is ‘from the beginning’.
Question 23
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions:
"To bury the hatchet" means:
"To bury the hatchet" means:
A To end a feud with an enemy
The meaning of the idiom ‘to bury the hatchet’ is ‘to end a quarrel or conflict and become friendly’.
Question 24
Choose the most appropriate option for each of the following questions:
"Amicus curiae" means:
"Amicus curiae" means:
B A friend of the court
The meaning of ‘Amicus curiae’ is ‘friend of the court’.
Question 25
Choose the correct option for each of the following questions:
Choose the correct option.
Choose the correct option.
B Please stop interfering in my romantic life.
The correct preposition to go along with ‘interfering’ in this sentence is ‘in’.
Question 26
Choose the correct option for each of the following questions:
Choose the correct option.
Choose the correct option.
D The Titanic did not reach its destination
The subject here is ‘The Titanic’ which is a singular one. Hence the pronoun that refers to it should also be singular i.e. ‘its’.
Question 27
Choose the correct option for each of the following questions:
Choose the correct option.
Choose the correct option.
C The Film Star got out of the car and smiled at the people.
‘Climb off’ is used when you have climbed something such as a tree, ladder etc.
There is a tense error in option b – it should be in the past tense ‘came out’.
‘Got off’ is generally used with public transport such as train, bus, aircraft etc that you board.
The correct choice here is ‘got out of’.
There is a tense error in option b – it should be in the past tense ‘came out’.
‘Got off’ is generally used with public transport such as train, bus, aircraft etc that you board.
The correct choice here is ‘got out of’.
Question 28
Choose the correct option for each of the following questions:
Choose the correct option.
Choose the correct option.
A Your grammar is very good, but you need to work on correcting your pronunciation.
Pronunciation is corrected, not managed, repaired or modified.
Question 29
Complete the proverb, in the following questions:
When _____ is bliss, it is _____ to be wise.
When _____ is bliss, it is _____ to be wise.
B Ignorance, folly
Recall the popular saying ‘Ignorance is bliss’. This sentence builds on this by saying that as a consequence, being wise becomes a folly.
Question 30
Complete the proverb, in the following questions:
______ waters run _____.
______ waters run _____.
D Still, deep
Recall the popular saying ‘Still waters run deep’ which means that a placid or quiet manner/exterior may conceal a passionate nature (on the inside).
Question 31
The Manhattan Project was intiated ______.
D To carry out nuclear research
Einstein urged President Franklin to launch an American programme on nuclear research. The matter was considered and a project called the Manhattan Project was initiated.
Question 32
Alfred eastablished the Nobel Prizes to ______.
B Ease his guilt and promote work for the betterment of mankind.
It is given in the passage that as he grew older, he began suffering from guilt of having invented the dynamite that was being used for destructive purposes. He established Nobel Prizes to ease his guilt and promote work for betterment of mankind.
Question 33
In paragraph 4, the word 'accomplished' means ___________.
A Completed successfully
The word “accomplished” means completed successfully.
Question 34
In the fifth paragraph, the word 'endorsement' means
B Expressing one's approval or support.
The word endorsement means expressing one’s approval or support.
Question 35
Working with arms and ammunition helped Alfred to amass _______.
C Wealth
Paragraph two last two lines.
Question 36
Immanuel's interest in dynamites influenced Alfred's inclination for working ________.
B with explosives
Second paragraph
Question 37
One of the paradoxes in Alfred's life was that he was _________.
D occupied yet lonely
“Paradoxically, Nobel’s life was a busy one yet he was lonely”.
Question 38
Einstein had the impression that the Germans would _______.
B be successful in making the world's first atomic bomb.
Paragraph five first two lines.
Question 39
The passage is _________.
D A descriptive essay.
Option “2” and “4” are close choices. In the passage the author explains how a person’s goal and life objectives change with time and may result in remorse and regret later on. The author goes on describing this by giving examples of Alfred Nobel and Albert Einstein. With the use of words and tone this passage will fall in the category of descriptive essay.
Question 40
The paradox, 'it's certain that nothing is certain in life', indicates the writer's
B Analytical mind
The author analyzed the actions of few eminent people and came to the conclusion that it is certain that nothing is certain in life – we can conclude that he has an analytical mind.
Section: Quantitative Aptitude
Question 1
Choose the most appropriate option:
The number of 'three digit numbers' which are multiples of 9 are:
The number of 'three digit numbers' which are multiples of 9 are:
C 100
Method-1:
Number of multiples of a number P from ‘A’ to ‘B’ can be directly found as:
= Quotient of B/P – Quotient of (A – 1)/P
In this question, this will be = Quotient of 999/9 – Quotient of (100 – 1)/9
= 111 – 11 = 100
Method-2:
We want numbers from 100 to 999 that are multiples of 9.
Now the first multiple of 9 in this range is 108, while the last multiple is 999.
Also these multiples form an Arithmetic Progression with common difference of 9.
Hence using the expression for the nth term of an AP:
999 = 108 + (n – 1) x 9
i.e. n = 891/9 + 1 = 99 + 1 = 100
Number of multiples of a number P from ‘A’ to ‘B’ can be directly found as:
= Quotient of B/P – Quotient of (A – 1)/P
In this question, this will be = Quotient of 999/9 – Quotient of (100 – 1)/9
= 111 – 11 = 100
Method-2:
We want numbers from 100 to 999 that are multiples of 9.
Now the first multiple of 9 in this range is 108, while the last multiple is 999.
Also these multiples form an Arithmetic Progression with common difference of 9.
Hence using the expression for the nth term of an AP:
999 = 108 + (n – 1) x 9
i.e. n = 891/9 + 1 = 99 + 1 = 100
Question 2
Choose the most appropriate option:
The value of a machine depreciates every year at the rate of 10% on its value at the beginning of that year. If the present value of the machine is ₹729, its worth three years ago was:
The value of a machine depreciates every year at the rate of 10% on its value at the beginning of that year. If the present value of the machine is ₹729, its worth three years ago was:
B ₹1,000
Let the machine’s worth three years ago be N.
Now the worth will decrease by 10% every year for three years
i.e. it will become 90% of its value thrice.
Hence present worth of the machine = 90% of 90% of 90% of N
i.e. 90/100 x 90/100 x 90/100 x N = 729
i.e. 729/1000 x N = 729 or N = ₹1000
Now the worth will decrease by 10% every year for three years
i.e. it will become 90% of its value thrice.
Hence present worth of the machine = 90% of 90% of 90% of N
i.e. 90/100 x 90/100 x 90/100 x N = 729
i.e. 729/1000 x N = 729 or N = ₹1000
Question 3
Choose the most appropriate option:
The angle subtended by the Minor segment of a circle at the centre is __________ the angle subtended by the Major segment at the centre of the circle.
The angle subtended by the Minor segment of a circle at the centre is __________ the angle subtended by the Major segment at the centre of the circle.
D Lesser than
Remember that angle subtended by a semi-circle at the centre is 180˚.
Now, the minor segment of a circle will clearly be smaller than a semi-circle so the angle subtended by it at the centre will be less than 180˚, while the major segment of a circle is bigger than a semi-circle so the angle subtended by it at the centre will be greater than 180˚.
Now, the minor segment of a circle will clearly be smaller than a semi-circle so the angle subtended by it at the centre will be less than 180˚, while the major segment of a circle is bigger than a semi-circle so the angle subtended by it at the centre will be greater than 180˚.
Question 4
Choose the most appropriate option:
What is the sum of all the natural numbers from 1 to 100?
What is the sum of all the natural numbers from 1 to 100?
B 5050
Formula for sum of ‘N’ consecutive integers starting from 1 is N(N + 1)/2
Hence, 1 + 2 + 3 + ... + 100 = 100 x 101/2 = 50 x 101 = 5050
Hence, 1 + 2 + 3 + ... + 100 = 100 x 101/2 = 50 x 101 = 5050
Question 5
Choose the most appropriate option:
A part of monthly hostel charges is fixed and the remaining depends on the number of days one has taken food in the mess. When a student A takes food for 20 days, she has to pay ₹1000 as hostel charges whereas a student B, who takes food for 26 days, pays ₹1180 as hostel charges. Find the fixed charges and the cost of food per day.
A part of monthly hostel charges is fixed and the remaining depends on the number of days one has taken food in the mess. When a student A takes food for 20 days, she has to pay ₹1000 as hostel charges whereas a student B, who takes food for 26 days, pays ₹1180 as hostel charges. Find the fixed charges and the cost of food per day.
D 400, 30
Method-1:
Simply check which option satisfies the given conditions.
Option a: Fixed = ₹300, variable = ₹30 per day
So total payment for 20 days = 300 + 20 x 30 = ₹900 which is wrong.
Option b: Fixed = ₹400, variable = ₹40 per day
So total payment for 20 days = 400 + 20 x 40 = ₹1200 which is also wrong.
Option c: Fixed = ₹200, variable = ₹20 per day
So total payment for 20 days = 200 + 20 x 20 = ₹600 which is also wrong.
Option d: Fixed = ₹400, variable = ₹30 per day
So total payment for 20 days = 400 + 20 x 30 = ₹1000
And total payment for 26 days = 400 + 26 x 30 = ₹1180
Clearly option d is the correct choice!
Method-2:
Let Fixed amount be ₹A and variable per day be ₹B.
Then, total payment for 20 days will be A + 20B = 1000 ... (1)
And, total payment for 26 days will be A + 26B = 1180 ... (2)
On subtracting (1) from (2) we get:
6B = 180 or B = ₹30 per day
Also A = 1000 – 20 x 30 = ₹400
Simply check which option satisfies the given conditions.
Option a: Fixed = ₹300, variable = ₹30 per day
So total payment for 20 days = 300 + 20 x 30 = ₹900 which is wrong.
Option b: Fixed = ₹400, variable = ₹40 per day
So total payment for 20 days = 400 + 20 x 40 = ₹1200 which is also wrong.
