Section: Verbal Ability
Question 1
According to the passage, egalitarianism will not survive if
D People's outlook towards it is not radically changed.
“If egalitarianism is to endure, it has to be based not on the possession of the maximum material goods by a few or by all but on voluntary, enlightened renunciation of those goods which cannot be shared by others or can be enjoyed only at the expense of others”.
Clearly “d” is the correct choice.
Clearly “d” is the correct choice.
Question 2
According to the passage, why does man value his possessions more than his life?
D Through his possessions he can preserve his name even after his death.
The answer can be found in the lines “Experience shows that man values his possessions even more than his life because in the former he sees the means for perpetuation and survival of his descendants even after his body is reduced to ashes”.
None of the choices seem correct.
Choices “c” and “d” are close as there is some mention of both.
Between these two, “c” can be eliminated for the use of word “only”.
None of the choices seem correct.
Choices “c” and “d” are close as there is some mention of both.
Between these two, “c” can be eliminated for the use of word “only”.
Question 3
According to the passage, which was the unfinished part of Gandhi's experiment?
C Establishment of an egalitarian society
Refer to the phrases “establishment of a new social order” & “this unfinished part of his experiment”.
The social order as mentioned later is egalitarianism.
The social order as mentioned later is egalitarianism.
Question 4
Which of the following statements is 'not true' in the context of the passage?
B Man values his life more than his possessions.
Both choices “a” and “b” are correct i.e. both of them are not true as per the passage.
Consider the lines “If egalitarianism is to endure, it has to be based not on the possession of the maximum material goods by a few or by all but on voluntary, enlightened renunciation of those goods” - not by compulsion as mentioned in "a".
Choice “b” is not true in saying that man values his life more than his possessions – it is the other way round in fact.
Therefore choice “b” is also correct.
As per the official CLAT answer key: Choice “b” is the correct answer.
Consider the lines “If egalitarianism is to endure, it has to be based not on the possession of the maximum material goods by a few or by all but on voluntary, enlightened renunciation of those goods” - not by compulsion as mentioned in "a".
Choice “b” is not true in saying that man values his life more than his possessions – it is the other way round in fact.
Therefore choice “b” is also correct.
As per the official CLAT answer key: Choice “b” is the correct answer.
Question 5
According to the passage, true egalitarianism will last only if
C People inculcate spiritual values instead of material values.
“If egalitarianism is to endure, it has to be based not on the possession of the maximum material goods by a few or by all but on voluntary, enlightened renunciation of those goods which cannot be shared by others or can be enjoyed only at the expense of others. This calls for substitution of material values by purely spiritual ones”. From these lines it is clear that choice “c” is the best answer.
Question 6
According to the passage, people ultimately overturn a social order ________
A which is based on coercion and oppression.
Choices “b” and “c” can be easily eliminated as nothing is mentioned about them in the passage.
It is mentioned in the passage that if egalitarianism is to endure material values need to substitute by spiritual ones, but that does not mean that people will overturn a social order which is not congenital to the spiritual values of the people. So choice “d” is also out.
From the lines “We have seen, in our time, attempts to achieve a kind of egalitarian society and the picture of it after it was achieved. But this was done, by and large, through the use of physical force” and “This enforced egalitarianism contains, in its bosom, the seed of its own destruction” – we can see that “a” is the least incorrect of the choices and hence the correct answer to this question..
It is mentioned in the passage that if egalitarianism is to endure material values need to substitute by spiritual ones, but that does not mean that people will overturn a social order which is not congenital to the spiritual values of the people. So choice “d” is also out.
From the lines “We have seen, in our time, attempts to achieve a kind of egalitarian society and the picture of it after it was achieved. But this was done, by and large, through the use of physical force” and “This enforced egalitarianism contains, in its bosom, the seed of its own destruction” – we can see that “a” is the least incorrect of the choices and hence the correct answer to this question..
Question 7
According to the passage, the root cause of class conflict is
B Dominant inherent acquisitive instinct in man.
It is mentioned in the third paragraph – “The root cause of class conflict is possessiveness or the acquisitive instinct”.
Question 8
Which of the following statements is 'not true' in the context of the passage?
D Ideal of new order is to secure maximum material satisfaction
Option “d” contradicts what is given in the passage. The passage states that the ideal of new order is to secure minimum material satisfaction and not maximum.
Question 9
Which of the following conclusions can be deduced from the passage?
C It is difficult to change the mind and attitude of men towards property.
Choice “a” is eliminated because of the use of the word alone.
Choice “b” can be eliminated as no indication is made whether after establishing this order no conflict between different classes will arise in the future. In fact the line “in establishing a social order on this pattern, there was a strong possibility of a conflict arising between diverse groups and classes of our own people”, suggests that there still might be a possibility of conflict.
Choice “c” is correct as it is mentioned in the passage that it is difficult to root out property (possessions) because of acquisitive instinct in man.
Choice “d” is incorrect as it contradicts the basic premise of the egalitarian society.
As per the CLAT answer key, however, choice “b” is correct.
Choice “b” can be eliminated as no indication is made whether after establishing this order no conflict between different classes will arise in the future. In fact the line “in establishing a social order on this pattern, there was a strong possibility of a conflict arising between diverse groups and classes of our own people”, suggests that there still might be a possibility of conflict.
Choice “c” is correct as it is mentioned in the passage that it is difficult to root out property (possessions) because of acquisitive instinct in man.
Choice “d” is incorrect as it contradicts the basic premise of the egalitarian society.
As per the CLAT answer key, however, choice “b” is correct.
Question 10
According to the passage, what does "adoption of the ideal of trusteeship" mean?
B Adoption of the ideal by the 'haves' for the benefit of ‘have-nots’.
From the lines in the last para “Mahatma Gandhi has shown us how the acquisitive instinct inherent in man can be transmuted by the adoption of the ideal of trusteeship by those who 'have' for the benefit of all those who 'have not’.", we can see that choice “b” is the correct answer.
Question 11
Choose the correct synonym out of the four choices given.
Lethargy
Lethargy
B listlessness
The meaning of ‘lethargy’ is ‘a lack of energy and enthusiasm’ which is the same as ‘listlessness’. While ‘serenity’ means ‘calmness’, ‘impassivity’ means ‘apathy or an absence of emotional reactions’ and ‘laxity’ means ‘lack of strictness or care’.
Question 12
Choose the correct synonym out of the four choices given.
Emaciated
Emaciated
C very thin
‘Emaciated’ means ‘very thin’.
Question 13
Choose the correct synonym out of the four choices given.
Latent
Latent
A concealed
The meaning of ‘latent’ is ‘hidden or concealed or existing but not yet fully developed/manifested’.
Question 14
Choose the correct synonym out of the four choices given.
Sporadic
Sporadic
C occasional
The meaning of ‘sporadic’ is ‘occurring at irregular intervals’ which is closest in meaning to ‘occasional’.
Question 15
Choose the correct synonym out of the four choices given.
Compendium
Compendium
D collection
A ‘compendium’ is a ‘collection of concise but detailed information about a particular subject’. The word that comes closest in meaning is ‘collection’.
Question 16
Choose the correct option out of the four choices given.
Give an example pertinent _______ the case.
Give an example pertinent _______ the case.
D to
The preposition that goes along with the adjective pertinent is ‘to’.
Question 17
Choose the correct option out of the four choices given.
My voice reverberated _______ the walls of the castle.
My voice reverberated _______ the walls of the castle.
C in
The context here makes it more apt for the meaning that my voice ‘reverberated’ in or within the walls of the castle. Note that ‘with’ and ‘on’ are totally out of context here. Also, ‘reverberate from’ would make sense if the voice were emanating outwards from the walls of the castle to the nearby areas – while this is indeed possible, the previous possibility is more probable.
Question 18
Choose the correct option out of the four choices given.
The reward was not commensurate _______ the work done by us.
The reward was not commensurate _______ the work done by us.
C with
It is usually apt to use the preposition ‘with’ along with the adjective ‘commensurate’ that means ‘corresponding in size or degree’.
Question 19
Choose the correct option out of the four choices given.
Our tragic experience in the recent past provides an index _______ the state of lawlessness in this region.
Our tragic experience in the recent past provides an index _______ the state of lawlessness in this region.
A of
An index is a ‘measure of something’ and so the preposition that best agrees with this noun is ‘of’.
Question 20
Choose the correct option out of the four choices given.
Your conduct smacks _______ recklessness.
Your conduct smacks _______ recklessness.
A of
The verb ‘smacks’ is almost always followed by the preposition ‘of’.
Question 21
Choose the correct option out of the four choices given.
A good judge never gropes _______ the conclusion.
A good judge never gropes _______ the conclusion.
D for
The verb ‘gropes’ means to ‘search blindly or uncertainly’, so clearly the preposition that agrees with it would be ‘for’.
Question 22
Choose the correct option out of the four choices given.
Nobody in our group is a genius _______ winning friends and in convincing people.
Nobody in our group is a genius _______ winning friends and in convincing people.
D at
It is common to use the preposition ‘at’ when referring to a particular trait that a person has such as ‘winning friends’, ‘convincing people’ etc.
Question 23
Choose the correct option out of the four choices given.
If you are averse _______ recommending my name, you should not hesitate to admit it.
If you are averse _______ recommending my name, you should not hesitate to admit it.
C to
The preposition ‘to’ is used along with the adjective ‘averse’.
Question 24
Choose the correct option out of the four choices given.
Religious leaders should not delve _______ politics.
Religious leaders should not delve _______ politics.
D into
The preposition ‘into’ is used along with the verb ‘delve’ which means ‘reach inside’.
Question 25
Choose the correct option out of the four choices given.
What you say has hardly any bearing _______ the lives of tribals.
What you say has hardly any bearing _______ the lives of tribals.
C on
When something has ‘a bearing on’ a situation or event, it is relevant to it!
Question 26
Select the correct meaning of the italicized idioms and phrases out of the four choices given.
He burnt his fingers by interfering in his neighbor’s affair.
He burnt his fingers by interfering in his neighbor’s affair.
A got himself into trouble
To ‘burn his fingers’ means to ‘get into trouble’.
Question 27
Select the correct meaning of the italicized idioms and phrases out of the four choices given.
Mr. Gupta, who is one of the trustees of a big charity, is suspected of feathering his own nest.
Mr. Gupta, who is one of the trustees of a big charity, is suspected of feathering his own nest.
D making money unfairly
The meaning of ‘to feather one’s own nest’ is “To utilize one's position at work for one's own monetary gain”.
Question 28
Select the correct meaning of the italicized idioms and phrases out of the four choices given.
Mrs. Hashmi has been in the blues for the last several weeks.
Mrs. Hashmi has been in the blues for the last several weeks.
C depressed
The meaning of ‘to be in the blues’ is “to be depressed or sad”.
Question 29
Select the correct meaning of the italicized idioms and phrases out of the four choices given.
For the first week, the apprentice felt like a fish out of water.
For the first week, the apprentice felt like a fish out of water.
D uncomfortable
‘A fish out of water’ is “One who does not feel comfortable in a new environment”.
Question 30
Select the correct meaning of the italicized idioms and phrases out of the four choices given.
His friends failed to see why he should ride the high horse just because he had won an election.
His friends failed to see why he should ride the high horse just because he had won an election.
B appear arrogant
To ‘ride the high horse’ means to “be proud and assume an attitude of moral superiority”.
Question 31
Given below are the jumbled sentences of a paragraph. The first and the last sentence of the jumbled paragraph are given in correct order. Arrange the middle sentences in the correct sequence.
i. On one hand we are proud of being Indians,
ii. on the other hand we behave as if we were still at the dawn of our civilization
iii. murders of our own brothers and sisters is not the way to please Ram or Rahim
iv. the citizens of the land where Buddha and Gandhi taught
v. the principles of love and non-violence,
vi. nor does it fetch us any prosperity.
i. On one hand we are proud of being Indians,
ii. on the other hand we behave as if we were still at the dawn of our civilization
iii. murders of our own brothers and sisters is not the way to please Ram or Rahim
iv. the citizens of the land where Buddha and Gandhi taught
v. the principles of love and non-violence,
vi. nor does it fetch us any prosperity.
D iv, v, ii, iii
The last sentence mentions “nor” – so the preceding sentence must talk of something else also that this thing doesn’t get us.
That 'something else' is in (iii): '"is not the way to please Ram or Rahim".
So we can sense that (iii) must precede (vi) – only choice “d” has this.
When we check this choice for the flow of ideas we can see that the paragraph makes coherent sense.
That 'something else' is in (iii): '"is not the way to please Ram or Rahim".
So we can sense that (iii) must precede (vi) – only choice “d” has this.