Option c: Fixed = ₹200, variable = ₹20 per day
So total payment for 20 days = 200 + 20 x 20 = ₹600 which is also wrong.
Option d: Fixed = ₹400, variable = ₹30 per day
So total payment for 20 days = 400 + 20 x 30 = ₹1000
And total payment for 26 days = 400 + 26 x 30 = ₹1180
Clearly option d is the correct choice!
Method-2:
Let Fixed amount be ₹A and variable per day be ₹B.
Then, total payment for 20 days will be A + 20B = 1000 ... (1)
And, total payment for 26 days will be A + 26B = 1180 ... (2)
On subtracting (1) from (2) we get:
6B = 180 or B = ₹30 per day
Also A = 1000 – 20 x 30 = ₹400
Question 6
Choose the most appropriate option:
A library has an average of 510 visitors on Sundays and 240 on other days. What is the average number of visitors per day in the month of June beginning with a Sunday?
A library has an average of 510 visitors on Sundays and 240 on other days. What is the average number of visitors per day in the month of June beginning with a Sunday?
C 285
Since 1st June is a Sunday 8th June, 15th June, 22nd June and 29th June will be Sundays
Total number of Sundays in June = 5
Hence, total visitors to the library on Sundays in June = 5 x 510 = 2550
Also the remaining 25 days in June will see 240 visitors.
So, total visitors to the library on other days in June = 25 x 240 = 6000
Thus, total visitors in June = 2550 + 6000 = 8550
Hence average number of visitors per day in June = 8550/30 = 285
Total number of Sundays in June = 5
Hence, total visitors to the library on Sundays in June = 5 x 510 = 2550
Also the remaining 25 days in June will see 240 visitors.
So, total visitors to the library on other days in June = 25 x 240 = 6000
Thus, total visitors in June = 2550 + 6000 = 8550
Hence average number of visitors per day in June = 8550/30 = 285
Question 7
Choose the most appropriate option:
12 defective pens are accidentally mixed with 132 good ones. It is not possible to just look at a pen and tell whether or not it is defective. One pen is taken out at random from this lot. Determine the probability that the pen taken out is a good one.
12 defective pens are accidentally mixed with 132 good ones. It is not possible to just look at a pen and tell whether or not it is defective. One pen is taken out at random from this lot. Determine the probability that the pen taken out is a good one.
B 11/12
Probability that a good pen is taken out from the lot = Number of good pens in the lot/Total pens in the lot
= 132/144 = 11/12
= 132/144 = 11/12
Question 8
Choose the most appropriate option:
A man earns ₹20 on the first day and spends ₹15 on the next day. He again earns ₹20 on the third day and spends ₹15 on the fourth day. If he continues to save in this way, how soon will he have ₹60 in hand?
A man earns ₹20 on the first day and spends ₹15 on the next day. He again earns ₹20 on the third day and spends ₹15 on the fourth day. If he continues to save in this way, how soon will he have ₹60 in hand?
D on 17th day
We can see that in every two days the man will have net earnings of 20 – 15 = ₹5
We want the earliest time when the man will have ₹60 in hand. But on the earliest such occasion, the man would have earned ₹20 on the last day.
Hence his net earnings till the day before the last = ₹40
Since his net earnings are ₹5 for every 2 days, time taken for net earnings to be ₹40 will be 40/5 x 2 = 16 days
Hence the man will have ₹60 on the 17th day.
We want the earliest time when the man will have ₹60 in hand. But on the earliest such occasion, the man would have earned ₹20 on the last day.
Hence his net earnings till the day before the last = ₹40
Since his net earnings are ₹5 for every 2 days, time taken for net earnings to be ₹40 will be 40/5 x 2 = 16 days
Hence the man will have ₹60 on the 17th day.
Question 9
Choose the most appropriate option:
60 kg of an alloy X is mixed with 100 kg of an alloy Y. If alloy X has lead and tin in the ratio of 3:2 and alloy Y has tin and copper in the ratio of 1:4, then the amount of tin in the new alloy is
60 kg of an alloy X is mixed with 100 kg of an alloy Y. If alloy X has lead and tin in the ratio of 3:2 and alloy Y has tin and copper in the ratio of 1:4, then the amount of tin in the new alloy is
D 44 kgs.
60 kg of alloy X (Lead : Tin = 3 : 2)
Amount of tin = 2/5th of 60 = 24 kg
100 kg of alloy Y (Tin : Copper = 1 : 4)
Amount of tin = 1/5th of 100 = 20 kg
Hence, total tin in the new alloy (mix of alloy X and alloy Y) = 24 + 20 = 44 kgs
Amount of tin = 2/5th of 60 = 24 kg
100 kg of alloy Y (Tin : Copper = 1 : 4)
Amount of tin = 1/5th of 100 = 20 kg
Hence, total tin in the new alloy (mix of alloy X and alloy Y) = 24 + 20 = 44 kgs
Question 10
Choose the most appropriate option:
Two consecutive even positive integers, sum of the squares of which is 1060 are:
Two consecutive even positive integers, sum of the squares of which is 1060 are:
B 22 and 24
Method-1:
Simply check the options one-by-one:
Option a: 122 + 142 = 144 + 196 = 340 clearly incorrect.
Option b: 222 + 242 = 484 + 576 = 1060 this is the correct choice.
Option c: 202 + 222 = 400 + 484 = 884 clearly incorrect.
Option d: 162 + 182 = 256 + 324 = 580 clearly incorrect.
Method-2:
Let the two consecutive even integers be N and N + 2.
Then N2 + (N + 2)2 = 1060
i.e. 2N2 + 4N + 4 = 1060
i.e. N2 + 2N – 528 = 0
i.e. N2 + 24N – 22N – 528 = 0
i.e. (N + 24)(N – 22) = 0
So N = 22 i.e. the numbers are 22 and 24.
Simply check the options one-by-one:
Option a: 122 + 142 = 144 + 196 = 340 clearly incorrect.
Option b: 222 + 242 = 484 + 576 = 1060 this is the correct choice.
Option c: 202 + 222 = 400 + 484 = 884 clearly incorrect.
Option d: 162 + 182 = 256 + 324 = 580 clearly incorrect.
Method-2:
Let the two consecutive even integers be N and N + 2.
Then N2 + (N + 2)2 = 1060
i.e. 2N2 + 4N + 4 = 1060
i.e. N2 + 2N – 528 = 0
i.e. N2 + 24N – 22N – 528 = 0
i.e. (N + 24)(N – 22) = 0
So N = 22 i.e. the numbers are 22 and 24.
Question 11
Choose the most appropriate option:
The traffic lights at three different signal points change after every 45 seconds, 75 seconds and 90 seconds respectively. If all change simultaneously at 7:20:15 hours, then they will change again simultaneously at
The traffic lights at three different signal points change after every 45 seconds, 75 seconds and 90 seconds respectively. If all change simultaneously at 7:20:15 hours, then they will change again simultaneously at
D 7:27:45 hours
The times taken by the three signals = 45 seconds, 75 seconds and 90 seconds
Hence, they will again change simultaneously after a common multiple of their individual times.
The earliest this will happen will be at LCM of (45, 75 and 90) i.e. 450 seconds or 7 minutes and 30 seconds
Hence time then will be 7:27:45 hours
Hence, they will again change simultaneously after a common multiple of their individual times.
The earliest this will happen will be at LCM of (45, 75 and 90) i.e. 450 seconds or 7 minutes and 30 seconds
Hence time then will be 7:27:45 hours
Question 12
Choose the most appropriate option:
A circular park, 42 m in diameter, has a path 3.5 m wide running around it on the outside. Find the cost of gravelling the path at ₹4 per m2
A circular park, 42 m in diameter, has a path 3.5 m wide running around it on the outside. Find the cost of gravelling the path at ₹4 per m2
C Rs. 2002
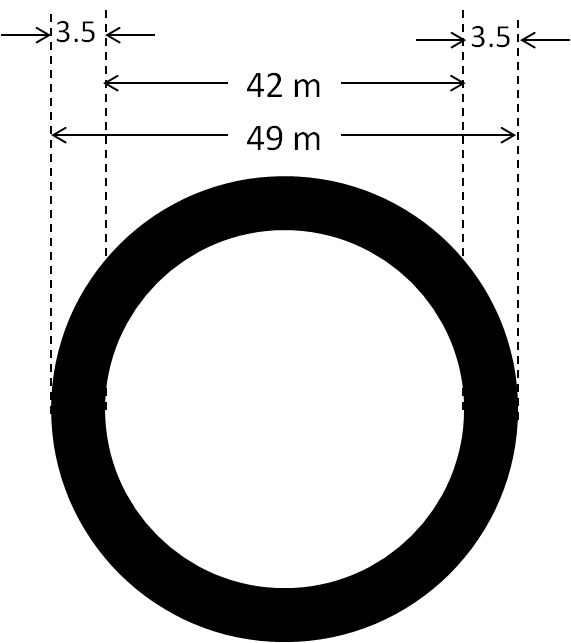
Given, inner diameter of the path = 42 m
Also width of the path = 3.5 m
Hence outer diameter of the path = 49 m
Hence area of the path = Area of outer circle – Area of inner circle = π(49/2)2 – π(42/2)2
= π(2401/4 – 441) = 22/7 x 637/4 = 500.5 m2
Cost of gravelling = ₹4 per m2
So total cost = 500.5 x 4 = ₹2002
Question 13
Choose the most appropriate option:
A train which is moving at an average speed of 40 kmph, reaches its destination on time. When its average speed reduces to 35 kmph, then it reaches its destination 15 minutes late. The distance travelled by the train is:
A train which is moving at an average speed of 40 kmph, reaches its destination on time. When its average speed reduces to 35 kmph, then it reaches its destination 15 minutes late. The distance travelled by the train is:
C 70 kms
Method-1:
Simply check the options one-by-one.