When we check this choice for the flow of ideas we can see that the paragraph makes coherent sense.
Question 32
Given below are the jumbled sentences of a paragraph. The first and the last sentence of the jumbled paragraph are given in correct order. Arrange the middle sentences in the correct sequence.
i. On the basis of experiments with rats
ii. health experts here say that
iii. exercise more and consume vitamins,
iv. they will live up to 100 years or more
v. if humans eat less,
vi. and be vigorous in their eighties and nineties.
i. On the basis of experiments with rats
ii. health experts here say that
iii. exercise more and consume vitamins,
iv. they will live up to 100 years or more
v. if humans eat less,
vi. and be vigorous in their eighties and nineties.
B ii, v, iii, iv
(ii) should follow (i). So choice “d” can be eliminated.
The pronoun “they” refers to “humans” so (v) should come before (iv).
Also, (v) must follow (ii) as it initiates the reason for the final conclusion that 'humans will be vigorous in their eighties and nineties'.
Finally, (iv) should precede (vi) as “and” is mentioned in (vi).
The pronoun “they” refers to “humans” so (v) should come before (iv).
Also, (v) must follow (ii) as it initiates the reason for the final conclusion that 'humans will be vigorous in their eighties and nineties'.
Finally, (iv) should precede (vi) as “and” is mentioned in (vi).
Question 33
Given below are the jumbled sentences of a paragraph. The first and the last sentence of the jumbled paragraph are given in correct order. Arrange the middle sentences in the correct sequence.
i. The release of atomic energy is the greatest achievement which science has yet attained
ii. but the first invention to which their discoveries were applied was a bomb
iii. the atom was split by physicists whose minds were set on the search for knowledge
iv. it was more deadly than any other weapon invented so far
v. it is with dread that scientists regard the first use to which their greatest discovery was put
vi. however, they are gratified by the numerous applications of atomic energy for peaceful and constructive population.
i. The release of atomic energy is the greatest achievement which science has yet attained
ii. but the first invention to which their discoveries were applied was a bomb
iii. the atom was split by physicists whose minds were set on the search for knowledge
iv. it was more deadly than any other weapon invented so far
v. it is with dread that scientists regard the first use to which their greatest discovery was put
vi. however, they are gratified by the numerous applications of atomic energy for peaceful and constructive population.
C iii, ii, iv, v
(ii), (iv) and (v) have a link among them – the common theme is the apprehension regarding atomic energy.
We just need to figure out their order.
We can see that (iii) will be appropriate only after (i).
Only choice “c” has (iii) after (i).
Checking choice “c” we can see that this is the correct order.
We just need to figure out their order.
We can see that (iii) will be appropriate only after (i).
Only choice “c” has (iii) after (i).
Checking choice “c” we can see that this is the correct order.
Question 34
Given below are the jumbled sentences of a paragraph. The first and the last sentence of the jumbled paragraph are given in correct order. Arrange the middle sentences in the correct sequence.
i. The problem of food is intimately connected with population
ii. wages will seldom rise in proportion to the rising prices
iii. the market is governed by demand and supply
iv. without enough food, such people lack health, strength of efficiency
v. if too many people demand goods to go round, prices will rise and poor classes will starve
vi. they fall an easy prey to all sorts of diseases.
i. The problem of food is intimately connected with population
ii. wages will seldom rise in proportion to the rising prices
iii. the market is governed by demand and supply
iv. without enough food, such people lack health, strength of efficiency
v. if too many people demand goods to go round, prices will rise and poor classes will starve
vi. they fall an easy prey to all sorts of diseases.
A iii, v, ii, iv
In (iv) there is use of “such people” – this means that “people” must be referred to earlier.
“People” are referred to in (v) – this implies that (v) should come before (iv).
So choices “b” and “c” are ruled out.
(iii) and (v) form a mandatory pair and are thus presented in option "a" which is the correct answer.
“People” are referred to in (v) – this implies that (v) should come before (iv).
So choices “b” and “c” are ruled out.
(iii) and (v) form a mandatory pair and are thus presented in option "a" which is the correct answer.
Question 35
Given below are the jumbled sentences of a paragraph. The first and the last sentence of the jumbled paragraph are given in correct order. Arrange the middle sentences in the correct sequence.
i. India's message has always been one of love and peace.
ii. our Buddha was the light of Asia
iii. it has been a source of light and wisdom to the rest of the world
iv. Ashoka, moved by the horrors of Kalinga War, adopted the message of non-violence
v. the greatest apostle of non-violence in recent years was Mahatma Gandhi
vi. he shook the foundation of the British rule in India through non-violence.
i. India's message has always been one of love and peace.
ii. our Buddha was the light of Asia
iii. it has been a source of light and wisdom to the rest of the world
iv. Ashoka, moved by the horrors of Kalinga War, adopted the message of non-violence
v. the greatest apostle of non-violence in recent years was Mahatma Gandhi
vi. he shook the foundation of the British rule in India through non-violence.
D iii, ii, iv, v
“It” in (iii) refers to India’s message – so (iii) and (i) are mandatory pair.
Only one option choice “d” has (iii) following (i) – so “d” is the correct choice.
Only one option choice “d” has (iii) following (i) – so “d” is the correct choice.
Question 36
Given below are a few commonly used foreign language phrases, select the correct answer from the four options given below.
Mala fide
Mala fide
B bad intention
The meaning of ‘mala fide’ is ‘in bad faith or with the intend to deceive’.
Question 37
Given below are a few commonly used foreign language phrases, select the correct answer from the four options given below.
Tabula rasa
Tabula rasa
A clean slate
The phrase ‘tabula rasa’ is a latin one that means “clean or blank slate”.
Question 38
Given below are a few commonly used foreign language phrases, select the correct answer from the four options given below.
Carte blanche
Carte blanche
B complete discretion
The meaning of ‘carte blanche’ is “full discretionary power”.
Question 39
Given below are a few commonly used foreign language phrases, select the correct answer from the four options given below.
De jure
De jure
C concerning law
The meaning of ‘de jure’ is “a state of affairs that is in accordance with law”.
Question 40
Given below are a few commonly used foreign language phrases, select the correct answer from the four options given below.
Raison d’etre
Raison d’etre
B reason for existence
The meaning of “raison d’etre” is “the most important reason or purpose for someone or something's existence”.
Section: Quantitative Aptitude
Question 1
P sells a table to Q at a profit of 10% and Q sells it to R at a profit of 12%. If R pays Rs. 246.40 for it, then how much had P paid for it?
A 200.00
Method-1: Check the options.
Since P’s cost price is less than that of R, options B, C and D can be ruled out. This only leaves (A).
In Option (A):
P = 200,
Q = 200 + 10% of 200 = 200 + 20 = 220
R = 220 + 12% of 220 = 220 + 26.4 = 246.4
Clearly this is the correct choice!
Method-2: Make equations.
Let P’s cost price be C.
Then, Q’s cost price = P’s selling price = C + 10% of C = C(1 + 0.1) = 1.1C
Also, R’s cost price = Q’s selling price = 1.1C + 12% of 1.1C = 1.1C(1 + 0.12) = 1.1C x 1.12
Hence, 1.1C x 1.12 = 246.4
i.e. C x 1.12 = 224 or C = 224 x 100/112 = Rs. 200
Method-3: Successive changes approach.
There are two successive increases in the price by 10% and 12% respectively.
So overall % increase = a + b + ab/100 = 10 + 12 + 120/100 = 23.2%
Now, if P paid Rs. C for it, R must have paid C + 23.2% of C
i.e. C(1 + 0.232) = 246.4
i.e. C = 246.4 x 1000/1232 = Rs. 200
Question 2
The least value of x, for which the expression x2 + x + 17 will not give a prime number, is
D 17
Option (D) seems the best choice as 172 + 17 + 17 = 17(17 + 2) = 17 x 19 which is not Prime.
Checking the options one-by-one:
Option (A): 72 + 7 + 17 = 49 + 24 = 73; a Prime
Option (B): 112 + 11 + 17 = 121 + 28 = 149; a Prime
Option (C): 132 + 13 + 17 = 169 + 30 = 199; a Prime
Option (D): 172 + 17 + 17 = 289 + 34 = 323; Not a Prime
Checking the options one-by-one:
Option (A): 72 + 7 + 17 = 49 + 24 = 73; a Prime
Option (B): 112 + 11 + 17 = 121 + 28 = 149; a Prime
Option (C): 132 + 13 + 17 = 169 + 30 = 199; a Prime
Option (D): 172 + 17 + 17 = 289 + 34 = 323; Not a Prime
Question 3
A train 300 meters long is running at a speed of 25 meters per second, it will cross a bridge 200 meters long in
C 20 seconds
When the train crosses the bridge, Crossing Distance = Train’s length + Bridge’s length = 500 m
We know, D = S x T
So, 500 = 25 x T or T = 500/25 = 20 seconds
We know, D = S x T
So, 500 = 25 x T or T = 500/25 = 20 seconds
Question 4
If 0.06% of a number is 84, then 30% of that number is
C 42000
Let the number be N.
Given, 0.06% of N = 84
i.e. 0.06/100 x N = 84
So, N = 84 x 100 x 100/6 = 140000
Now, 30% of N = 30/100 x 140000 = 42000
Given, 0.06% of N = 84
i.e. 0.06/100 x N = 84
So, N = 84 x 100 x 100/6 = 140000
Now, 30% of N = 30/100 x 140000 = 42000
Question 5
A sum was divided among P, Q & R. R got double than P who got double than Q. If the difference between the shares of Q and R is Rs. 3675.00, then the sum in rupees is
B 8575
Given, R = 2P and P = 2Q
i.e. P = 2Q and R = 4Q
Also, R – Q = 3675
i.e. 4Q – Q = 3675
i.e. Q = 3675/3 = 1225
So, P = 2 x 1225 = 2450 and R = 4Q = 4900
Hence total sum = 1225 + 2450 + 4900 = Rs. 8575
i.e. P = 2Q and R = 4Q
Also, R – Q = 3675
i.e. 4Q – Q = 3675
i.e. Q = 3675/3 = 1225
So, P = 2 x 1225 = 2450 and R = 4Q = 4900
Hence total sum = 1225 + 2450 + 4900 = Rs. 8575
Question 6
If the ratio of the areas of two squares is 25:36, then the ratio of their perimeters is
A 5 : 6
Let A and B be the sides of the two squares
Then, Ratio of areas A2 : B2 = 25 : 36 = 52 : 62
On taking a square root, A : B = 5 : 6
Now ratio of perimeters = 4A : 4B = A : B = 5 : 6
Then, Ratio of areas A2 : B2 = 25 : 36 = 52 : 62
On taking a square root, A : B = 5 : 6
Now ratio of perimeters = 4A : 4B = A : B = 5 : 6
Question 7
The denominator of a fraction is greater than its numerator by 11. If 8 is added to both its numerator and denominator, then it becomes 3/4. The fraction is
D 25/36
We can simply check the conditions on the given options:
Clearly options A, B and C have difference of numerator and denominator not equal to 11.
In Option (D), 25/36 à Difference = 11 and (25 + 8)/(36 + 8) = 33/44 = 3/4
Hence option D is the correct choice!
Clearly options A, B and C have difference of numerator and denominator not equal to 11.
In Option (D), 25/36 à Difference = 11 and (25 + 8)/(36 + 8) = 33/44 = 3/4
Hence option D is the correct choice!
Question 8
If the volume of a sphere is divided by its surface area, we obtain 27 cm. The radius of the sphere is
B 81 cm
Volume/Surface Area = 27
i.e. (4πR3/3)/(4πR2) = R/3 = 27
i.e. R = 81
i.e. (4πR3/3)/(4πR2) = R/3 = 27
i.e. R = 81
Question 9
One-third of one fourth of a number is 12. Then the number is
B 144
Given, 1/3 x 1/4 x N = 12
i.e. N = 12 x 12 = 144
i.e. N = 12 x 12 = 144
Question 10
In the number series 4, 10, 23, 50, 104, 216, 439 the wrong number is
C 104
The nth term in this series is equal to double the previous term increased by n:
4
2 x 4 + 2 = 10
2 x 10 + 3 = 23
2 x 23 + 4 = 50
2 x 50 + 5 = 105
2 x 105 + 6 = 216
2 x 216 + 7 = 439
Hence incorrect number is 104.
4
2 x 4 + 2 = 10
2 x 10 + 3 = 23
2 x 23 + 4 = 50
2 x 50 + 5 = 105
2 x 105 + 6 = 216
2 x 216 + 7 = 439
Hence incorrect number is 104.
Question 11
The price of 2 trousers and 4 shirts is Rs. 1,600. With the same amount one can buy 1 trouser and 6 shirts. If one wants to buy 12 shirts, he has to pay
A Rs. 2400
Let T and S be price of a trouser and shirt respectively.
Then, 2T + 4S = 1600 and T + 6S = 1600
i.e. 2(T + 2S) = 1600 and T + 6S = 1600
i.e. T + 2S = 800 and T + 6S = 1600
On subtracting: 6S – 2S = 4S = 800
Clearly, 12S = Rs. 2400
Then, 2T + 4S = 1600 and T + 6S = 1600
i.e. 2(T + 2S) = 1600 and T + 6S = 1600
i.e. T + 2S = 800 and T + 6S = 1600
On subtracting: 6S – 2S = 4S = 800
Clearly, 12S = Rs. 2400
Question 12
A dealer buys an article for Rs. 380.00. What price should he mark so that after allowing a discount of 5% he still makes a profit of 25% on the article?
A Rs. 500
Given, CP = 380 and profit = 25%
So, SP = CP + profit = 380 + 25/100 x 380 = 380 + 95 = 475
Now SP = 475 and discount = 5%
And, SP = MP – discount
Let MP be Rs. M
Then, 475 = M – 5/100 x M = 95M/100
So, M = 475 x 100/95 = 500
Hence, MP = Rs. 500
So, SP = CP + profit = 380 + 25/100 x 380 = 380 + 95 = 475
Now SP = 475 and discount = 5%
And, SP = MP – discount
Let MP be Rs. M
Then, 475 = M – 5/100 x M = 95M/100
So, M = 475 x 100/95 = 500
Hence, MP = Rs. 500
Question 13
In a factory, the production of scooters rose to 48400 from 40000 in 2 years. The rate of growth per annum is
B 10%
This is a case of compounded growth per annum, so we use the formula:
A = P(1 + R/100)T
i.e. 48400 = 40000 x (1 + R/100)2
i.e. (1 + R/100)2 = 484/400
On taking square root:
i.e. (1 + R/100) = 22/20 = 11/10
i.e. R/100 = 11/10 – 1 = 1/10
So, R = 100/10 = 10% per annum
A = P(1 + R/100)T
i.e. 48400 = 40000 x (1 + R/100)2
i.e. (1 + R/100)2 = 484/400
On taking square root:
i.e. (1 + R/100) = 22/20 = 11/10
i.e. R/100 = 11/10 – 1 = 1/10
So, R = 100/10 = 10% per annum
Question 14
The sum of two numbers is 2490. If 6.5% of one number is equal to 8.5% of the other, the numbers are
A 1411 and 1079
Let the numbers be A and B.
Given, 6.5% of A = 8.5% of B
i.e. 6.5/100 x A = 8.5/100 x B
i.e. 65A = 85B or A/B = 85/65 = 17/13
Hence ratio of numbers is 17 : 13 and their sum is 2490
Then by the concept of “Parts of a whole”:
A = 17/30 x 2490 = 17 x 83 = 1411
And B = 13/30 x 2490 = 13 x 83 = 1079
Given, 6.5% of A = 8.5% of B
i.e. 6.5/100 x A = 8.5/100 x B
i.e. 65A = 85B or A/B = 85/65 = 17/13
Hence ratio of numbers is 17 : 13 and their sum is 2490
Then by the concept of “Parts of a whole”:
A = 17/30 x 2490 = 17 x 83 = 1411
And B = 13/30 x 2490 = 13 x 83 = 1079
Question 15
120 men had food provision for 200 days. After 5 days, 30 men died of an epidemic. The food will last for further
B 260 days
Let a man eat 1 unit of food. Then 120 men will eat 120 units each day
Then, initial provisions = 120 x 200 = 24000 units
Then, amount eaten by 120 men in 5 days = 120 x 5 = 600 units
So provisions left = 24000 – 600 = 23400 units
Now there will be 90 men left; they will eat 90 units each day
If the food lasts for N more days now:
23400 = 90 x N or N = 23400/90 = 260 days
Then, initial provisions = 120 x 200 = 24000 units
Then, amount eaten by 120 men in 5 days = 120 x 5 = 600 units
So provisions left = 24000 – 600 = 23400 units
Now there will be 90 men left; they will eat 90 units each day
If the food lasts for N more days now:
23400 = 90 x N or N = 23400/90 = 260 days
Question 16
Out of the total income, X spends 20% on house rent and 70% of the remaining amount on household expenditure. If X saves Rs. 1800, the total income is
C Rs. 7500
Method-1:
Let income be X.
Then, House Rent = 20% of X = 0.2X
Remaining income = X – 0.2X = 0.8X
Now, Household Expenditure = 70% of the remaining income = 0.7 x 0.8X = 0.56X
So, total expenses = 0.2X + 0.56X = 0.76X
But, Savings = Income – Expenses
Hence, X – 0.76X = 1800
or X = 1800 x 100/24 = Rs. 7500
Method-2:
We can check each option:
Option (A):
X = Rs. 8000, Rent = 20% of 8000 = 1600, HH = 70% of (8000 – 1600) = 70/100 x 6400 = 4480
Savings = 8000 – 1600 – 4480 = 8000 – 6080 ≠ 1800
Option (B):
X = Rs. 9500, Rent = 20% of 9500 = 1900, HH = 70% of (9500 – 1900) = 70/100 x 7600 = 5320
Savings = 9500 – 1900 – 5320 = 9500 – 7220 ≠ 1800
Option (D):
X = Rs. 8500, Rent = 20% of 8500 = 1700, HH = 70% of (8500 – 1700) = 70/100 x 6800 = 4760
Savings = 8500 – 1700 – 4760 = 8500 – 6460 ≠ 1800
Option (C):
X = Rs. 7500, Rent = 20% of 7500 = 1500, HH = 70% of (7500 – 1500) = 70/100 x 6000 = 4200
Savings = 7500 – 1500 – 4200 = 7500 – 5700 = 1800
Clearly option (C) is the correct choice!
Let income be X.
Then, House Rent = 20% of X = 0.2X
Remaining income = X – 0.2X = 0.8X
Now, Household Expenditure = 70% of the remaining income = 0.7 x 0.8X = 0.56X
So, total expenses = 0.2X + 0.56X = 0.76X
But, Savings = Income – Expenses
Hence, X – 0.76X = 1800
or X = 1800 x 100/24 = Rs. 7500
Method-2:
We can check each option:
Option (A):
X = Rs. 8000, Rent = 20% of 8000 = 1600, HH = 70% of (8000 – 1600) = 70/100 x 6400 = 4480
Savings = 8000 – 1600 – 4480 = 8000 – 6080 ≠ 1800
Option (B):
X = Rs. 9500, Rent = 20% of 9500 = 1900, HH = 70% of (9500 – 1900) = 70/100 x 7600 = 5320
Savings = 9500 – 1900 – 5320 = 9500 – 7220 ≠ 1800
Option (D):
X = Rs. 8500, Rent = 20% of 8500 = 1700, HH = 70% of (8500 – 1700) = 70/100 x 6800 = 4760
Savings = 8500 – 1700 – 4760 = 8500 – 6460 ≠ 1800
Option (C):
X = Rs. 7500, Rent = 20% of 7500 = 1500, HH = 70% of (7500 – 1500) = 70/100 x 6000 = 4200
Savings = 7500 – 1500 – 4200 = 7500 – 5700 = 1800
Clearly option (C) is the correct choice!
Question 17
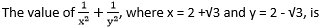
C 14
Given, x = 2 + √3 and y = 2 - √3
So, 1/x = 1/(2 + √3) and 1/y = 1/(2 – √3)
On rationalizing the denominators we get:
1/x = (2 – √3)/(4 – 3) = (2 - √3)
and 1/y = (2 + √3)/(4 – 3) = (2 + √3)
So, 1/x2 + 1/y2 = (2 – √3)2 + (2 + √3)2 = 4 + 3 – 4√3 + 4 + 3 + 4√3 = 14
So, 1/x = 1/(2 + √3) and 1/y = 1/(2 – √3)
On rationalizing the denominators we get:
1/x = (2 – √3)/(4 – 3) = (2 - √3)
and 1/y = (2 + √3)/(4 – 3) = (2 + √3)
So, 1/x2 + 1/y2 = (2 – √3)2 + (2 + √3)2 = 4 + 3 – 4√3 + 4 + 3 + 4√3 = 14
Question 18
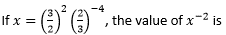
A <img alt="" src="/img/images/Picture50.png" style="height:34px; width:34px" />
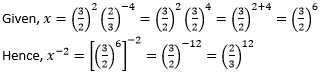
Question 19
When 16x4 + 12x3 – 10x2 + 8x + 20 is divided by 4x – 3, the quotient and the remainder are, respectively
D 4x<sup>3</sup> + 6x<sup>2</sup> + 2x + 7/2 and 61/2
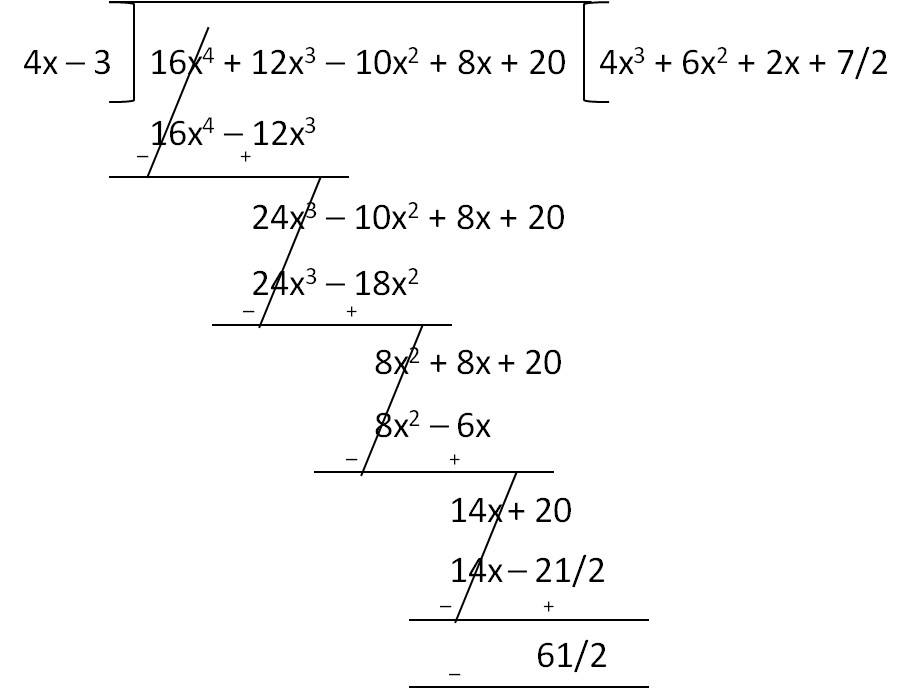
Question 20
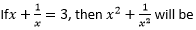
D 7
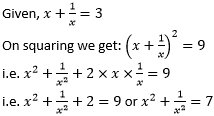
Section: General Knowledge
Question 1
Who said that, ‘Man is a social animal’?
B Aristotle
Arostotle
Question 2
World Computer Literacy day is celebrated on
C December 2
December 2
Question 3
Whose teaching inspired the French Revolution?
A Rousseau
Rousseau
Question 4
The II Africa-India Summit was held in May 2011 in
D Addis Ababa
Addis Ababa
Question 5
The famous Akshardham temple is situated in the city of
B Gandhinagar
Gandhinagar
Question 6
Who out of the following was the recipient of Dhyan Chand Award in 2011?
C Shabbir Ali
Shabbir Ali
Question 7
Name the annual fair of Rajasthan that is famous for its camel trading event.
B Pushkar Mela
Pushkar Mela
Question 8
The 38th G-8 summit will be held in 2012 in
A USA
USA
Question 9
Who was awarded the Nobel Prize for literature in 2011?
C Tomas Transtromer
Tomas Transtromer
Question 10
Who was awarded the UNESCO King Sejong Literacy Prize in 2011?
B National Literacy Service, Burundi
National Literacy Service, Burundi
Question 11
December 10 is observed as
D Human Rights day
Human Rights day
Question 12
Which is the largest gland in human body?
B Liver
Liver
Question 13
The book titled ‘The Google Story’ has been authored by
A David A. Vice
David A. Vice
Question 14
Which strait separates Europe from Africa
B Gibralter
Gibralter
Question 15
Taiwan was earlier known as
C Formosa
Formosa
Question 16
Identify the Indian Tennis player who has turned Hollywood filmmaker?
D Ashok Amritraj
Ashok Amritraj
Question 17
Where will the next Olympic Games be held in 2012?