Option a: 80 kms
Initial time taken = 80/40 = 2 hours or 120 minutes
New time taken = 80/35 = 20/7 hours = 20/7 x 60 = 171.4 minutes i.e. 51.4 minutes late
Option b: 40 kms
Initial time taken = 40/40 = 1 hour or 60 minutes
New time taken = 40/35 = 8/7 hours = 8/7 x 60 = 480/7 = 68.5 minutes i.e. 8.5 minutes late
Option c: 70 kms
Initial time taken = 70/40 = 7/4 hours = 7/4 x 60 = 105 minutes
New time taken = 70/35 = 2 hours or 120 minutes i.e. 15 minutes late
Option d: 35 kms
Initial time taken = 35/40 = 7/8 hours = 7/8 x 60 = 52.5 minutes
New time taken = 35/35 = 1 hour or 60 minutes i.e. 7.5 minutes late
Clearly option c is the correct choice.
Method-2:
Let the distance be D kms.
Then time taken initially = D/40 hours = D/40 x 60 minutes = 3D/2 minutes
New time taken = D/35 hours = D/35 x 60 = 12D/7 minutes
Since the train now arrives 15 minute late:
So, 12D/7 = 3D/2 + 15
i.e. (24D – 21D)/14 = 15
i.e. D = 15 x 14/3 = 70 kms
Simply check the options one-by-one.
Option a: 80 kms
Initial time taken = 80/40 = 2 hours or 120 minutes
New time taken = 80/35 = 20/7 hours = 20/7 x 60 = 171.4 minutes i.e. 51.4 minutes late
Option b: 40 kms
Initial time taken = 40/40 = 1 hour or 60 minutes
New time taken = 40/35 = 8/7 hours = 8/7 x 60 = 480/7 = 68.5 minutes i.e. 8.5 minutes late
Option c: 70 kms
Initial time taken = 70/40 = 7/4 hours = 7/4 x 60 = 105 minutes
New time taken = 70/35 = 2 hours or 120 minutes i.e. 15 minutes late
Option d: 35 kms
Initial time taken = 35/40 = 7/8 hours = 7/8 x 60 = 52.5 minutes
New time taken = 35/35 = 1 hour or 60 minutes i.e. 7.5 minutes late
Clearly option c is the correct choice.
Method-2:
Let the distance be D kms.
Then time taken initially = D/40 hours = D/40 x 60 minutes = 3D/2 minutes
New time taken = D/35 hours = D/35 x 60 = 12D/7 minutes
Since the train now arrives 15 minute late:
So, 12D/7 = 3D/2 + 15
i.e. (24D – 21D)/14 = 15
i.e. D = 15 x 14/3 = 70 kms
Question 14
Choose the most appropriate option:
4 The mean of 72 items was found to be 63. If two of the items were misrecorded as 27 and 9 instead of 72 and 90 respectively, find the correct mean.
4 The mean of 72 items was found to be 63. If two of the items were misrecorded as 27 and 9 instead of 72 and 90 respectively, find the correct mean.
A 64.75
Initial average of 72 items = 63
Hence, initial sum of observations = 63 x 72
Now, to correct the mistakes this sum will be increased by (72 – 27) + (90 – 9) = 126
Hence correct sum of observations = 63 x 72 + 126
Hence new mean = Sum/72 = (63 x 72 + 126)/72 = 63 + 126/72 = 63 + 7/4 = 63 + 1.75 = 64.75
Hence, initial sum of observations = 63 x 72
Now, to correct the mistakes this sum will be increased by (72 – 27) + (90 – 9) = 126
Hence correct sum of observations = 63 x 72 + 126
Hence new mean = Sum/72 = (63 x 72 + 126)/72 = 63 + 126/72 = 63 + 7/4 = 63 + 1.75 = 64.75
Question 15
Choose the most appropriate option:
A man buys Rs. 20 shares paying 9% dividend. The man expects to have an interest of 12% on his money. The market value of each share is
A man buys Rs. 20 shares paying 9% dividend. The man expects to have an interest of 12% on his money. The market value of each share is
B Rs. 15
Note that dividend is paid on the face value of the share i.e. ₹20
Dividend earnings on each share = 9% of 20 = ₹1.8
But the man expects an interest of 12% on the market value of each share.
So 1.8 = 12% of Market value
i.e. Market value = 1.8 x 100/12 = ₹15
Dividend earnings on each share = 9% of 20 = ₹1.8
But the man expects an interest of 12% on the market value of each share.
So 1.8 = 12% of Market value
i.e. Market value = 1.8 x 100/12 = ₹15
Question 16
Choose the most appropriate option:
A patient in a hospital is given soup daily in a cylindrical bowl of diameter 7 cm. If the bowl is filled with soup to a height of 4 cm, how much soup the hospital has to prepare daily to serve 250 patients?
A patient in a hospital is given soup daily in a cylindrical bowl of diameter 7 cm. If the bowl is filled with soup to a height of 4 cm, how much soup the hospital has to prepare daily to serve 250 patients?
C 38.5 litres
Volume of soup in each filled bowl = πR2H = 22/7 x (7/2)2 x 4 = 154 cm3 = 154/1000 litres
So soup needed for 250 patients = 154/1000 x 250 = 154/4 = 38.5 litres
So soup needed for 250 patients = 154/1000 x 250 = 154/4 = 38.5 litres
Question 17
Choose the most appropriate option:
The angles between the hands of a clock when the time is 4:25 am is:
The angles between the hands of a clock when the time is 4:25 am is:
C 17½ degrees
Speed of minute hand = 6˚ per minute (it covers 360˚ in 60 minutes)
Speed of hour hand = ½˚ per minute (it covers 360˚ in 12 hours)
Relative speed of minute hand w.r.t. hour hand = 6 – ½ = 5½˚ per minute
Now since 12 hourly divisions in a clock cover 360˚, each hourly division will cover 360/12 = 30˚
So, at 4:00 the angle between the two hands = 4 x 30˚ = 120˚
Now this will change (actually reduce) at the rate of 5½˚ or 11/2˚ per minute.
So angle at 4:25 = 120 – 11/2 x 25 = 120 – 275/2 = 120˚ - 137.5˚ = –17.5˚
Note: This angle is negative because the minute hand crosses the hour hand, while initially it was behind the hour hand. The negative sign simply indicates that the minute hand is ahead of the hour hand by 17.5˚.
Speed of hour hand = ½˚ per minute (it covers 360˚ in 12 hours)
Relative speed of minute hand w.r.t. hour hand = 6 – ½ = 5½˚ per minute
Now since 12 hourly divisions in a clock cover 360˚, each hourly division will cover 360/12 = 30˚
So, at 4:00 the angle between the two hands = 4 x 30˚ = 120˚
Now this will change (actually reduce) at the rate of 5½˚ or 11/2˚ per minute.
So angle at 4:25 = 120 – 11/2 x 25 = 120 – 275/2 = 120˚ - 137.5˚ = –17.5˚
Note: This angle is negative because the minute hand crosses the hour hand, while initially it was behind the hour hand. The negative sign simply indicates that the minute hand is ahead of the hour hand by 17.5˚.
Question 18
Choose the most appropriate option:
A shop gives 15% discount on the purchase of a T.V. If paid for in cash immediately, a further discount of 12% is given. If the marked price is ₹15,000, what is the price of the T.V if cash purchase is made?
A shop gives 15% discount on the purchase of a T.V. If paid for in cash immediately, a further discount of 12% is given. If the marked price is ₹15,000, what is the price of the T.V if cash purchase is made?
B ₹11,220
Method-1:
MP = ₹15000
First discount = 15% of 15000 = ₹2250
So MP after first discount = 15000 – 2250 = ₹12750
Now second discount = 12% of 12750 = ₹1530
So final SP = 12750 – 1530 = ₹11220
Method-2:
There are two discounts here which can be cumulated by the formula a + b + ab/100 (Note discounts will be negative %changes)
So overall change = – 15 – 12 + (–15)( –12)/100 = –27 + 1.8 = –25.2%
So the final price will be 15000 – 25.2/100 x 15000 = 15000 – 3780 = ₹11220
MP = ₹15000
First discount = 15% of 15000 = ₹2250
So MP after first discount = 15000 – 2250 = ₹12750
Now second discount = 12% of 12750 = ₹1530
So final SP = 12750 – 1530 = ₹11220
Method-2:
There are two discounts here which can be cumulated by the formula a + b + ab/100 (Note discounts will be negative %changes)
So overall change = – 15 – 12 + (–15)( –12)/100 = –27 + 1.8 = –25.2%
So the final price will be 15000 – 25.2/100 x 15000 = 15000 – 3780 = ₹11220
Question 19
Choose the most appropriate option:
If a boy is standing at the top of the tower and another boy is at the ground at some distance from the foot of the tower, then the angle of elevation and depression between the boys when both look at each other will be
If a boy is standing at the top of the tower and another boy is at the ground at some distance from the foot of the tower, then the angle of elevation and depression between the boys when both look at each other will be
D Equal
See the figure below:
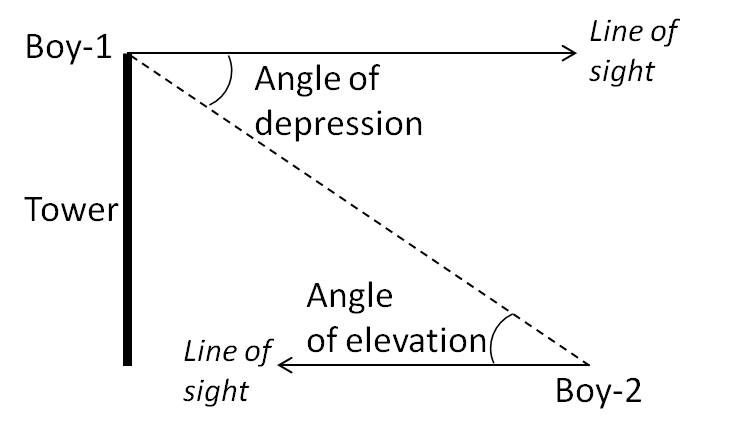
Clearly the lines of sights for the two boys are parallel to each other.