C London
London
Question 18
Which of the following teams has won the Santosh Trophy Football Championship in 2011?
B West Bengal
West Bengal
Question 19
Excess of money supply as compared to supply of goods results in
D Inflation
Inflation
Question 20
The largest living flightless bird is
C Ostrich
Ostrich
Question 21
Which of the following oceans has the shape of the English letter ‘S’?
A Atlantic
Atlantic
Question 22
Which is the longest shipping canal in the world?
C White Sea-Baltic Canal
White Sea-Baltic Canal
Question 23
Le Corbusier, the architect of Chandigarh was a national of
C France
France
Question 24
India became a member of UNO in
A 1945
1945
Question 25
To which country does India export the largest quantity of iron ore?
B Japan
Japan
Question 26
The longest highway in India runs from
D Varanasi to Kanyakumari
Varanasi to Kanyakumari
Question 27
The longest irrigation canal in India is called
B Indira Gandhi Canal
Indira Gandhi Canal
Question 28
Leukemia is a disease related to
C Blood
Blood
Question 29
In which city was Osama Bin Laden killed in May 2011?
B Abbottabad
Abbottabad
Question 30
The XI Five Year Plan envisaged the highest growth in the sector of
C Services
Services
Question 31
Light year is a unit of
A Distance
Distance
Question 32
The IV summit of BRICS was held in New Delhi on
C 29th March 2012
29th March 2012
Question 33
An indigenous nuclear submarine still under construction has been named as
C Arihant
Arihant
Question 34
Government of India has launched a publicity campaign for census 2011 in association with which of the following UN organization?
C United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
Question 35
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) completed how many years of operation in 2011?
D 6 years
6 years
Question 36
The first ever formula one race in India was held in
A Greater Noida
Greater Noida
Question 37
Name the actor who has been honoured with the Dadasaheb Phalke Award in 2012.
C Soumitra Chatterjee
Soumitra Chatterjee
Question 38
In which city was the Arab Summit held in the last week of March 2012?
A Baghdad
Baghdad
Question 39
The two Supreme Court Judges who delivered the famous 2-G judgment in February 2012 were
B Justice G.S. Singhvi and Justice A.K. Ganguly
Justice G.S. Singhvi and Justice A.K. Ganguly
Question 40
Who presides over the joint sitting of both houses of Parliament?
A Speaker of Lok Sabha
Speaker of Lok Sabha
Question 41
Christian Lagarde heads the
C International Monetary Fund
International Monetary Fund
Question 42
The seat of International Criminal Court is at
A The Hague
The Hague
Question 43
First Indian to ski to North Pole is
B Ajeet Bajaj
Ajeet Bajaj
Question 44
First woman Director General of Police in India was
A Kanchan Choudhary
Kanchan Choudhary
Question 45
Which countries co-hosted the One-day cricket World Cup in 2011?
A India, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka
India, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka
Question 46
Priyanka Chopra has been named National Ambassador of
B UNICEF
UNICEF
Question 47
Who is leading in the Republican primaries to contest the American Presidential election scheduled in November 2012?
D Mitt Romney
Mitt Romney
Question 48
Supreme Court recently declared ‘Salva Judum’ unconstitutional. What is ‘Salva Judam’?
B An armed civilian group formed to combat Maoists
An armed civilian group formed to combat Maoists
Question 49
As per the Indian Union Budget of 2012-13, the income-tax exemption limit for persons below 65 years of age is
B Rs. 200000
Rs. 200000
Question 50
The U. N. Climate Change Conference 2011 was held in
C Durban
Durban
Section: Logical Reasoning
Question 1
Given below are some statements followed by two arguments. Read carefully and decide which of the arguments strongly support the statement.
Statement:
Should the pay scale and conditions of service of government employees be made applicable to private sector employees?
Arguments:
(i) No, this will develop inertia, inefficiency and would adversely affect spirit of competition.
(ii) Yes, this will enhance dedication to work and institutional loyalty
Statement:
Should the pay scale and conditions of service of government employees be made applicable to private sector employees?
Arguments:
(i) No, this will develop inertia, inefficiency and would adversely affect spirit of competition.
(ii) Yes, this will enhance dedication to work and institutional loyalty
A Argument (i) is strong.
(i) is strong since any changes made without merit/reason may lead to unwarranted consequences.
(ii) is weak as it assumes that the conditions of government employees are better than those of private employees.
(ii) is weak as it assumes that the conditions of government employees are better than those of private employees.
Question 2
Given below are some statements followed by two arguments. Read carefully and decide which of the arguments strongly support the statement.
Statement:
Should a strong institution of ombudsman be created in India?
Arguments:
(i) Yes, this will bring transparency and accountability in the administration
(ii) No, this will develop lack of initiative and flexibility in the administration.
Statement:
Should a strong institution of ombudsman be created in India?
Arguments:
(i) Yes, this will bring transparency and accountability in the administration
(ii) No, this will develop lack of initiative and flexibility in the administration.
A Argument (i) is strong.
According to us, actually, both these are weak arguments; but as per CLAT’s official key, “a” was the answer.
Question 3
Given below are some statements followed by two arguments. Read carefully and decide which of the arguments strongly support the statement.
Statement:
Should internal assessment in colleges and universities be abolished?
Arguments:
(i) Yes, this will eliminate the possibility of favoritism.
(ii) No, teaching faculty will lose control over the students and this would adversely affect their academic growth.
Statement:
Should internal assessment in colleges and universities be abolished?
Arguments:
(i) Yes, this will eliminate the possibility of favoritism.
(ii) No, teaching faculty will lose control over the students and this would adversely affect their academic growth.
C Both (i) and (ii) are strong.
Both are strong arguments and hence “c” is the correct answer.
Question 4
Given below are some statements followed by two arguments. Read carefully and decide which of the arguments strongly support the statement.
Statement:
Should military training be made compulsory for all college and university students?
Arguments:
(i) Yes, this will develop in them a sense of punctuality and discipline
(ii) No, military training should be given only to those students who are physically fit.
Statement:
Should military training be made compulsory for all college and university students?
Arguments:
(i) Yes, this will develop in them a sense of punctuality and discipline
(ii) No, military training should be given only to those students who are physically fit.
A Argument (i) is strong.
Argument (i) is strong.
Question 5
Given below are some statements followed by two arguments. Read carefully and decide which of the arguments strongly support the statement.
Statement:
Should students’ union in colleges and universities be abolished?
Arguments:
(i) Yes, it detracts students from academic and career development.
(ii) No, all great leaders have been students’ union leaders.
Statement:
Should students’ union in colleges and universities be abolished?
Arguments:
(i) Yes, it detracts students from academic and career development.
(ii) No, all great leaders have been students’ union leaders.
A Argument (i) is strong.
Argument (i) is strong.
Question 6
Given below are some statements followed by two arguments. Read carefully and decide which of the arguments strongly support the statement.
Statement:
Should the age of marriage be raised to 25 years for boys and 21 for girls?
Arguments:
(i) No, it is difficult to change a social practice in Indian conditions.
(ii) Yes, by that age people develop a sense of responsibility and also complete their education.
Statement:
Should the age of marriage be raised to 25 years for boys and 21 for girls?
Arguments:
(i) No, it is difficult to change a social practice in Indian conditions.
(ii) Yes, by that age people develop a sense of responsibility and also complete their education.
B Argument (ii) is strong.
Argument (ii) is strong.
Question 7
Each question contains six statements followed by four sets of combination of three. Choose the set in which the statements are logically related.
Statements:
(i) X and Y are siblings.
(ii) X and Y do not quarrel.
(iii) Siblings are known to quarrel often.
(iv) X and Y quarrel often.
(v) All those who quarrel are siblings.
(vi) X and Y cannot be siblings.
Statements:
(i) X and Y are siblings.
(ii) X and Y do not quarrel.
(iii) Siblings are known to quarrel often.
(iv) X and Y quarrel often.
(v) All those who quarrel are siblings.
(vi) X and Y cannot be siblings.
C i, iii, iv
In this question choices a, b and d can be easily eliminated as the statements contradict the conclusions.
Choice “c” is the correct answer.
Choice “c” is the correct answer.
Question 8
Each question contains six statements followed by four sets of combination of three. Choose the set in which the statements are logically related.
Statements:
(i) All mangoes are fruits.
(ii) All mangoes are green.
(iii) All mangoes are oval shaped.
(iv) All fruits are sweet.
(v) All mangoes are sweet.
(vi) All fruits are expensive.
Statements:
(i) All mangoes are fruits.
(ii) All mangoes are green.
(iii) All mangoes are oval shaped.
(iv) All fruits are sweet.
(v) All mangoes are sweet.
(vi) All fruits are expensive.
B i, iv, v
As can be seen from the figure, “b” is correct.
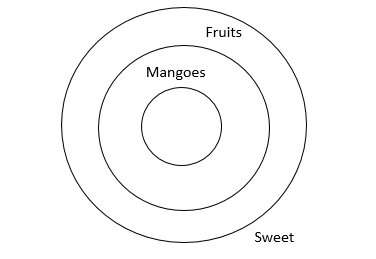
Question 9
Each question contains six statements followed by four sets of combination of three. Choose the set in which the statements are logically related.
Statements:
(i) All frogs are amphibians.
(ii) All amphibians are not frogs.
(iii) All amphibians are cold blooded.
(iv) All frogs lay eggs.
(v) All amphibians lay eggs.
(vi) Frogs are cold blooded.
Statements:
(i) All frogs are amphibians.
(ii) All amphibians are not frogs.
(iii) All amphibians are cold blooded.
(iv) All frogs lay eggs.
(v) All amphibians lay eggs.
(vi) Frogs are cold blooded.
A i, iii, vi
As can be seen from the figure, “a” is correct.
Question 10
Each question contains six statements followed by four sets of combination of three. Choose the set in which the statements are logically related.
Statements:
(i) Some men are of short- height.
(ii) Short-heighted men are intelligent.
(iii) Sudhir is a man.
(iv) Sudhir is of short-height.
(v) Sudhir is intelligent.
(vi) All men are intelligent.
Statements:
(i) Some men are of short- height.
(ii) Short-heighted men are intelligent.
(iii) Sudhir is a man.
(iv) Sudhir is of short-height.
(v) Sudhir is intelligent.
(vi) All men are intelligent.
C ii, iv, v
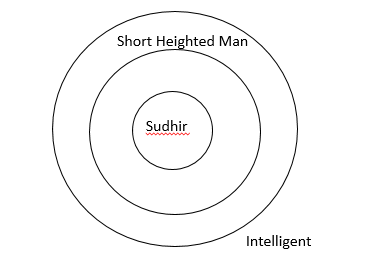
As can be seen from the figure, “c” is correct.
Question 11
Of the four alternatives given in each of the following questions, find the one which is different from the rest.
D Valley-Depth
All the other pairs are antonyms. In this the words are not antonyms.
Question 12
Of the four alternatives given in each of the following questions, find the one which is different from the rest.
C Eye-Ear
Ankle is an extension of foot, finger of wrist. Only choice “c” doesn’t share this relationship and so is the correct choice.
Question 13
Of the four alternatives given in each of the following questions, find the one which is different from the rest.
B Goat-Hen
Choices “a”, “c” and “d” are pair of animals that are hostile to each other, in fact the second animal is the prey of the first animal. This relationship does not exist in choice “b”.
Question 14
Each question below has two statements followed by four conclusions I, II, III and IV. You have to accept the given statements to be true, even if they appear to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the two statements:
Statement One:
All girls are students.
Statement Two:
All doctors are students.
Conclusions:
I. All girls are students.
II. Some students are girls.
III. Some students are doctors.
IV. All doctors are girls.
Statement One:
All girls are students.
Statement Two:
All doctors are students.
Conclusions:
I. All girls are students.
II. Some students are girls.
III. Some students are doctors.
IV. All doctors are girls.
D Only I and II and III follows.
This is a very simple question. Conclusions I, II and III, all could be drawn using a single statement. Option “d” has all three of them and is the correct choice.
Question 15
Each question below has two statements followed by four conclusions I, II, III and IV. You have to accept the given statements to be true, even if they appear to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the two statements:
Statement One:
All researchers are sociologists
Statement Two:
Some researchers are professors.
Conclusions:
I. All researchers are professors.
II. Some researchers are professors.
III. Some professors are sociologists.
IV. Some sociologists are researchers.
Statement One:
All researchers are sociologists
Statement Two:
Some researchers are professors.
Conclusions:
I. All researchers are professors.
II. Some researchers are professors.
III. Some professors are sociologists.
IV. Some sociologists are researchers.
B Only II and IV follow.