So when they look at each other the angles of elevation and depression will form alternate interior angles between the parallel lines of sight lines.
Hence these angles will be equal.

Clearly the lines of sights for the two boys are parallel to each other.
So when they look at each other the angles of elevation and depression will form alternate interior angles between the parallel lines of sight lines.
Hence these angles will be equal.
Question 20
If the product of zeroes of the polynomial ax2 – 6x – 6 is 4, find the value of 'a'
A -3/2
Product of zeroes of the quadratic ax2 + bx + c will be equal to c/a
So –6/a = 4 or a = –6/4 = –3/2
So –6/a = 4 or a = –6/4 = –3/2
Section: General Knowledge
Question 1
India signed the "Paris Agreement on Climate Change" in April, 2016 at:
C New Delhi
New Delhi
Question 2
The country which cloned a buffalo calf first is:
A India
India
Question 3
Mars is also known as the:
C Red Planet
Red Planet
Question 4
In 2015, Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi launched a new campaign, "Start-up India, Stand up India". The campaign is aimed at:
B Promoting bank financing for start-ups and offer incentives to boost entrepreneurship and job creation.
Promoting bank financing for start-ups and offer incentives to boost entrepreneurship and job creation.
Question 5
Who is the author of "Crime & Punishment"?
B Fyodor Dostoevsky
Fyodor Dostoevsky
Question 6
Power to summon the Houses of the Parliament is vested with:
B President
President
Question 7
Which country is the first developed nation to default on debt of IMF?
D Greece
Greece
Question 8
Which State of India was declared in January, 2016 as the "first organic farming State of India"?
B Sikkim
Sikkim
Question 9
Punjabi has become the _____________ most common language in the Parliament of Canada.
D Third
Third
Question 10
Which State has become the first State to introduce compulsory gender education at the graduate level?
A Telangana
Telangana
Question 11
The highest peace time gallantry award Ashok Chakra was awarded posthumously during 2016 to:
A Mohan Nath Goswami
Mohan Nath Goswami
Question 12
The Constitution (One Hundredth Amendment) Act, 2015 was enacted to give effect to:
A The transfer of certain territories by India to Bangladesh and transfer of certain territories from Bangladesh to India
The transfer of certain territories by India to Bangladesh and transfer of certain territories from Bangladesh to India
Question 13
The Currency of Thailand is:
A Baht
Baht
Question 14
Parliament of India consists of:
D President, House of the People and Council of States
President, House of the People and Council of States
Question 15
The direction to hold floor test to prove majority in the Legislative Assembly of Uttarakhand, to be held on 10th May, 2016 has been give n on 6th May, 2016, by
A The Supreme Court of India
The Supreme Court of India
Question 16
Which organization has the motto 'Be Prepared'?
C Boys' Scout
Boys' Scout
Question 17
Under the Constitution of India the official language of the Union is:
D Hindi in Devanagari Script
Hindi in Devanagari Script
Question 18
At the Asian Indoor Athletics Championships held at Doha in February, 2016, who among women won the gold medal in Long Jump?
B Mayooka Johny of India
Mayooka Johny of India
Question 19
The "Paris Agreement" was adopted in the twenty first session of Conference of Parties in the month of:
A December, 2015
December, 2015
Question 20
Who was conferred the Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna award during August, 2015?
D Sania Mirza
Sania Mirza
Question 21
Who is the President of Sri Lanka?
D Maithripala Sirisena
Maithripala Sirisena
Question 22
Who has scored the fastest century in a Test Cricket match?
C Brendon McCullum, New Zealand
Brendon McCullum, New Zealand
Question 23
Who is the Chairperson of NITI Aayog?
B Sh. Narendra Modi
Sh. Narendra Modi
Question 24
Who is the Chairperson of National Human Rights Commission?
D Justice H.L. Dattu
Justice H.L. Dattu
Question 25
Who was the Constitutional Advisor to the Constituent Assembly in framing the Indian Constitution?
C Sir B.N. Rau
Sir B.N. Rau
Question 26
In April 2016, The Duke and Duchess of Cambridge visited India. Their names are:
C Prince William and Kate Middleton
Prince William and Kate Middleton
Question 27
In case the President of India wants to resign, he shall address his resignation to the:
B Vice President
Vice President
Question 28
Name the Indian Gymnast who has become the first female Indian Gymnast to qualify for the Olympics.
A Dipa Karmakar
Dipa Karmakar
Question 29
In case of death of both the President and Vice-President of India, who shall act as the President of India?
C Chief Justice of India
Chief Justice of India
Question 30
Who is the Union Finance Minister of India?
C Mr. Arun Jaitly
Mr. Arun Jaitly
Question 31
Who is the Chairman of National Green Tribunal?
C Justice Swatanter Kumar
Justice Swatanter Kumar
Question 32
Which State has the largest number of foreign students in India?
D Karnataka
Karnataka
Question 33
Who lit the torch from the sun's rays reflected in a parabolic mirror during the Olympic flame lighting ceremony for the Rio 2016 Olympic Games at the site of ancient Olympia in Greece on 22nd April, 2016?
A Katerina Lehou
Katerina Lehou
Question 34
The Parliament of which country became first Parliament in the world to run entirely on Solar Power?
C Pakistan
Pakistan
Question 35
Prime Minister, Mr. Narendra Modi, in March, 2016, launched an ambitious programme "Setu Bharatam". The programme is aimed at:
B Making all National Highways railway level crossing free by 2019
Making all National Highways railway level crossing free by 2019
Question 36
How many Indian Universities/Institutes figure among the top 200 in BRICS rankings?
B 16
16
Question 37
Which day is celebrated as "World Consumer Rights Day"?
A 15th March
15th March
Question 38
Who was crowned as the winner of Femina Miss India 2016 and who will represent India at the Miss World pageant?
D Priyadarshini Chatterjee
Priyadarshini Chatterjee
Question 39
___________ is the fastest planet to revolve around the Sun.
A Mercury
Mercury
Question 40
Who has written the book "Indomitable Spirit"?
A Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam
Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam
Question 41
The Rajya Sabha in April, 2016 passed two Bills, which had already been passed by the Lok Sabha earlier, repealing certain outdated/old laws. The Bills intended to repeal:
B 1053 laws
1053 laws
Question 42
"Beyond the Lines - An Autobiography" is authored by:
B Mr. Kuldip Nayar
Mr. Kuldip Nayar
Question 43
The maximum number of 'Smokeless Villages' are found in the State of:
D Karnataka
Karnataka
Question 44
In an attempt to curb black money, the Government has made PAN mandatory for all financial transactions exceeding Rupees:
C 2 lakhs
2 lakhs
Question 45
In which of the following States/Union Territories, the Election Commission has decided to hold election in a single phase on May 16, 2016?
C Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Pondicherry.
Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Pondicherry.
Question 46
Name the country that has six Deputy Prime Ministers
C Nepal
Nepal
Question 47
Country's first 'visually challenged friendly' railway station is:
D Mysuru
Mysuru
Question 48
The largest diaspora in the world is from:
C India
India
Question 49
A Japanese maglev, which is the fastest passenger train in the world, has broken its own record in 2015. The train reached ___________ kmph in the test run.
C 603
603
Question 50
In January, 2016, at the first stage, the Union Ministry of Urban Development unveiled the list of ________ cities for smart cities mission out of 98 shortlisted cities:
C 20
20
Section: Logical Reasoning
Question 1
Who is good in driving scooter, tractor and auto rickshaw but not good in driving car?
B E
Using all the clues we will get the table as follows:-
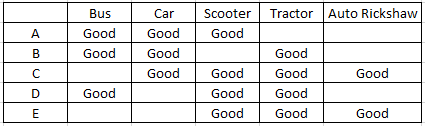
E is good in driving scooter, tractor and auto rickshaw but not good in driving car.

E is good in driving scooter, tractor and auto rickshaw but not good in driving car.
Question 2
Who is good in driving scooter, tractor and bus?
B D

D is good in driving scooter, tractor and bus.
Question 3
Who is good in driving tractor, scooter, car and auto rickshaw but not bus?
A C

C is good in driving tractor, scooter, car and auto rickshaw but not bus.
Question 4
Statement:
The next meeting of the executive board of a company will be held after six months.
Assumptions:
I. Existing executive board will be dissolved before six months
II. The company will remain in function after six months
The next meeting of the executive board of a company will be held after six months.
Assumptions:
I. Existing executive board will be dissolved before six months
II. The company will remain in function after six months
B Assumption II is implicit.
Since the meeting will be help after six months it can be safely assumed that the company will remain to function at least till the next meeting which is after six months. There is no information from which the first could be implied.
Question 5
Statement:
In the State of Zuminisia, people prefer to travel by X airline instead of Y airline, as X airline has advanced German security system and 99% on time operations.
Assumptions:
I. Airline X with advanced German security system and record on time operation is perceived better than airline Y.
II. Had advanced German security system and on time performance record of Y airline been implemented, it would have been preferred over airline X.
In the State of Zuminisia, people prefer to travel by X airline instead of Y airline, as X airline has advanced German security system and 99% on time operations.
Assumptions:
I. Airline X with advanced German security system and record on time operation is perceived better than airline Y.
II. Had advanced German security system and on time performance record of Y airline been implemented, it would have been preferred over airline X.
A Assumption I is implicit.
I can be inferred as these are two features given about airline X. II cannot be implied because if these two are implemented and passengers are charged more than what airline X charge the passengers might still prefer to fly with airline X.
Question 6
Statement:
To attend a convocation ceremony scheduled to be held on Thursday at GM University, Chennai, Mr X left for Chennai on Tuesday by train.
Assumptions:
I. Mr X may reach home on Saturday
II. Mr X may reach the University on Wednesday
To attend a convocation ceremony scheduled to be held on Thursday at GM University, Chennai, Mr X left for Chennai on Tuesday by train.