Use elimination technique in this question. Conclusion II is the repeat of the statement II so it has to be correct. Only option “b” has II as one of the conclusions and so this has to be the correct choice. You don’t have to check for any other conclusion.
Question 16
Each question below has two statements followed by four conclusions I, II, III and IV. You have to accept the given statements to be true, even if they appear to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the two statements:
Statement One:
Some democracies are dictatorship.
Statement Two:
No dictatorship is a monarchy.
Conclusions:
I. No democracy is a monarchy.
II. No dictatorship is a democracy.
III. Some democracies are monarchy.
IV. Some dictatorships are democracies.
Statement One:
Some democracies are dictatorship.
Statement Two:
No dictatorship is a monarchy.
Conclusions:
I. No democracy is a monarchy.
II. No dictatorship is a democracy.
III. Some democracies are monarchy.
IV. Some dictatorships are democracies.
B Only IV follows.
“IV” can be concluded from statement 1. So the answer has to be between “b” and “d”. So we will now check for conclusion I.
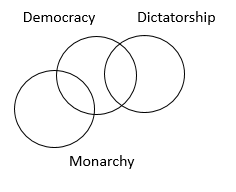
We can see from the figure that conclusion I cannot be drawn, so the correct answer will be “b”.

We can see from the figure that conclusion I cannot be drawn, so the correct answer will be “b”.
Question 17
The following questions comprise of one or more statements. Answer the questions on the basis of the given statement(s). Accept the factual assumptions required by the question, even if you believe that the statement is false.
Statements:
I. Cheese is bad for people with high-cholesterol.
II. Sumeet does not eat cheese.
Assuming that (i) and (ii) are true, which of the following statement follows?
Statements:
I. Cheese is bad for people with high-cholesterol.
II. Sumeet does not eat cheese.
Assuming that (i) and (ii) are true, which of the following statement follows?
D None of the above.
CLAT has given “c” as the correct answer. From the given statement we can conclude that, for people suffering from high – cholesterol , it is advisable not to eat cheese; but we cannot decide whether they are eating cheese or not.
Question 18
The following questions comprise of one or more statements. Answer the questions on the basis of the given statement(s). Accept the factual assumptions required by the question, even if you believe that the statement is false.
Statement:
I. Democrats are secularists.
Which of the following statements, if true, would show that the above statement is false?
Statement:
I. Democrats are secularists.
Which of the following statements, if true, would show that the above statement is false?
B My father is a democrat but he is not secularist.
This proves the given statement as false because from this we know that there is at least one democrat (my father) who is not a secularist.
Question 19
The following questions comprise of one or more statements. Answer the questions on the basis of the given statement(s). Accept the factual assumptions required by the question, even if you believe that the statement is false.
Statement:
“Where there is a cloud, there is a rain.”
Which of the following statements, if true, would show that the above statement is false?
Statement:
“Where there is a cloud, there is a rain.”
Which of the following statements, if true, would show that the above statement is false?
A Sometimes there is cloud, but there is no rain.
Two statements could prove this wrong – 'There was cloud but no rain', and 'There is no rain but there is cloud'.
The first is given in “a” and is the correct answer.
The first is given in “a” and is the correct answer.
Question 20
Who amongst the following friends is not good in Mathematics but good in Hindi?
A W
Using the information we can get the table as follows:
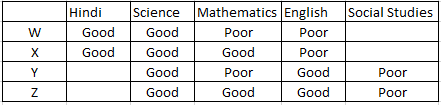

Question 21
Which of the following pairs of friends are good, both in English and Science?
C Y and Z
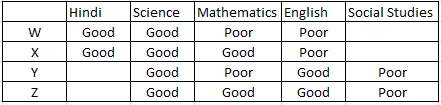
Y and Z are both good in English and Science.
Question 22
Which of the following statements is definitely true?
B All four friends are good in Science
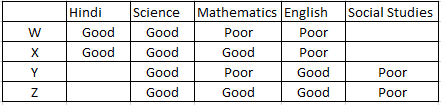
Only option “b” is correct that all four friends are good in Science.
Question 23
Select the statement which logically follows the two given statements.
Statements:
I. No athletes are vegetarians.
II. All players are athletes.
III. Therefore -------------
Statements:
I. No athletes are vegetarians.
II. All players are athletes.
III. Therefore -------------
A no players are vegetarians
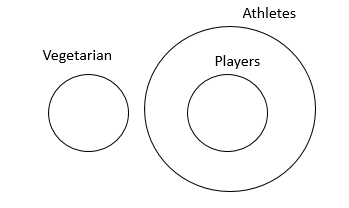
As can be seen from the figure “a” is correct.
Question 24
Select the statement which logically follows the two given statements.
Statements:
I. All persons who have done any creative work can be responsible critics
II. Z has not done any creative work
III. Therefore ---------------
Statements:
I. All persons who have done any creative work can be responsible critics
II. Z has not done any creative work
III. Therefore ---------------
B Z cannot be a responsible critic
As per the CLAT answer key “b” is the correct answer but we believe that it is not possible even to draw “b” as a conclusion (See diagram below).
Statement I can be interpreted as 'If creative work, then responsible critic' which can further be interpreted as 'All creative work is equal to responsible critic'.
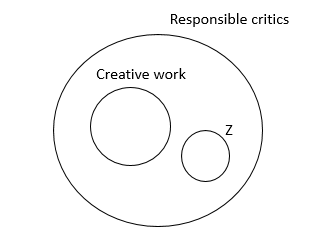
As we can see from the above figure, Z can still be a responsible critic despite his not having done any creative work.
Statement I can be interpreted as 'If creative work, then responsible critic' which can further be interpreted as 'All creative work is equal to responsible critic'.

As we can see from the above figure, Z can still be a responsible critic despite his not having done any creative work.
Question 25
Select the statement which logically follows the two given statements.
Statement:
I. One who has squared a circle is not a mathematician
II. Therefore ---------------
Statement:
I. One who has squared a circle is not a mathematician
II. Therefore ---------------
A No one who has squared a circle is a mathematician
Option A just rephrases the given statement. If A (One who has squared a circle) then not B (not a mathematician).
So it means No A = B.
So it means No A = B.
Question 26
Statement: The Supreme Court of India is encouraging Public Interest Litigation Reasons:
I. To increase the reach of justice to the disadvantaged sections of society
II. To quicken the pace of Justice
Identify the correct reason for the aforementioned statement.
I. To increase the reach of justice to the disadvantaged sections of society
II. To quicken the pace of Justice
Identify the correct reason for the aforementioned statement.
B I is the correct reason of the statement
Only I is correct - PILs have nothing to do with the pace of justice.
Question 27
Yoga has become a very popular exercise, but it may not be for everyone. If you are interested in high energy and fast workouts, yoga may not be the best choice. Therefore, evaluate your fitness requirement before joining yoga classes.
This paragraph best supports the statement that:
This paragraph best supports the statement that:
C Before opting for Yoga, assess your fitness requirements
Such questions are best solved using elimination technique.
Choice “a” is out as in the information provided no comparison is been made between yoga and high energy exercise in terms of popularity.
It is not mentioned that yoga is “changing“ the concept of fitness, so "b" can be eliminated.
Similarly, it does not say that yoga is a holistic fitness regime, so "d" can be ruled out.
“c” is the best choice as it is mentioned that one should evaluate his/her fitness requirement before joining yoga classes.
Choice “a” is out as in the information provided no comparison is been made between yoga and high energy exercise in terms of popularity.
It is not mentioned that yoga is “changing“ the concept of fitness, so "b" can be eliminated.
Similarly, it does not say that yoga is a holistic fitness regime, so "d" can be ruled out.
“c” is the best choice as it is mentioned that one should evaluate his/her fitness requirement before joining yoga classes.
Question 28
Statistics allows us to understand the reality. It indicates developmental directions. Statistics is good for exposing reality, but it can also be manipulated to perpetuate untruth and misunderstanding. Data has power to mislead people.
This paragraph best supports the statement that:
This paragraph best supports the statement that:
D Numbers can be used to mislead people.
From the phrase “it can also be manipulated to perpetuate untruth”, we can infer that numbers can be used to mislead people.
Question 29
Technology has developed out of stone tools which were used in ancient times. At first, development of new technology was slow, but after neo-liberal economic policy was adopted there has been a tremendous growth in technology sector.
This paragraph best supports the statement that:
This paragraph best supports the statement that:
C Today new technologies are developing at a fast pace
“At first, development …..was slow….there has been a tremendous growth in technology sector” – from this “c” can be inferred.
Question 30
Given below is a pair of events I and II. You have to decide their nature of relationship. Assume that the given information is correct and final.
I. Prices of toys in the market have gone down.
II. Government has reduced import duty on toys.
I. Prices of toys in the market have gone down.
II. Government has reduced import duty on toys.
C II. is the main cause and I is the main effect
To solve cause and effect question use a simple technique – just put therefore between the two sentences and see if the sentence makes sense.
Government has reduced import duty on toys, therefore, prices of toys in the market have gone down. So II is the main cause and I the effect.
Government has reduced import duty on toys, therefore, prices of toys in the market have gone down. So II is the main cause and I the effect.
Question 31
Given below is a pair of events I and II. You have to decide their nature of relationship. Assume that the given information is correct and final.
I. Inflation rate in India has come down
II. Reserve Bank of India has increased interest rate.
I. Inflation rate in India has come down
II. Reserve Bank of India has increased interest rate.
C II. is the main cause and I is the main effect
To solve cause and effect question use a simple technique – just put therefore between the two sentences and see if the sentence makes sense.
Reserve Bank of India has increased interest rate, therefore, inflation rate in India has come down. (Since, with higher interest rate there is less money supply which leads to a reduction in inflation rate. Even if you don’t know this much the information provided was sufficient to identify a cause and effect relationship between the two sentences.)
So II is the main cause and I is the effect.
Reserve Bank of India has increased interest rate, therefore, inflation rate in India has come down. (Since, with higher interest rate there is less money supply which leads to a reduction in inflation rate. Even if you don’t know this much the information provided was sufficient to identify a cause and effect relationship between the two sentences.)
So II is the main cause and I is the effect.
Question 32
Given below is a pair of events I and II. You have to decide their nature of relationship. Assume that the given information is correct and final.
I. More and more students are opting for legal education
II. Bar Council of India has introduced Bar Examination
I. More and more students are opting for legal education
II. Bar Council of India has introduced Bar Examination
D II. is an effect but I is not the main cause
To solve cause and effect question use a simple technique – just put therefore between the two sentences and see if the sentence makes sense.
There is no apparent cause and effect relationship between I and II.
So either “b” or “d” could be the correct answer.
As per the official key “d” was the correct answer.
There is no apparent cause and effect relationship between I and II.
So either “b” or “d” could be the correct answer.
As per the official key “d” was the correct answer.
Question 33
Given below is a pair of events I and II. You have to decide their nature of relationship. Assume that the given information is correct and final.
I. Sea level is steadily rising
II. Global Warming is a serious problem which the world is facing
I. Sea level is steadily rising
II. Global Warming is a serious problem which the world is facing
C II. is the main cause and I is the main effect
To solve cause and effect question use a simple technique – just put therefore between the two sentences and see if the sentence makes sense.
Global Warming is a serious problem which the world is facing, therefore, sea level is steadily rising.
So II is the main cause and I the effect.
Global Warming is a serious problem which the world is facing, therefore, sea level is steadily rising.
So II is the main cause and I the effect.
Question 34
Given below is a pair of events I and II. You have to decide their nature of relationship. Assume that the given information is correct and final.
I. Financial Institutions are largely unregulated
II. Today, world is passing through a serious phase of economic crisis
I. Financial Institutions are largely unregulated
II. Today, world is passing through a serious phase of economic crisis
A I. is the main cause and II is the main effect
To solve cause and effect question use a simple technique – just put therefore between the two sentences and see if the sentence makes sense.
Financial Institutions are largely unregulated, therefore, today, world is passing through a serious phase of economic crisis.
So I is the main cause and II the effect.
Financial Institutions are largely unregulated, therefore, today, world is passing through a serious phase of economic crisis.
So I is the main cause and II the effect.
Question 35
An argument is given below, on the basis of that argument; find out the parallel argument from the given list of subsequent arguments
Argument: Himalayan Sparrows are disappearing. This bird is an Indian bird; therefore, Indian birds are disappearing.
Subsequent Arguments:
Argument: Himalayan Sparrows are disappearing. This bird is an Indian bird; therefore, Indian birds are disappearing.
Subsequent Arguments:
C Snow tigers are an endangered species; all endangered species must be protected; therefore snow-tiger must be protected
The argument could be broken into A (Himalayan sparrows) is a subset of B (disappearing), A is C (Indian bird), and therefore B is C.