Assumptions:
I. Mr X may reach home on Saturday
II. Mr X may reach the University on Wednesday
B Assumption II is implicit.
Ideally the answer should be either choice 3 or 4. Since both the assumptions have the word “may” we would suggest choice 3 as the correct answer. However, as per the CLAT answer key the correct answer is 2.
Question 7
Which of the following is a pair of females in the family?
B AD
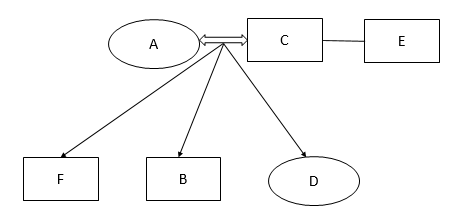
AD is a pair of females in the family.
Question 8
Who is the mother of B?
B F

A is the mother of B.
Question 9
Statement I: In last two years, there is a considerable reduction in cancellation of flights due to fog in North India.
Statement II: In last two years, there is a considerable improvement in passenger amenities on all airports of North India.
Statement II: In last two years, there is a considerable improvement in passenger amenities on all airports of North India.
A Both statements I and II are effects of independent causes.
There is no cause and effect relationship between the two statements. In such cases we suggest you mark your answer as both are independent effects.
Question 10
Statement I: The Government, by legislation has decided to make all public information available to general public.
Statement II: Before passing of legislation, general public did not have access to public information.
Statement II: Before passing of legislation, general public did not have access to public information.
C Statement II is the cause and statement I is its effect.
In cause and effect questions put “therefore” between two statements and see if it makes sense.
Before passing of legislation, general public did not have access to public information, therefore, the Government, by legislation has decided to make all public information available to general public.
Before passing of legislation, general public did not have access to public information, therefore, the Government, by legislation has decided to make all public information available to general public.
Question 11
Identify the statement which cannot be false.
C All radii of any given circle are of equal length.
This is a mathematical principle.
Question 12
An old woman decided to divide her gold among her daughter and daughters -in-law. She first kept exactly half of the gold for her daughter. Then she divided the rest of her gold among her daughters-in-law. The eldest one got 26 grams more than the youngest daughter-in-law. The middle one got wice as the youngest one. If the eldest daughter-in-law got 66 grams of gold, how much was received by the daughter.
C 186 grams
Eldest got 66 grams of gold. This means the youngest would have got 66 – 20 = 40. This means the middle one would have got 2 x 40 = 80. Together they received 66 + 40 + 80 = 186 grams of gold. The daughter received the same quantity as the three of the daughter – in – laws combined.
Question 13
Find the odd one out from the following group.
WINDSHIELD, SPARK PLUG, CLUTCH PEDAL, CAR, ENGINE
WINDSHIELD, SPARK PLUG, CLUTCH PEDAL, CAR, ENGINE
A Car
Others are a part of a car.
Question 14
Four statements are given below. Group two of them in such a way that one is logically incorrect and the other is verifiable as a matter of fact
(a) The Sun does not rise in the East.
(b) A straight line is the shortest distance between any two points.
(c) Every circle has a centre.
(d) The maximum duration of a total solar eclipse is about 7.5 minutes
(a) The Sun does not rise in the East.
(b) A straight line is the shortest distance between any two points.
(c) Every circle has a centre.
(d) The maximum duration of a total solar eclipse is about 7.5 minutes
C [a, d]
“a” is definitely not correct – so the correct choice has to start with “a”. “b” and “c” are facts and need not be verified while “d” could be verified as a matter of fact. Thus the correct choice is 3.
Question 15
This question consists of a related pair of words, followed by four pairs of words. Choose the pair that best represents a similar relations hip as the one expressed in the given pair of words:
SANDERLING : BIRD
SANDERLING : BIRD
A Mastiff : Dog
Just like Sanderling is a bird, Mastiff is a dog.
Question 16
From among the given options, identify the statement which means the same as the statement 'The dual nature of light is an enigma'.
D The nature of light is an enigma.
The subject of the statement is “nature of light” and that it is an enigma. The choice that comes very close to this is choice 4 which is almost a paraphrase of the given statement.
Question 17
Which word in the following group DOES NOT belong to the others?
PROSPER, EXCITE, THRIVE, FLOURISH
PROSPER, EXCITE, THRIVE, FLOURISH
B Excite
1, 3 and 4 all mean to succeed especially in material terms while excite means cause to feel very enthusiastic and eager.
Question 18
Examine the following numbers and identify the next number:
45; 43; 40; 36; 31; 25; ....
45; 43; 40; 36; 31; 25; ....
D 18
The logic is -2, -3, -4 and so on. The next number will be 25 – 7 = 18.
Question 19
If it is true that 'All humans are imperfect', then which one of the following is necessarily true?
C Every human is imperfect.
From “All humans are imperfect” we can conclude that “Every human is imperfect”.
Question 20
If it is false that 'Men always pray to God', then which one of the following statements is true?
A Men seldom pray to God.
Amongst the given choices 1 is the best choice.
Question 21
Geeta is twice the present age of Seema. If age of Seema is 20 years now, how many years ago Geeta was three times Seema's age?
A 10
Seema currently is 20 years now so Geeta’s age is 20 x 2 = 40. Ten years ago Seema would have been 10 years old and Geeta 30 years old, that is, thrice the age of Seema.
Question 22
In certain code MAIL is written as ZNVY then how will FILM be written in that code?
A SVYZ
The pattern is M + 13 = Z, A + 13 = N, I + 13 = V and L + 13 = Y. By the same logic FILM will become SVYZ.
Question 23
You are given a 60inch long ribbon, and you are instructed to cut 60 1-inch long strips out of this ribbon. The time taken to cut one strip i s one second. So how long will it take to cut 60 strips?
D 59 seconds
You need to cut the 60 inch long ribbon 59 times to get 60 such pieces. To cut one strip it takes one second so to cut 50 strips it will take 59 seconds.
Question 24
If it is true that 'Religious fundamentalism is dangerous to the society', then which one of the following statements can also be true?
A Disrespect for other religions is dangerous to the society.
Religious fundamentalism refers to the belief of an individual or a group of individuals in the absolute authority of a sacred religious text or teachings of a particular religious leader, prophet, and/ or God. From this choice 1 is the best answer.
Question 25
If it is true that 'Good governance implies law and order in society' then identify the statement which has to be accepted along with the given statement?
A An able government very effectively uses laws to promote peace.
Governance is a responsibility of government – with this in mind choice 1 is the best answer.
Question 26
If it is false that 'There is at least one octogenarian in the room', then which one of the following is probable?
A No one in the room is an octogenarian.
Choice 1 is the obvious answer as at least ‘one octogenarian in the room’ is incorrect.
Question 27
A, B, C and D have got some money with them. If A gives 8 rupees to B, B will have as much as C has and A will have 3 rupees less than what C has. Also if A takes 6 rupees from C, A will have twice as much money as D. If B and D together have 50 rupees, how much money does A and B have respectively?
D 40, 27
In such questions it is best to work with option choices. In choice “4” If A gives 8 rupees to B he will be left with rupees 32, B and C will have 35 which is rupees 3 more than A. On the other hand if A takes rupees 6 from C he will have 40 + 6 = 46, C will have 35 – 6 = 29 and B will have 27. It is given that in this case A will have twice the amount of D which means D should have 46/2 = 23. It is also given than B + D will be equal to rupees 50. In this case B has rupees 27 and D 23, so this option choice satisfies all the conditions and is the correct answer.
Question 28
Who among the following is the odd one in the following group of persons?
Chief Justice of India, Attorney General of India, Solicitor General, Advocate General
Chief Justice of India, Attorney General of India, Solicitor General, Advocate General
A Chief Justice of India.
Chief Justice of India will be correct answer because he is a Judge and rest are Lawyers for Govt.
Question 29
In a bag, there are some diamonds. In another bag, there are one fourth the number more than the number of diamonds in the first bag. If the difference in the number of diamonds in the first and second bag is 3, how many diamonds are there in the first bag?
C 12
This is again a very simple question and you must work with the option choices. The correct choice will be one which when divided by 4 will give 3 as the answer. Choice 3, that is, 12 is the correct answer.
Question 30
Mr. X, the President of a club arrived in a meeting at 10 minutes to 12 30 hrs. Mr X came earlier by 20 minutes than the other participating members in the meeting, who arrived late by 30 minutes. At what time was the meeting scheduled?
A 1210 hrs
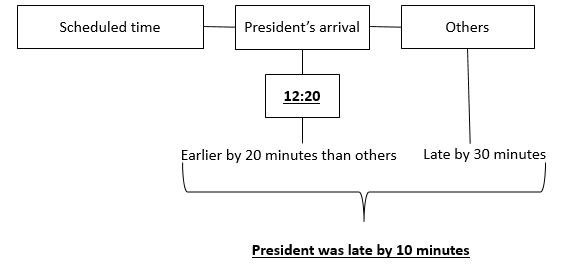
From the information provided, we can conclude that the President is late by 10 minutes, so the scheduled time of meeting was 12:10.
Question 31
In a class, student X has 8th position from the top and 84th from the bottom. How many students are there in the class?
C 91
The correct answer will be 8 + 84 – 1(to eliminate double counting of the position) = 91
Question 32
There is some relationship between the figures given in the series. Find out the missing one from the alternatives given below.


D <img alt="" src="/img/images/Pictur114.png" style="height:67px; width:81px" />
This questions was cancelled as it was mentioned in the website of CLAT that no visual reasoning question will be asked.
Question 33
If Oceans are Deserts, then Waves are:
C Sand Dunes
Oceans are not found in Deserts, similarly waves are not found in sand dunes.
Question 34
Assume that both premises, 'No innocent person should be punished' and 'Socrates is innocent' are true. Then which one of the following options is necessarily true?
D Socrates should not be punished.
Because one of the premise is should not be punished, therefore, the conclusion will be should not be punished versus is not punished.