DO NOT invest you time in figuring out whether this is a correct argument or not.
You just have to identify a choice that exhibits a similar relationship.
That relationship can be seen in choice “c”. A (Snow tigers) is subset of B (endangered species), B is a subset of C and so A is a subset of C.
DO NOT invest you time in figuring out whether this is a correct argument or not.
You just have to identify a choice that exhibits a similar relationship.
That relationship can be seen in choice “c”. A (Snow tigers) is subset of B (endangered species), B is a subset of C and so A is a subset of C.
Question 36
Each question below is followed by arguments. Choose the most appropriate choice from the options given
Question: Should Judicial Activism be discouraged?
Argument I: No, it would lead to executive dictatorship
Argument II: Yes, Judiciary should stay in the constitutional limits
Question: Should Judicial Activism be discouraged?
Argument I: No, it would lead to executive dictatorship
Argument II: Yes, Judiciary should stay in the constitutional limits
D Both the arguments are weak
In both I and II sufficient ground is not covered, therefore they are weak arguments.
For instance, I is arbitrary and an exaggeration since no reason is given as to how it will lead to executive dictatorship. Same is the case with II.
For instance, I is arbitrary and an exaggeration since no reason is given as to how it will lead to executive dictatorship. Same is the case with II.
Question 37
Each question below is followed by arguments. Choose the most appropriate choice from the options given
Question: Should the Judiciary be independent of Executive and Legislature?
Argument I: Yes, this is necessary to ensure impartiality in the administration of Justice
Argument II: No, it will develop inertia in Executive and Legislature
Question: Should the Judiciary be independent of Executive and Legislature?
Argument I: Yes, this is necessary to ensure impartiality in the administration of Justice
Argument II: No, it will develop inertia in Executive and Legislature
A Argument I is strong
Impartial Judiciary is the cornerstone of democracy. Courts should not be subject to improper influence from the other branches of government or from private or partisan interests.
Question 38
Each question below is followed by arguments. Choose the most appropriate choice from the options given
Question: Should E-Governance be introduced at every level of public administration?
Argument I: Yes, it will reduce corruption
Argument II: No, it will lead to unemployment
Question: Should E-Governance be introduced at every level of public administration?
Argument I: Yes, it will reduce corruption
Argument II: No, it will lead to unemployment
A Argument I is strong
E-governance will ensure that the government is transparent in its dealings, is accountable for its activities and is faster in its responses as part of good governance.
II is weak, the use of technology most times leads to reduction in employment in that area but it also leads to efficiency and creates employment in other areas. It just leads to reallocation of resources.
As per CLAT answer key the correct answer is “c”.
II is weak, the use of technology most times leads to reduction in employment in that area but it also leads to efficiency and creates employment in other areas. It just leads to reallocation of resources.
As per CLAT answer key the correct answer is “c”.
Question 39
Each question below is followed by arguments. Choose the most appropriate choice from the options given
Question: Should there be a world Government?
Argument I: Yes, it will eliminate inter-state conflicts
Argument II: No, Rich and Powerful countries will dominate it
Question: Should there be a world Government?
Argument I: Yes, it will eliminate inter-state conflicts
Argument II: No, Rich and Powerful countries will dominate it
B Argument II is strong
World government will lead to dominance of rich powerful and developed countries. Every country will strive for concentration of power and conquer the world.
Question 40
“Some philosophers believe that a concept which cannot be verified can still be valid because of its inner logic which ennobles it.”
In the light of the above statement, decide the status of the statement given below.
Statement: “Every person has certain inherent and inalienable rights which must be protected by Rule of Law.”
In the light of the above statement, decide the status of the statement given below.
Statement: “Every person has certain inherent and inalienable rights which must be protected by Rule of Law.”
A True
Recognition of the inherent dignity and of the equal and inalienable rights of all members of the human family is the foundation of freedom, justice and peace in the world. Everyone has the right to life, liberty and security of person which must be protected by Rule of Law.
Section: Legal Aptitude
Question 1
Principle: Only Parliament or State Legislatures have the authority to enact laws on their own. No law made by the State can take away a person’s fundamental right.
Facts: Parliament enacted a law, which according to a group of lawyers is violating the fundamental rights of traders. A group of lawyers files a writ petition challenging the Constitutional validity of the statute seeking relief to quash the statute and further direct Parliament to enact a new law.
Facts: Parliament enacted a law, which according to a group of lawyers is violating the fundamental rights of traders. A group of lawyers files a writ petition challenging the Constitutional validity of the statute seeking relief to quash the statute and further direct Parliament to enact a new law.
C The court can quash the existing law if it violates fundamental rights but cannot direct Parliament to make a new law.
The court can quash the existing law if it violates fundamental rights but cannot direct Parliament to make a new law. Law making power lies solely with the parliament and parliament is not supposed to take orders of the court in its law making process. Courts are the custodian of rights and interpreter of laws.
Question 2
Principle: When one person signifies to another his willingness to do or abstain from doing anything, with a view to obtaining the assent of that person to such an act or abstinence, he is said to have made a proposal.
Fact: “Ramanuj telegraphed to Shyam Sunder, writing: “Will you sell me your Rolls Royce CAR? Telegram the lowest cash price.” Shyam Sunder also replied by telegram: “Lowest price for CAR is Rs. 20 lakh.” Ramanuj immediately sent his consent through telegram stating: “I agree to buy the CAR for Rs. 20 lakh asked by you.” Shyam Sunder refused to sell the car.
Fact: “Ramanuj telegraphed to Shyam Sunder, writing: “Will you sell me your Rolls Royce CAR? Telegram the lowest cash price.” Shyam Sunder also replied by telegram: “Lowest price for CAR is Rs. 20 lakh.” Ramanuj immediately sent his consent through telegram stating: “I agree to buy the CAR for Rs. 20 lakh asked by you.” Shyam Sunder refused to sell the car.
C It was not a valid offer because willingness to enter into a contract was absent
The principle clearly states that for a proposal to be made, you need to signal to the other party your willingness to do or abstain from doing something. Here Shyam Sunder replied by just providing the lowest car price. Shyam Sunder providing that does not in any way signify that he was willing to sell the car. All he did was inform Ramanauj about the lowest price. It was not a valid offer because willingness to enter into a contract was absent.
Question 3
Principle: Every person, who is of the age of majority, is competent to contract according to the law to which he is subject.
Facts: A minor mortgaged his house in favour of Thakur Das, a money lender, to secure a loan of Rs. 20000. A part of this, i.e. Rs. 10500 was actually advanced to him. While considering the proposed advance, the attorney who was acting for the money lender, received information that the plaintiff was still a minor. Subsequently the minor commenced an action stating that he was underage when he executed the mortgage and the same should, therefore, be cancelled. He prayed for setting aside the mortgage. The mortgagee money lender prayed for the refund of Rs. 10500 from the minor.
Facts: A minor mortgaged his house in favour of Thakur Das, a money lender, to secure a loan of Rs. 20000. A part of this, i.e. Rs. 10500 was actually advanced to him. While considering the proposed advance, the attorney who was acting for the money lender, received information that the plaintiff was still a minor. Subsequently the minor commenced an action stating that he was underage when he executed the mortgage and the same should, therefore, be cancelled. He prayed for setting aside the mortgage. The mortgagee money lender prayed for the refund of Rs. 10500 from the minor.
B A minor’s contract is void ab initio, any money advanced to a minor cannot be recovered.
The principle quite clearly states that only those people are competent to contract who have attained the age of majority. Therefore all contracts made by minors are invalid from the outset, i.e. they are void ab initio. If a contract is void ab initio that would mean that neither party has to fulfill any promises that have been made. Therefore the minor does not have to fulfil any obligation to Thakur Das. Therefore the correct answer is (b).
Question 4
Principle: A person is said to be of sound mind for the purpose of making a contract if, at the time when he makes it, he is capable of understanding it and of forming a rational judgment as to its effect upon his interests.
Facts: Mr. X who is usually of sound state of mind, but occasionally of unsound state of mind, enters into a contract with Mr. Y when he was of unsound state of mind. Mr. Y having come to know about this fact afterwards, wants to file a suit against Mr. X
Facts: Mr. X who is usually of sound state of mind, but occasionally of unsound state of mind, enters into a contract with Mr. Y when he was of unsound state of mind. Mr. Y having come to know about this fact afterwards, wants to file a suit against Mr. X
A Mr. X cannot enter into contract because he is of unsound state of mind when he entered into contract.
A cannot enter into contract because he is of unsound mind, when he entered into contract and there is no question of proving the validity of an agreement which is declared void ab initio.
Question 5
Principle:
(1) The state shall not deny to any person equality before the law and equal protection of the laws within the territory of India.
(2) The State shall not discriminate against any citizen on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex and place of birth or any of them.
Facts: The Government of Rajasthan, passed an order providing for reservations for the Scheduled Castes/ Scheduled Tribes and Socially and Educationally Backward Classes (including Muslims), and Women, in all institutions of higher education, including private educational institutions, both aided as well as unaided, in the following manner: Scheduled Caste- 15%; Scheduled Tribe- 7.5%, Socially and Educationally Backward Classes (including Muslims) - 27%
I. The reservation policy of the government is violative of the principle of equality envisaged in the Constitution
II. The reservation policy is unconstitutional because it is based on ‘caste’ which is a prohibited marker
III. Reservation does not violate equality clause as it entails “like should be treated like and unlike should be treated differently.”
IV. Reservation does not violate equality clause as the Constitution itself enables the State to make special provision for the advancement of socially and educationally backward classes of citizens or for the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
(1) The state shall not deny to any person equality before the law and equal protection of the laws within the territory of India.
(2) The State shall not discriminate against any citizen on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex and place of birth or any of them.
Facts: The Government of Rajasthan, passed an order providing for reservations for the Scheduled Castes/ Scheduled Tribes and Socially and Educationally Backward Classes (including Muslims), and Women, in all institutions of higher education, including private educational institutions, both aided as well as unaided, in the following manner: Scheduled Caste- 15%; Scheduled Tribe- 7.5%, Socially and Educationally Backward Classes (including Muslims) - 27%
I. The reservation policy of the government is violative of the principle of equality envisaged in the Constitution
II. The reservation policy is unconstitutional because it is based on ‘caste’ which is a prohibited marker
III. Reservation does not violate equality clause as it entails “like should be treated like and unlike should be treated differently.”
IV. Reservation does not violate equality clause as the Constitution itself enables the State to make special provision for the advancement of socially and educationally backward classes of citizens or for the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
D III and IV both are correct answers
Right to equality is not absolute in nature. Constitution itself enables the State to make special provision for the advancement and upliftment of socially and educationally backward classes of citizens or for the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
Question 6
Principle: Nothing is an offence merely by reason of its being done with the knowledge that it is likely to cause harm, if it be done without any criminal intention to cause harm, and in good faith for the purpose of preventing or avoiding other harm to a person or property.
Facts: Mr. Sharman, the Captain of a steam vessel, suddenly and without any fault or negligence on his part, finds himself in such a position that, before he can stop his vessel, he must inevitably run down a boat B, with twenty or thirty passengers on board, unless he changes the course of his vessel, and that, by changing his course, he must incur the risk of running down a boat C with only two passengers on board and which he may possibly clear.
Facts: Mr. Sharman, the Captain of a steam vessel, suddenly and without any fault or negligence on his part, finds himself in such a position that, before he can stop his vessel, he must inevitably run down a boat B, with twenty or thirty passengers on board, unless he changes the course of his vessel, and that, by changing his course, he must incur the risk of running down a boat C with only two passengers on board and which he may possibly clear.
A Sharman has committed no offence because this was done out of necessity
Amongst the given options, (b) is alluring but (a) is the most appropriate option as it directly and strictly corresponds to the principle which lays down that if a person commits an act causing damage in order to prevent a greater harm, he is not liable in tort.
Question 7
Principle: Willful rash driving is an offense.
Facts: Mr. Tiwari was driving his car after drinking alcohol. Police books him for willful negligent driving. Is the act of the police lawful?
Facts: Mr. Tiwari was driving his car after drinking alcohol. Police books him for willful negligent driving. Is the act of the police lawful?
A No, because Mr. Tiwari was not driving rashly; he was drunk while driving.
Drunken driving may amount to negligent driving but a person who drives in delirious state of mind cannot be said to have driven ‘rash’.
Question 8
Principle: Whoever, intending to take dishonestly any movable property out of the possession of any person without that person’s consent, moves that property with an intention to take it, is said to commit theft.