Question 35
A 2100 member team consisting of Team Leaders and Athletes is attending a National Athletic Meet. For every 20 Athletes, there is one Team Leader. How many Team Leaders would be there in the team?
A 100
The best way to approach this question is to go by options. Team leaders + athletes must equal 2100. If we check for option 1 – for every team leader we need 20 athletes so for 100 team leaders there will be 100 x 20 = 2000 athletes. So the total members in this case will be 100 (team leaders) + 2000 (athletes) = 2100 team members. So this is the correct answer.
Question 36
Choose the pair of words from the options that best represents a similar relationship as the one expressed in the following pair of words.
WAITER: RESTAURANT
WAITER: RESTAURANT
B Teacher: School
Restaurant is fixed and a waiter works in it, similarly a teacher teaches in a school.
Question 37
examine the series and identify the missing number:
46, 44, 40, 38, 34, ...
46, 44, 40, 38, 34, ...
B 32
The pattern is -2, -4, -2, -4 and so on. The missing number is 34 – 2 = 32.
Question 38
Identify the argument which cannot be accepted
B All wives are married. Therefore, all married people are wives.
We think the question is incorrect. As per the CLAT answer key 2 is the correct answer.
Question 39
Identify the statement which cannot be true.
B All bachelors are faithful to their wives.
Bachelors by definition are not married.
Question 40
If it is false that 'Animals are seldom aggressive', then which one of the following statements conveys the same meaning?
D Sometimes animals are aggressive.
1 and 2 are easier to eliminate as they contradict what is given in the statement. Between 3 and 4, 4 is correct as the statement says animals, that is, more than 1.
Section: Legal Aptitude
Question 1
Principle: Intentional application of force to another person is action able in law.
Facts: 'P' and 'D' are unknown to each other. When 'P' is about to sit on a chair, 'D' intentionally pulls it away as a result of which 'P' falls on the floor and is injured.
Facts: 'P' and 'D' are unknown to each other. When 'P' is about to sit on a chair, 'D' intentionally pulls it away as a result of which 'P' falls on the floor and is injured.
B 'D' is liable as he intentionally caused injury to P.
'D' is liable as he intentionally caused injury to P. Pulling the chair intentionally amounts to application of force.
Question 2
Principle: 1. Wagering agreement are void. 2. Collateral agreement to wagering contracts are valid.
Facts: XYZ Bank lends Rs. 40,000 to Sabu in order to enable him to award as prize to Randeep who is the winner of horse race. Later Sabu refused to pay the prize stating that horse racing is wagering agreement. Can XYZ Bank recover money from Sabu.
Facts: XYZ Bank lends Rs. 40,000 to Sabu in order to enable him to award as prize to Randeep who is the winner of horse race. Later Sabu refused to pay the prize stating that horse racing is wagering agreement. Can XYZ Bank recover money from Sabu.
A Yes it is only a collateral agreement to horse racing and therefore the bank can recover the money from Sabu.
It is only a collateral agreement to horse racing and therefore the bank can recover the money from Sabu.
Question 3
Principle : Where a person lawfully does anything for another person, or delivers anything to him, not intending to do so or to provide gratuitously, and such other person takes the benefits of that; the latter is bound to compensate the former for something done or thing provided, or not restore, the thing so delivered.
Facts: Trader 'A' delivers certain eatables at 'B's house by mistake. 'B' consmed the eatables without asking anything. Which of the following derivations is correct?
Facts: Trader 'A' delivers certain eatables at 'B's house by mistake. 'B' consmed the eatables without asking anything. Which of the following derivations is correct?
A 'B' is bound to pay 'A' for the eatables.
This is a problem related to quasi contract which is an obligation that law creates in the absence of an agreement between the parties to prevent the unjust enrichment of a person at the expense of other. 'B' is bound to pay 'A' for the eatables.
Question 4
Principle: Consent is a good defence in a civil action for tort but the act should be the same for which consent was given.
Facts: 'B' was formally invited by 'A' to his house. 'B' after sitting for some time in drawing room, moved to the bed room of the house. 'A' sued 'B' for trespass.
Facts: 'B' was formally invited by 'A' to his house. 'B' after sitting for some time in drawing room, moved to the bed room of the house. 'A' sued 'B' for trespass.
D 'B' has committed trespass as there was no consent of 'A' for entry in the Bed room.
Consent is a defence in a civil action for tort provided that act was same for which consent was given. Here “B” was formally invited by “A” to his house. A formal invitation does not include the consent to move to a person’s bedroom. In other words, his invitation ended the moment he moved to the bed room. Hence the act done by “B” was not consented by “A”. So he is liable for trespass.
Question 5
Principle: Whoever takes away any moveable thing form the land of any person without that person's consent, he is said to have committed theft.
Facts: During his visit to the house of 'C', 'A' asked 'B' the son of 'C', to accompany 'A' to the forest. Neither 'A' nor 'B' informed 'C' in this regard. 'B' accompanied 'A' to the forest.
Facts: During his visit to the house of 'C', 'A' asked 'B' the son of 'C', to accompany 'A' to the forest. Neither 'A' nor 'B' informed 'C' in this regard. 'B' accompanied 'A' to the forest.
B 'A' has not committed theft.
‘B’ the son of ‘C’ is not a moveable thing rather he is a person within the meaning of law. A human being himself is never a subject of theft. Moveable thing as mentioned in the principle means ‘property’. . 'A' has not committed theft.
Question 6
Principle: The communication of a proposal is complete when it comes to the knowledge of the person to whom it is made.
Facts: 'A' sent a letter making a proposal to 'B' to purchase the house of 'B'.
Facts: 'A' sent a letter making a proposal to 'B' to purchase the house of 'B'.
A The communication of proposal is complete when 'B' reads the letter.
Offer is complete the moment it comes to the knowledge of the intended acceptor. The communication of proposal is complete when 'B' reads the letter.
Question 7
Principle: Law does not penalise for wrongs which are of trivial nature.
Facts: In the course of a discussion, 'A' threw a file of papers at the t able which touched the hands of 'B'.
Facts: In the course of a discussion, 'A' threw a file of papers at the t able which touched the hands of 'B'.
D 'A' is not liable for his act, as it was of trivial nature.
'A' is not liable for his act, as it was of trivial nature. Throwing file on the table, even of touches the body part of the person will not attract any penal liability.
Question 8
Principle: Copyright law protects only work. 'Work' means cinema to graphic film but does not include performance by an actor in a cine matographic film.
Facts: Alia Bhatt acted in a movie
Facts: Alia Bhatt acted in a movie
B The acting of Alia Bhatt cannot be protected under copyright law.
The acting of Alia Bhatt cannot be protected under copyright law as the principle clearly states that performance by an actor in a cinematographic film cannot be protected as a work in copyright law.
Question 9
Principle: Import means bringing some consignment into India from a foreign country.
Facts: A consignment from Sri Lanka entered the territorial waters of India. However, this consignment never crossed the Indian custom barrier nor did it enter into the stream of commerce in India.
Facts: A consignment from Sri Lanka entered the territorial waters of India. However, this consignment never crossed the Indian custom barrier nor did it enter into the stream of commerce in India.
C The consignment was imported into India.
Principle simply incorporates the word India which is a broader concept and includes territory of India irrespective of Custom Barrier or Commercial Stream of India. It will be considered that the consignment has been imported into India the moment it entered the territorial boundary of India.
Question 10
Principle: A person is said to have committed assault when an apprehension is caused in the mind of a person that he is about to use physical force against his body.
Facts: 'A' abuses 'B' while he was sitting in a moving train, by aggressively shaking his fists when 'B' was standing on the railway platform at a distance.
Facts: 'A' abuses 'B' while he was sitting in a moving train, by aggressively shaking his fists when 'B' was standing on the railway platform at a distance.
C A has not committed assault against 'B'.
As per the facts when ‘A’ abused ‘B’ by shaking his fists he was sitting in a moving train and ‘B’ was standing on the railway platform at a distance. Hence, we can conclude that there is no apprehension in the mind of 'B’ that ‘A’ is about to use force and therefore there is no assault.
Question 11
Principle: Sale of liquor is illegal. All agreements relating to prohibited items do not exist in the eyes of law.
Facts: 'A' entered into an agreement with 'B' for the sale of liquor. 'A' failed to supply the agreed quantity of liquor to 'B'.
Facts: 'A' entered into an agreement with 'B' for the sale of liquor. 'A' failed to supply the agreed quantity of liquor to 'B'.
C 'B' cannot bring any legal action against 'A'.
'B' cannot bring any legal action against 'A’ because as per the principle, Liqour is an illegal item and not agreement can be made enforceable which pertains to illegal or prohibited item.
Question 12
Principle: Nothing is an offence which is done by a child under twelve years of age, who has not attained sufficient maturity of understanding to judge the nature and consequences of his conduct on that occasion.
Facts: Himesh, 11 years old boy, picks up a gold ring worth Rs 5000/-lying on a table in his friend's house and immediately sells it for Rs 2000/-, and misappropriates the money.
Facts: Himesh, 11 years old boy, picks up a gold ring worth Rs 5000/-lying on a table in his friend's house and immediately sells it for Rs 2000/-, and misappropriates the money.
D Himesh would not be protected under the principle stated above because his acts show that he was sufficiently mature to understand the nature and consequences of his conduct.
As per the given facts, Himesh picked up the gold ring worth Rs.5000 from his friend’s house sold it for Rs. 2000 and misappropriated the money. His act shows that he had the requisite mental element to understand the nature of his act. Hence, even if he was below the age of 12 years, the presence of requisite mental element makes him liable for his act.
Question 13
Principle: One who dishonestly misappropriates or converts to his own use or sells any movable property belonging to another, is guilt y of the offence of misappropriation.
Facts: 'A' takes property belonging to 'Z' out of Z's possession, in good faith, believing when he takes it, that the property belongs to himself. Subsequently, 'A', on discovering his mistake, without disclosing the actual facts, dishonestly sells the property to a stranger.