Facts: Y cuts down a tree on Z’s ground, with the intention of dishonestly taking it out of Z’s possession without Z’s consent. Y could not take away the tree.
Facts: Y cuts down a tree on Z’s ground, with the intention of dishonestly taking it out of Z’s possession without Z’s consent. Y could not take away the tree.
A Y can be prosecuted for theft
On reading the principle the following things can be ascertained; in order to commit theft you must
(i) intend to take dishonestly any movable property out of the possession of any person;
(ii) without that person’s consent, move that property with an intention to take it.
Here both the ingredients of theft are satisfied, Y has been able to move the tree by cutting it. Moving the property in order to take it is an essential ingredient as provided by the principle. Therefore the correct answer is (a).
(i) intend to take dishonestly any movable property out of the possession of any person;
(ii) without that person’s consent, move that property with an intention to take it.
Here both the ingredients of theft are satisfied, Y has been able to move the tree by cutting it. Moving the property in order to take it is an essential ingredient as provided by the principle. Therefore the correct answer is (a).
Question 9
Principle: Injuria Sine Damnum i.e. Injury (violation of legal right) without damage
Facts: X, who was the returning officer at a polling booth in Amethi, wrongly refused to register a duly tendered vote of Y in the recent UP elections, even though Y was an eligible voter. The candidate in whose favour Y wanted to vote, was declared elected.
Give the appropriate answer-
Facts: X, who was the returning officer at a polling booth in Amethi, wrongly refused to register a duly tendered vote of Y in the recent UP elections, even though Y was an eligible voter. The candidate in whose favour Y wanted to vote, was declared elected.
Give the appropriate answer-
C Y cannot sue X because there is no injury or damage caused to Y
Right to vote is legal right which has been violated. Even if no damage has been caused to Y still he can sue since injuria has been caused to Y. Injuria here means violation of legal right
Question 10
Principle: Nothing is an offence which is done by a person who, at the time of doing it, by reason of unsound state of mind, is incapable of knowing the nature of the act, or something that he is doing is either wrong or contrary to law.
Fact: X takes his son Y who is three years old, for bathing to the well. He throws his son inside the well so that the son can have a good bath. After 10 minutes he also jumps into the well to take bath and get his son out of the well. Both were rescued by the villagers but his son was found dead.
Fact: X takes his son Y who is three years old, for bathing to the well. He throws his son inside the well so that the son can have a good bath. After 10 minutes he also jumps into the well to take bath and get his son out of the well. Both were rescued by the villagers but his son was found dead.
C X has done no offence as he can plead the defense of unsound state of mind
In the given facts, A takes his three year old for a bath and ‘throws his son’ inside the well. Although it is nowhere mentioned in the facts that A was of unsound mind, we can assume the same as no prudent man would throw a three year old into the well for a bath. This should have been taken as a hint and hence option (c) becomes the most appropriate answer.
Question 11
Principle: Ignorance of Fact is excused but ignorance of law is no excuse
Fact: X was a passenger from Zurich to Manila in a Swiss Plane. When the plane landed at the Airport of Bombay on 28 Nov. 1962 it was found on searching that X carried 34 kg of Gold Bars on his person and that he had not declared it in the ‘Manifest for Transit’. On 26th Nov. 1962 the Government of India had issued a notification modifying its earlier exemption, making it mandatory now that the gold must be declared in the “Manifest” of the aircraft.
Fact: X was a passenger from Zurich to Manila in a Swiss Plane. When the plane landed at the Airport of Bombay on 28 Nov. 1962 it was found on searching that X carried 34 kg of Gold Bars on his person and that he had not declared it in the ‘Manifest for Transit’. On 26th Nov. 1962 the Government of India had issued a notification modifying its earlier exemption, making it mandatory now that the gold must be declared in the “Manifest” of the aircraft.
C X can be prosecuted because ignorance of law is not excusable
Ignorantia juris non excusat: Ignorance of law is not an excuse. However, this piece of information will not have any bearing on the answer as the fact remains that George was ignorant of the new law. There is no exception given (and otherwise also) to this rule. Hence, option (c) is the most appropriate answer.
Question 12
Principle: Proposal (communication) + Acceptance (communication) + Consideration = Contract. The communication of a proposal is complete when it comes to the knowledge of the person to whom it is made.
Facts: X’s nephew absconded from home. He sent his servant in search of the boy.
After the servant had left, X by handbills offered to pay Rs. 501 to anybody finding his nephew. The servant came to know of this offer only after he had already traced the missing child. He, therefore, brought an action to recover the reward.
Facts: X’s nephew absconded from home. He sent his servant in search of the boy.
After the servant had left, X by handbills offered to pay Rs. 501 to anybody finding his nephew. The servant came to know of this offer only after he had already traced the missing child. He, therefore, brought an action to recover the reward.
A His action would fail because he was not aware of the offer
Communication of a proposal is complete when it comes to the knowledge of the person to whom it is made. And this becomes the relevant question after reading the facts. In this case, the servant came to know of the offer only after he had already traced the missing child. He had no knowledge about the proposal as there was no communication of it. Another important ingredient that is missing here is the servants’ acceptance. The contract is, therefore, not complete. Hence Option (a) is the most appropriate.
Question 13
Principle: Agreements, the meaning of which is not certain, or not capable of being made certain, are void.
Facts: A horse was bought for a certain price coupled with a promise to give Rs.500 more if the horse is proved lucky.
Facts: A horse was bought for a certain price coupled with a promise to give Rs.500 more if the horse is proved lucky.
B This agreement is void for uncertainty because it is very difficult to determine what luck, bad or good, the horse has brought to the buyer.
This agreement is void for uncertainty because it is very difficult to determine what luck, bad or good, the horse has brought to the buyer. In light of the given principle, the agreement is absolutely void and unenforceable. Such types of agreements are considered as ‘a matter of chance which may or may not happen’ are uncertain and therefore not encouraged in law.
Question 14
Principle: Mere silence as to the facts likely to affect the willingness of a person to enter into a contract is not a fraud, unless the circumstances of the case are such that, on close examination it is found to be the duty of the person keeping silent to speak, or unless his silence is, in itself, equivalent to speech.
Facts: X sells by auction to Y, a horse which X knows to be of unsound state of mind. X says nothing to Y about the horse’s unsound state of mind. Give the correct answer-
Facts: X sells by auction to Y, a horse which X knows to be of unsound state of mind. X says nothing to Y about the horse’s unsound state of mind. Give the correct answer-
C X cannot be held liable, because he did not say anything positive about the mental state of the horse.
‘X’ cannot be held liable as he never said overtly about the horse nor he was under any such circumstances that his silence would have amounted to fraud.
Question 15
Principle: Any direct physical interference with goods in somebody’s possession without lawful justification is called trespass of goods.
Facts: Z purchased a car from a person who had no title to it and sent it to a garage for repair. X believing wrongly that the car was his, removed it from the garage.
Facts: Z purchased a car from a person who had no title to it and sent it to a garage for repair. X believing wrongly that the car was his, removed it from the garage.
B X cannot be held responsible for trespass of goods as he was under a wrong belief.
Apply the given principle strictly, X has committed tortious wrong/trespass to goods as he interefered with goods in somebody’s possession. Mistaken belief is not a lawful justification in torts.
Question 16
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): A void contract is not necessarily illegal
Reason (R): Every illegal contract is void.
Assertion (A): A void contract is not necessarily illegal
Reason (R): Every illegal contract is void.
A Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Every illegal contract is void but a void contract is not necessarily illegal.
Question 17
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): The Indian Constitution was adopted on 26th November, 1949.
Reason (R): Law Day is celebrated in India on 26th November every year.
Assertion (A): The Indian Constitution was adopted on 26th November, 1949.
Reason (R): Law Day is celebrated in India on 26th November every year.
A Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Since the Indian Constitution was adopted on 26th November, 1949 therefore Law Day is celebrated in India on 26th November every year.
Question 18
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): The state shall not make any law, which takes away or abridges the rights conferred by Part III (Fundamental Rights) and any law made in contravention of this clause shall, to the extent of the contravention, be void.
Reason (R): The fundamental rights are the rights reserved by the people and for this reason they are eternal and sacrosanct.
Assertion (A): The state shall not make any law, which takes away or abridges the rights conferred by Part III (Fundamental Rights) and any law made in contravention of this clause shall, to the extent of the contravention, be void.
Reason (R): The fundamental rights are the rights reserved by the people and for this reason they are eternal and sacrosanct.
A Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
The state shall not make any law, which takes away or abridges the rights conferred by Part III (Fundamental Rights) and any law made in contravention of this clause shall, to the extent of the contravention, be void. The fundamental rights are the rights reserved by the people and for this reason they are eternal and sacrosanct.
Question 19
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): Directive Principles of State Policy contained in Part IV shall not be enforceable by any court, but the principles therein laid down are nevertheless fundamental in the governance of the country and it shall be the duty of the State to apply these principles in making laws.
Reason (R): Directive Principles of State Policy and Fundamental Rights are both complementary to each other but in case of any controversy fundamental rights will prevail.
Assertion (A): Directive Principles of State Policy contained in Part IV shall not be enforceable by any court, but the principles therein laid down are nevertheless fundamental in the governance of the country and it shall be the duty of the State to apply these principles in making laws.
Reason (R): Directive Principles of State Policy and Fundamental Rights are both complementary to each other but in case of any controversy fundamental rights will prevail.
A Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
DPSP are fundamental in the governance of the country and it shall be the duty of the State to apply these principles in making laws. Directive Principles of State Policy and Fundamental Rights are both complementary to each other but in case of any controversy fundamental rights will prevail.
Question 20
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): All minorities, whether based on religion or language, shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
Reason (R): Institutions established by the minorities are not entitled to governmental aid and government is not under an obligation to give aid.
Assertion (A): All minorities, whether based on religion or language, shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
Reason (R): Institutions established by the minorities are not entitled to governmental aid and government is not under an obligation to give aid.
C A is true but R is false
All minorities, whether based on religion or language, shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice. Institutions established by the minorities are entitled to governmental aid and government is under an obligation to give aid.
Question 21
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): The right to move the Supreme Court under Article 32 of the Constitution by appropriate proceedings for the enforcement of the fundamental rights is guaranteed as a fundamental right.
Reason (R): Supreme Court of India has been appointed as the guardian of the Constitution.
Assertion (A): The right to move the Supreme Court under Article 32 of the Constitution by appropriate proceedings for the enforcement of the fundamental rights is guaranteed as a fundamental right.
Reason (R): Supreme Court of India has been appointed as the guardian of the Constitution.
A Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Since, Supreme Court of India has been appointed as the guardian of the Constitution. The right to move the Supreme Court under Article 32 of the Constitution by appropriate proceedings for the enforcement of the fundamental rights is guaranteed as a fundamental right.
Question 22
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): If the budget presented to the Rajya Sabha in not passed in the stipulated period, the budget proposals are not affected.
Reason (R): The Lok Sabha is more powerful, in financial matters, than the Rajya Sabha.
Assertion (A): If the budget presented to the Rajya Sabha in not passed in the stipulated period, the budget proposals are not affected.
Reason (R): The Lok Sabha is more powerful, in financial matters, than the Rajya Sabha.
A Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Lok Sabha is more powerful, in financial matters, than the Rajya Sabha. Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 23
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): In the Event of violation of any legal right (tort) the aggrieved party is entitled to recover unliquidated damages.
Reason (R): The object of awarding damages to the aggrieved party is to put him in the same position in which he would have been if the wrong would not have been committed. Damages are therefore, assessed on that basis.
Assertion (A): In the Event of violation of any legal right (tort) the aggrieved party is entitled to recover unliquidated damages.
Reason (R): The object of awarding damages to the aggrieved party is to put him in the same position in which he would have been if the wrong would not have been committed. Damages are therefore, assessed on that basis.
A Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A. Since, the object of awarding damages to the aggrieved party is to put him in the same position in which he would have been if the wrong would not have been committed therefore in the event of violation of any legal right (tort) the aggrieved party is entitled to recover unliquidated damages.
Question 24
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): During inflation, there is increase in money supply and rise in price level.
Reason (R): The rise in prices is due to shortage in supply of essential consumer goods.
Assertion (A): During inflation, there is increase in money supply and rise in price level.
Reason (R): The rise in prices is due to shortage in supply of essential consumer goods.
A Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
There is increase in money supply and rise in price level due to shortage in supply of essential consumer goods. Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 25
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): X, because of unsound state of mind and not knowing the nature of the act, attacks Y, who in self defense and in order to ward off the attack hits him thereby injuring him. Y has not committed an offence.
Reason (R): Y had a right of private defense against X under Section 98 of the Indian Penal Code.