Facts: 'A' takes property belonging to 'Z' out of Z's possession, in good faith, believing when he takes it, that the property belongs to himself. Subsequently, 'A', on discovering his mistake, without disclosing the actual facts, dishonestly sells the property to a stranger.
B 'A' is guilty of an offence of misappropriation.
“A” had no dishonest intention when he took the property out of the possession of “Z” as he honestly believed that the property belonged to him. But his intention was malafide when he sold the property despite knowing the fact that the property belonged to “Z”. Hence, he is liable for misappropriation of property.
Question 14
Principle: Letters or words not describing quality of things can be registered as a trade mark.
Facts: Ram made an application for registration of alphabet 'B' written in a fancy style as trade mark to be applied on packets and cartons of shoes manufactured by him.
Facts: Ram made an application for registration of alphabet 'B' written in a fancy style as trade mark to be applied on packets and cartons of shoes manufactured by him.
C The alphabet 'B' can be registered as trade mark.
As per the principle, even if the alphabet 'B' written in a fancy style does not describe quality of things, yet it can be registered as a Trademark. Hence, it can be registered.
Question 15
Principle: Defamation is the publication of a statement which tends to lower reputation of a person in the estimation of other members of the society generally.
Facts: 'A' writes a highly offensive and derogatory letter about 'B', and sends it directly to 'B' in a sealed cover.
Facts: 'A' writes a highly offensive and derogatory letter about 'B', and sends it directly to 'B' in a sealed cover.
B A' is not liable to 'B' for defamation, since there is no publication to any other person in whose estimation the reputation of 'B' could be brought down.
‘A' is not liable to 'B' for defamation, since there is no publication to any other person in whose estimation the reputation of 'B' could be brought down.
Question 16
Principle: Existence of all the alleged facts is relevant, whether they occurred at the same time and place or at different times and places.
Facts: 'A', a citizen of England, is accused of committing murder of 'B' in India by taking part in a conspiracy hatched in England.
Facts: 'A', a citizen of England, is accused of committing murder of 'B' in India by taking part in a conspiracy hatched in England.
D The facts that 'A' citizen of England is accused of commission of murder in India and of conspiracy hatched in England are relevant facts.
The facts that 'A' citizen of England is accused of commission of murder in India and of conspiracy hatched in England are relevant facts for holding A liable.
Question 17
Principle: An agreement without free consent can be enforces only at the option of the party whose consent was not free.
Facts: A obtains the consent of 'B' to enter into an agreement by put ting a gun on the head of B's girlfriend.
Facts: A obtains the consent of 'B' to enter into an agreement by put ting a gun on the head of B's girlfriend.
A 'B' can enforce the agreement.
As per the principle, if a person’s consent was not obtained freely an agreement, only he has the option to enforce the agreement. Hence, in this case only “B” has the option to enforce the agreement.
Question 18
Principle: Acceptance of proposal must be the exact mirror image of the proposal.
Facts: 'A' made a proposal to 'B' to sell a chair for Rs. 500. 'B' expressed his desire to buy the said chair for Rs. 400.
Facts: 'A' made a proposal to 'B' to sell a chair for Rs. 500. 'B' expressed his desire to buy the said chair for Rs. 400.
C 'B' has not accepted the proposal of 'A'.
Acceptance must be absolute and unqualified. For a valid acceptance, B cannot superimpose a counter condition. B must accept the offer as it is i.e. for Rs. 500/-.
Question 19
Principle: Mere silence as to facts likely to affect the decision of a person to enter into a contract is not fraud.
Facts: 'A' sells to 'B' (A's daughter who is minor) a horse which 'A' knows to be unsound. 'A' says nothing to 'B' about the unsoundness of the horse.
Facts: 'A' sells to 'B' (A's daughter who is minor) a horse which 'A' knows to be unsound. 'A' says nothing to 'B' about the unsoundness of the horse.
C 'A' has not committed fraud.
'A' has not committed fraud. ‘A’ is under no primary duty to disclose the defects unless he is placed under a duty to speak and disclose about the defects in horse.
Question 20
Principle: A person, who is usually of unsound mind, but occasionally normal, may make a contract when he is not of unsound mind.
Facts: 'A' generally remains in the state of unsound mind and rarely becomes capable of understanding the things.
Facts: 'A' generally remains in the state of unsound mind and rarely becomes capable of understanding the things.
A 'A' can make a contract when normal.
'A' can make a contract when he is mentally sound. The basic principle is that a person can enter into a contract when he is of sound mind and that soundness of mind must exist at the time of entering into contract.
Question 21
Principle: In case where there is an infringement of legal right even without any actual loss or damage, the person whose right is infringed has a cause of action.
Facts: 'P' was wrongfully prevented by the Returning officer from exercising his vote in an assembly election. Still he ('P') brought an action claiming damages. Which of the following derivations is correct?
Facts: 'P' was wrongfully prevented by the Returning officer from exercising his vote in an assembly election. Still he ('P') brought an action claiming damages. Which of the following derivations is correct?
B 'P' would succeed in his action, as he was wrongfully prevented from exercising his legal right of voting in that election.
This is a case of injuria sine damnum i.e infringement of legal right without actual damage for which cause for action arises in law. In this case although no actual damage has occurred to “P” but still there is a cause for action as his legal right is infringed because he was wrongfully prevented from exercising his vote.
Question 22
Principle: There are certain acts which, though harmful, are not wrongful in law; therefore, do not give legal right to bring action in law, to the person who suffers from such acts.
Facts: 'Prakash' has a rice mill. His neighbour, Shanti, sets up another rice mill and offers a tough competition to Prakash. As a consequence, Prakash's profits fall down. He brings a suit against Shanti for damages.
Facts: 'Prakash' has a rice mill. His neighbour, Shanti, sets up another rice mill and offers a tough competition to Prakash. As a consequence, Prakash's profits fall down. He brings a suit against Shanti for damages.
B Prakash cannot succeed in his claim for damages, as it is a case of damage without infringement of any legal right.
This is a case of damnun sine injuria i.e. damage without the infringement of any legal right. As there is no infringement of legal right hence no action arises in law against other person. In this case, establishment of another mill by Shanti may have cause him monetary damage but has not infringed upon any legal right of Prakash. Hence, no claim for payment of damages arises against Shanti.
Question 23
Principle: A condition to a contract can also be complied with after the happening of the event to which such a condition is attached.
Facts: 'A' promises to pay Rs. 5000 to 'B' on the condition that he shall marry with the consent of 'C', 'D' and 'E'. 'B' marries without the consent of 'C', 'D' and 'E', but obtains their consent after the marriage.
Facts: 'A' promises to pay Rs. 5000 to 'B' on the condition that he shall marry with the consent of 'C', 'D' and 'E'. 'B' marries without the consent of 'C', 'D' and 'E', but obtains their consent after the marriage.
B 'B' has not fulfilled the condition.
'B' has not fulfilled the condition because he obtained the consent at a time when it was immaterial.
Question 24
Principle: Killing is not murder if the offender, whilst deprived of the power of self-control by intense and sudden provocation, causes the death of the person who gave the provocation.
Facts: 'A', a man found his girlfriend sleeping, in her own bed room, with another man named 'B'. 'A' did not do anything but went to his home, picked a gun and cartridges, returned to the girlfriend's bed room with loaded gun but found the place empty. After fifteen days he saw his girlfriend dining in a restaurant. Without waiting for even a second, 'A' fired five bullets at his girlfriend who died on the spot.
Facts: 'A', a man found his girlfriend sleeping, in her own bed room, with another man named 'B'. 'A' did not do anything but went to his home, picked a gun and cartridges, returned to the girlfriend's bed room with loaded gun but found the place empty. After fifteen days he saw his girlfriend dining in a restaurant. Without waiting for even a second, 'A' fired five bullets at his girlfriend who died on the spot.
C 'A' did not kill his girlfriend under intense and sudden provocation.
In this question, the death was not caused under sudden provocation. Here, “A” can be said to be under sudden and grave provocation while he attempted to kill his girlfriend in bedroom, but not when he actually killed his girlfriend (when he saw her dining) as there was a gap of fifteen days. Hence, “A” is guilty of murder.
Question 25
Principle: Whoever by words or writing conveys to others any imputation concerning any person's reputation is said to defame that person.
Facts: During a marriage ceremony, 'A' circulated a pamphlet saying that 'S', sister of the bride, is a thief, she has stolen the shoes of the bridegroom.
Facts: During a marriage ceremony, 'A' circulated a pamphlet saying that 'S', sister of the bride, is a thief, she has stolen the shoes of the bridegroom.
C 'A' has defamed 'S'.
'A' has defamed 'S' because as per the principle, conveying any imputation concerning any person's reputation is said to defame that person.
Question 26
Principle: Causing of an effect partly by an act and partly by an omission is an offence.
Facts: 'A' confined her daughter 'D' in a room. 'A' also did not provide any food to her daughter 'D'. Consequently, 'D' died of starvation.
Facts: 'A' confined her daughter 'D' in a room. 'A' also did not provide any food to her daughter 'D'. Consequently, 'D' died of starvation.
B 'A' committed the offence of causing death of 'D'.
'A' committed the offence of causing death of 'D' by doing an act (confining her) and not providing her food (omission) and the composite effect of this is death.
Question 27
Principle: Whoever does not arrest the killer and report the matter to the concerned authorities commits an offence.
Facts: 'A', a woman, sees 'B', another woman, killing a third woman 'C'. 'A' neither attempted to arrest 'B' nor informed the concerned authorities.
Facts: 'A', a woman, sees 'B', another woman, killing a third woman 'C'. 'A' neither attempted to arrest 'B' nor informed the concerned authorities.
B 'A' has committed an offence.
The given principle is clearly being applicable to facts, 'A' neither attempted to arrest 'B' nor informed the concerned authorities he liable.
Question 28
Principle: False imprisonment is a tort (wrong) which means the total restraint of a person's liberty without lawful justification.
Facts: A part of a public road had been closed for spectators of a boat race. 'P' wanted to enter but he was prevented by 'D' and other policemen because he had not paid the admission fee. 'P' was able to enter the enclosure by other means but was unable to go where he wanted to go. The policemen refused access to where he wanted to go but allowed him to remain where he was or to go back. 'P' remained within the enclosure and refused to leave. Subsequently, 'P' sued 'D' for false imprisonment.
Facts: A part of a public road had been closed for spectators of a boat race. 'P' wanted to enter but he was prevented by 'D' and other policemen because he had not paid the admission fee. 'P' was able to enter the enclosure by other means but was unable to go where he wanted to go. The policemen refused access to where he wanted to go but allowed him to remain where he was or to go back. 'P' remained within the enclosure and refused to leave. Subsequently, 'P' sued 'D' for false imprisonment.
D 'D' could not be made liable for false imprisonment, as he did not totally restrict P's movements.
False Imprisonment as total restraint upon a person’s liberty. In this case, although “D” exercised restraint upon “P” but he was not totally restrained as he still had the option to go back .Also there was a lawful justification as he had not paid the admission fee. Hence, in this case “D” cannot be made liable for false imprisonment.
Question 29
Principle: An independent contractor is one who is employed to do some work of his employer. He is engaged under a contract for services. He undertakes to produce a given result, and in the actual execution of the work, he is not under the direct control or following directions of his employer. He may use his own discretion in execution of the work assigned.
In general, an employer is not liable for the torts (wrongful acts) of his independent contractor. But, the employer may be held liable if he directs him to do some careless acts.
Facts: Ramesh hired a taxi-cab to go to Delhi Airport. As he started l ate from his home, he kept on urging the taxi-driver to drive at a high speed and driver followed the directions? and ultimately due to high speed an accident took place causing injuries to a person.
In general, an employer is not liable for the torts (wrongful acts) of his independent contractor. But, the employer may be held liable if he directs him to do some careless acts.
Facts: Ramesh hired a taxi-cab to go to Delhi Airport. As he started l ate from his home, he kept on urging the taxi-driver to drive at a high speed and driver followed the directions? and ultimately due to high speed an accident took place causing injuries to a person.
A Ramesh would be held liable for damages as he exercised the control by giving directions to the driver.
The employer is liable if he himself directs him to do any careless act. In this case, Ramesh directed the taxi driver to drive at a high speed which ultimately led to the accident.
Question 30
Principle: Nothing is an offence, which is done by accident or misfortune, and without any criminal intention or knowledge in the doing of a lawful act in a lawful manner by lawful means and with proper car e and caution.
Facts: 'A' takes up a gun, not knowing whether it is loaded or not, points it playfully at 'B' and pulls the trigger. Consequently, 'B' falls dead.
Facts: 'A' takes up a gun, not knowing whether it is loaded or not, points it playfully at 'B' and pulls the trigger. Consequently, 'B' falls dead.
A 'B's death is not accidental, as there was want of proper care and caution on the part of 'A'.
Although “A” did not know whether the gun was loaded or not, “A” pulled the trigger. We can assume that “A” had no bad intention and the act was done by accident but there he did not take proper care and caution which is also one of the conditions which needs to be fulfilled.
Question 31
Principle: An agreement may be entered into orally or in writing, or by conduct.
Facts: 'A' went to the shop of 'B' and picked a toothbrush and gave a cheque of Rupees twenty to 'B' and left the shop.
Facts: 'A' went to the shop of 'B' and picked a toothbrush and gave a cheque of Rupees twenty to 'B' and left the shop.
D There was an agreement between 'A' and 'B'.
This is a case of implied agreement i.e. agreement entered into by the conduct. Here, “A” took the toothbrush from the shop of “B” and left a cheque of twenty rupees. His conduct shows that he was willing to buy the toothbrush so he left the cheque. Therefore, an agreement has occurred between the two.
Question 32
Principle: Law never enforces an impossible promise.
Facts: 'A' made a promise to 'B' to discover treasure by magic.
Facts: 'A' made a promise to 'B' to discover treasure by magic.
A Law will not enforce the promise.
Discovery of treasure by magic is an impossible act in the eyes of law hence the agreement is void and cannot be enforced.
Question 33
Principle: Consent is a good defence for civil action in tort. But consent must include both knowledge of risk and assumption of risk, i.e., readiness to bear harm.
Facts: A lady passenger was aware that the driver of the cab, in which she opted to travel was little intoxicated. The cab met with an accident and lady got injured.
Facts: A lady passenger was aware that the driver of the cab, in which she opted to travel was little intoxicated. The cab met with an accident and lady got injured.
C Lady is entitled to claim compensation as she only knew about risk and there was no assumption of risk.
In the given facts if the driver had told the lady that he is on a break as he is slightly drunk, and the lady still asked him to drive the car anyways, that would have resulted in lady assuming the risk as well. But here although the lady has knowledge of the risk (as she knew the driver was intoxicated) but she did not agree to bear the harm which may arise due to the action of the driver. Hence, the required conditions for consent are not satisfied. Therefore the lady is entitled for compensation.
Question 34
Principles:
- A person is said to abet the doing of a thing when he instigates any other person to do that thing.
- Mere acquiescence, however, does not amount to instigation.
C 'B' abetted 'A' to kill 'C'.
According to the given principle, a person abets the doing of a thing if he instigates any other person to do that thing. Instigation in this case simply means propelling someone to do something which is unlawful. In the given facts “B” merely said “A” to do as he pleases which in no way amounts to propulsion on part of B to kill “C”. Hence he has not committed the offence of abetment.
Question 35
Principles:
- A servant is one who is employed to do some work for his employer (master). He is engaged under a contract of service. He works directly under the control and directions of his master.
- In general, the master is vicariously liable for those torts (wrongful acts) of his servant which are done by the servant in the course of his employment.
C 'M' could not be made liable for the act of 'C', as his (C's) act of d riving the vehicle was not in the course of his employment.
The master is vicariously liable for the acts of his servant done within the course of employment.
In this case, “C” was appointed by “M” exclusively to work as a conductor. While he was driving the vehicle, though in some way he was working for “M” but the act was not related to what he was employed for. We can clearly establish that his act falls outside the course of employment.
In this case, “C” was appointed by “M” exclusively to work as a conductor. While he was driving the vehicle, though in some way he was working for “M” but the act was not related to what he was employed for. We can clearly establish that his act falls outside the course of employment.
Question 36
'alibi' means a plea by an accused person that he
B was present elsewhere
'Alibi' means a plea by an accused person that he was present elsewhere from the place where crime is alleged to have committed.
Question 37
Under the Constitution of India restriction on freedom of religion can not be placed on the ground of
B Social justice
Under the Constitution of India restriction on freedom of religion cannot be placed on the ground of social Justice.
Question 38
If an authority is holding information about another in a 'fiduciary capacity', the information under the Right to Information Act, 2005 may not be obtainable. 'Fiduciary relationship' is based on:
C Trust
'Fiduciary relationship' is a relation based on trust and confidence. For instance, Doctor- Patient, Lawyer-Client etc.
Question 39
Which one of the following is not a Directive Principle of State Policy under Part IV of the Constitution of India?
A Promotion of adult education.
There are total 11 Fundamental Duties under Article 51 A of the Constitution of India. Promotion of adult education is a Directive Principle of State Policy and not a Fundamental Duty.
Question 40
'audi alteram partem' means
B Giving opportunity of hearing of the other side.
'Audi alteram partem' is a rule of Natural Justice which means that the Judge must give a right of fair hearing to all the parties to a case before pronouncing the judgement. No person must be left unheard.
Question 41
Which among the following was described by Dr. B. R. Ambedkar as the "heart and soul of the Constitution of India"?
A Right to Constitutional Remedies
Dr. B. R. Ambedkar held Right to Constitutional Remedies as the "heart and soul of the Constitution of India"
Question 42
'obiter dicta' means
D An opinion given by the court not necessary for the decision.
'Obiter dicta' means an opinion given by the court not necessary for the decision.
Question 43
Under the Constitution of India 'Right to Pollution Free Environment' has emerged as a fundamental right from the right to
A Life and personal liberty under Article 21
'Right to Pollution Free Environment' has emerged as a fundamental right from the right to life and personal liberty under Article 21 of the Constitution of India.
Question 44
'persona non grata' means
B An unacceptable person
'Persona non grata' is a latin phrase which means an unacceptable person.
Question 45
The object of which one of the following writs is to prevent a person to hold public office which he is not legally entitled to hold?
A Quo warranto
Quo Warranto is a writ issued against a person who has unlawfully held or usurped a public post for which he was not entitled or eligible. It prevents a person to hold public office which he is not legally entitled to hold.
Question 46
Which among the following does not belong to the 'right to freedom of religion'?
D Freedom of speech and expression.
Freedom of speech and expression is part of Article 19 {1} (a) and is not covered under freedom of religion.
Question 47
'lis pendens' means
A A pending suit
The Latin term lis pendens translates as “suit pending.” This legal term refers to a written notice of a civil lawsuit concerning the title to, or an ownership interest in, a specific real property has been recorded on the property.
Question 48
Which Indian State has prescribed minimum educational qualification for candidates contesting panchayat polls?
D Haryana
Haryana has prescribed minimum educational qualification for candidates contesting panchayat polls.
Question 49
As per law the minimum age for the marriage of a boy and a girl in India is
C 21 years and 18 years respectively
Prohibition of Child Marriage Act states that a girl in India can marry not before 18 years of age if Female and 21 years of age if Male.
Question 50
The Supreme Court of India has struck down the Constitution (Ninetyninth Amendment) Act, 2014 as unconstitutional. It is related to
A National Judicial Appointment Commission
The Supreme Court of India has struck down the Constitution (Ninety Ninth Amendment) Act, 2014 as unconstitutional rendering National Judicial Appointment Commission as abolished. The case was Supreme Court Advocates On Record Association Vs. Union of India (2016).