Assertion (A): X, because of unsound state of mind and not knowing the nature of the act, attacks Y, who in self defense and in order to ward off the attack hits him thereby injuring him. Y has not committed an offence.
Reason (R): Y had a right of private defense against X under Section 98 of the Indian Penal Code.
A Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Right of self defence is available even against those persons who would have been otherwise not liable because their act falls within the exceptions provided in IPC therefore, both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 26
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): X and Y independently entertained the idea to kill Z. Accordingly; each of them separately inflicted wounds on Z who died as a consequence. X and Y are liable for murder under 34 IPC.
Reason (R): When a criminal act is done by several persons in furtherance of common intention of all, each of such persons is liable as if the whole act was done by him alone.
Assertion (A): X and Y independently entertained the idea to kill Z. Accordingly; each of them separately inflicted wounds on Z who died as a consequence. X and Y are liable for murder under 34 IPC.
Reason (R): When a criminal act is done by several persons in furtherance of common intention of all, each of such persons is liable as if the whole act was done by him alone.
D A is false but R is true
As per section 34 of Indian Penal Code, when a criminal act is done by several persons in furtherance of common intention of all, each of such persons is liable as if the whole act was done by him alone but in the given case, X and Y independently entertained the idea to kill Z therefore they will not be liable under the principle of common intention.
Question 27
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): A person claims compensation for his non-gratuitous act.
Reason (R): A person who enjoys benefit from lawful, non-gratuitous act of another must compensate him even though there is no contract.
Assertion (A): A person claims compensation for his non-gratuitous act.
Reason (R): A person who enjoys benefit from lawful, non-gratuitous act of another must compensate him even though there is no contract.
A Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Since, a person claims compensation for his non-gratuitous act therefore, a person who enjoys benefit from lawful, non-gratuitous act of another must compensate him even though there is no contract. Such instances fall under the principle of Quasi Contract.
Question 28
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): Freedom of Speech is the most important civil liberty of people in a democratic polity.
Reason (R): State can regulate free speech in the interest of public order.
Assertion (A): Freedom of Speech is the most important civil liberty of people in a democratic polity.
Reason (R): State can regulate free speech in the interest of public order.
B Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of A
Freedom of speech is the most important civil liberty of people in a democratic polity however, State can regulate free speech in the interest of public order. Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 29
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): Austin’s concept of law is known as imperative theory
Reason (R): Austin emphasized on the commanding character of law.
Assertion (A): Austin’s concept of law is known as imperative theory
Reason (R): Austin emphasized on the commanding character of law.
A Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Imperative theory is based on the premise of commanding character of law and John Austin propounded this theory.
Question 30
Instructions (166 to 180): Each of the next nine questions consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Assertion’ (A) and other as ‘Reason’ (R). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answers.
Assertion (A): The essence of joint liability under section 149 of the IPC is that the criminal act must have been done with a view to fulfil the common object of an unlawful assembly.
Reason (R): Any sudden and provocative act done by a member of an unlawful assembly would render the other members of that assembly liable.
Assertion (A): The essence of joint liability under section 149 of the IPC is that the criminal act must have been done with a view to fulfil the common object of an unlawful assembly.
Reason (R): Any sudden and provocative act done by a member of an unlawful assembly would render the other members of that assembly liable.
C A is true but R is false
Any sudden and provocative act done by a member of an unlawful assembly would not render the other members of that assembly liable rather in order for liability to arise under Section 149, the members of assembly must be aware of the purpose of such assembly. A is true but R is false.
Question 31
The following are enshrined in the Preamble of the Constitution of India
I. Equality of status and of opportunity
II. Liberty of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship
III. Justice-social, economic and political
IV. Fraternity assuring the dignity of the individual
V. Unity and Integrity of the nation
Which of the following is the correct order in which they appear in the preamble?
I. Equality of status and of opportunity
II. Liberty of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship
III. Justice-social, economic and political
IV. Fraternity assuring the dignity of the individual
V. Unity and Integrity of the nation
Which of the following is the correct order in which they appear in the preamble?
B III-II-I-IV-V
WE, THE PEOPLE OF INDIA, having solemnly resolved to constitute India into a [SOVEREIGN SOCIALIST SECULAR DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC] and to secure to all its citizens:
JUSTICE, social, economic and political;
LIBERTY of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship;
EQUALITY of status and of opportunity; and to promote among them all
FRATERNITY assuring the dignity of the individual and the [unity and integrity of the Nation];
JUSTICE, social, economic and political;
LIBERTY of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship;
EQUALITY of status and of opportunity; and to promote among them all
FRATERNITY assuring the dignity of the individual and the [unity and integrity of the Nation];
Question 32
Which one of the following statements is correct?
Right to free and compulsory education for all children of the age of 6 to 14 years is:
Right to free and compulsory education for all children of the age of 6 to 14 years is:
A a fundamental right enforceable in law
Right to free and compulsory education for all children of the age of 6 to 14 years is a fundamental right enforceable in law.
Question 33
Affirmative action connotes:
I. Measures taken by the state to help the socially disadvantaged groups
II. Positive discrimination
III. Strict quotas for the socially and educationally backward class in school/college admissions and jobs.
Which of the above mentioned is true?
I. Measures taken by the state to help the socially disadvantaged groups
II. Positive discrimination
III. Strict quotas for the socially and educationally backward class in school/college admissions and jobs.
Which of the above mentioned is true?
D II and III only
Positive discrimination as well as strict quotas for the socially and educationally backward class in school/college admissions and jobs.
Question 34
Identify the correct statement:
A Federalism implies a system of government which embodies a division of powers between a central and a number of regional authorities
Federalism implies a system of government which embodies a division of powers between a central and a number of regional authorities. Other options seems close but option (a) is most appropriate.
Question 35
Consider the following statements:
I. In a recent Supreme Court verdict pronounced by Justice Markandeya Katju and Justice Gyan Sudha Mishra, the court upheld the constitutionality of the Haj subsidy
II. Muslims are not the only beneficiaries of the secular state’s generosity. Hindus have also received substantial financial support from the Government
With reference to the statements mentioned above, which of the following is correct?
I. In a recent Supreme Court verdict pronounced by Justice Markandeya Katju and Justice Gyan Sudha Mishra, the court upheld the constitutionality of the Haj subsidy
II. Muslims are not the only beneficiaries of the secular state’s generosity. Hindus have also received substantial financial support from the Government
With reference to the statements mentioned above, which of the following is correct?
C Both I and II
Muslims are not the only beneficiaries of the secular state’s generosity. Hindus have also received substantial financial support from the Government.
Question 36
X, a married woman, agreed to live in adultery with B and also agreed to serve him as his housekeeper. In return, B agreed to pay X Rs. 500 per month for living in adultery and Rs. 500 per month for housekeeping. The agreement is
C Void as to the first object but valid with respect to the second object
The objective of first part of contract being adultery therefore it’s void but a contract for housekeeping is neither unlawful nor against public policy hence valid. Therefore, C is the most appropriate option.
Question 37
Ramu applied for the post of Director in an organization. The governing body of the organization passed a resolution appointing him to the post. After the meeting, one of the members of the governing body informed him privately of the resolution.
Subsequently, the resolution was rescinded. Ramu claims damages. Which one of the following is the correct legal proposition in the case?
Subsequently, the resolution was rescinded. Ramu claims damages. Which one of the following is the correct legal proposition in the case?
B Ramu cannot claim damages as there was no formal communication
Ramu cannot claim damages as there was no formal communication. Rescission of decision must have been communicated to Ramu through proper channel.
Question 38
The Railway authorities allowed a train to be over crowded. In consequence, a legitimate passenger Mr. X got his pocket picked. Choose the appropriate answer:
C Mr. X cannot sue railway authorities because there was no infringement of his legal right and mere fact that the loss was caused does not give rise to a cause of action
There is no correlation between allowing a train to be over crowded and pick pocketing as one is not the obvious consequence of other. Mr. X cannot sue railway authorities because there was no infringement of his legal right and mere fact that the loss was caused does not give rise to a cause of action
Question 39
Z is carried off by a tiger. X fires at the tiger, knowing that the shot might kill Z, but with no intention to kill Z, and in good faith trying to save Z. X’s shot, however, gives Z a mortal wound. Choose the correct option –
C X has not committed any offence, as the act was in good faith and for the benefit of Z.
Z is carried off by a tiger. X fires at the tiger knowing it to be likely that the shot may kill Z, but not intending to kill Z, and in good faith intending Z’s benefit.
X’s shot gives Z a mortal wound. Clearly A has committed no offence.
X’s shot gives Z a mortal wound. Clearly A has committed no offence.
Question 40
Ms. Usha wants to file a suit against Bhagyalaxmi Theatre praying for a permanent injunction (stay order) restraining the theatre from running the film named “Jai Santoshi Maa”. Her contention is that the film hurt her religious feelings and sentiments as Goddess Saraswati, Laxmi and Parvati were depicted as jealous and were ridiculed.
A She cannot file a suit because injury to religious feelings is not a legally recognized right.
She can file a suit as injury to religious feelings has been legally recognized as a right (injuria sine damnum)
Question 41
Match schedule one and two and choose the appropriate answer-
| Schedule I | Schedule II |
| i. Concurrent list | 1. Constitution of Japan |
| ii. Rule of Law | 2. Constitution of Ireland |
| iii. DIrective Principle of State Policy | 3. British Constitution |
| iv. Procedure established by law | 4. Constitution of Australia |
D i-4, ii-3, iii-2, iv-1
Our Constitution is a bag of borrowings. Moreover, Government of India Act, 1935 has also played a major role in the draft of the Constitution, since many provisions have been taken from this Act of 1935 as well.
Question 42
P, Q and R made a joint promise to give S a sum of Rs.3000. S recovered the whole amount from P. Q was declared insolvent and cannot give anything. Which statement out of the following is correct?
C P can recover Rs.1500 from R
Since, S has been declared insolvent, P can recover Rs.1500 from R
Question 43
X went to Y’s house and forgot his bag which contained 1 kg sweets. Y’s children consumed the sweets. Decide the liability of Y.
A Y is bound to pay the price of sweets to X
Y is bound to pay the price of sweets to X since Y’s children have consumed it he will have to compensate. Also that the consumption was without X’s consent and therefore the liability to pay arises.
Question 44
Which one of the following is not correct?
B Right to life and personal liberty includes right to carry on any trade and profession
Right to life and personal liberty is a Fundamental Right under Article 21 and does not includes right to carry on any trade and profession as it is distinct fundamental right under Article 19 of the Constitution of India.
Question 45
Y makes an attempt to steal some jewels by breaking open a box and finds, after opening the box, that there is no jewel in it. Choose the appropriate answer.
B Y is guilty of attempt to commit theft.
Y is guilty of attempt to commit theft.
Question 46
A lady wanted to get a railway ticket but finding a crowd near the ticket window at the station, asked Raju, who was near the window, to get a ticket for her and handed him money for the same. Raju took the money and instead of getting the ticket, ran away with it. What offence has been committed by Raju?
B Criminal breach of trust
Raju is liable of criminal breach of trust. Since the lady had herself entrusted money to Raju and whenever a person breaches trust he liable for the said offence.
Question 47
The Right to Equality is guaranteed by-
A Article 14 to 18
The Right to Equality is guaranteed under Articles 14 to 18 of the Constitution of India. Article 14 is the general while article 15 and 16 are exceptions in the form of positive discrimination and Article 17 and 18 provides for abolition of untouchability and tiles respectively which are also a form and manner of ensuring equality.
Question 48
Mr. Samay was severely hurt while working in his factory and fell unconscious. He was rushed to a hospital by his fellow workers. In the hospital (at emergency/casualty ward) the doctors opined that he should be operated immediately. While conducting preliminary examinations, he was found to be HIV positive. The doctors are in a dilemma regarding what should they do first-
A Doctors should operate first
It does not matter whether the patient was HIV positive, doctor should operate first.
Question 49
Match the schedule I and II and choose the appropriate answer-
Schedule I Schedule II
i Republic 1. Head of the state is elected by the people
ii Secular 2. State does not recognize any religion as religion of the state
iii Democracy 3. The government which gets authority from the will of the people
Schedule I Schedule II
i Republic 1. Head of the state is elected by the people
ii Secular 2. State does not recognize any religion as religion of the state
iii Democracy 3. The government which gets authority from the will of the people
A i-1, ii-2, iii-3
These are the features incorporated in the preamble of the Constitution.
Question 50
In which of the following cases can a Constitutional amendment be passed just by a simple majority in Parliament?
B Change in the name and boundaries of states
Change in the name and boundaries of states can be passed just by a simple majority in Parliament. It neither requires a special majority nor ratification of states.

