Section: Verbal Ability
Question 1
Directions: From each set of sentences given below in question 1 to 10, choose the sentence that is grammatically correct.
D A few judges have cut short their vacation to clear the long pending cases.
In this question elimination of options is the easiest approach.
In option (c) the singular verb ‘has’ is used with the plural noun ‘judges’, so this can be eliminated.
In option (b), the pronoun is missing before ‘vacation’, while in option (a) the article ‘a’ is used for plural noun ‘cases’ so these can be eliminated as well.
In option (c) the singular verb ‘has’ is used with the plural noun ‘judges’, so this can be eliminated.
In option (b), the pronoun is missing before ‘vacation’, while in option (a) the article ‘a’ is used for plural noun ‘cases’ so these can be eliminated as well.
Question 2
Directions: From each set of sentences given below in question 1 to 10, choose the sentence that is grammatically correct.
B Where's Hari? Here he is, right in front of us!
Use elimination of options:
Option (c): When asking ‘Where is Hari?’, it is common to abstract as “Where’s Hari?” and not “Wheres’ Hari?”. This choice can be eliminated.
The phrase ‘Here is he’ is wrong in option (a), while in option (d), this is posed incorrectly as a question ‘Is he here’. So these options can be eliminated as well.
Option (c): When asking ‘Where is Hari?’, it is common to abstract as “Where’s Hari?” and not “Wheres’ Hari?”. This choice can be eliminated.
The phrase ‘Here is he’ is wrong in option (a), while in option (d), this is posed incorrectly as a question ‘Is he here’. So these options can be eliminated as well.
Question 3
Directions: From each set of sentences given below in question 1 to 10, choose the sentence that is grammatically correct.
D Customs officers do not allow passengers to carry banned items into or out of the country.
In option (a), the possessive (officer’s) is wrongly used.
In option (b), the verb ‘does not allow’ is singular while its subject ‘officers’ is plural.
In option (c), the verb has been made plural incorrectly (do not allows).
The correct choice is (d).
In option (b), the verb ‘does not allow’ is singular while its subject ‘officers’ is plural.
In option (c), the verb has been made plural incorrectly (do not allows).
The correct choice is (d).
Question 4
Directions: From each set of sentences given below in question 1 to 10, choose the sentence that is grammatically correct.
A Neither this nor that machine is working.
In options (c) and (d) the conjunction is incorrect – instead of ‘neither-nor’ these have used ‘neither-and’ and ‘neither-but’ respectively.
In option (b), the verb form is incorrect – the verb should agree with the singular noun ‘machine’ and hence should be ‘is working’.
In option (b), the verb form is incorrect – the verb should agree with the singular noun ‘machine’ and hence should be ‘is working’.
Question 5
Directions: From each set of sentences given below in question 1 to 10, choose the sentence that is grammatically correct.
C I shall do an MBA online, and continue with my present job.
In options (a) and (b), the article ‘a’ has been used before a noun that begins with vowel sound (MBA), so these are incorrect.
In option (d), the conjunction ‘but’ has been incorrectly used as the second phrase is not opposing the first one.
In option (d), the conjunction ‘but’ has been incorrectly used as the second phrase is not opposing the first one.
Question 6
Directions: From each set of sentences given below in question 1 to 10, choose the sentence that is grammatically correct.
D As soon as I boarded the train, I realized that I had left my wallet at home.
In option (c), the first verb ‘board’ is in present tense while the second verb ‘realized’ is in the past tense. However, the second action either happens along with or just after the first one so this is clearly incorrect.
In option (b), this is in reverse i.e. the first verb ‘boarded’ is in past tense, while the second verb ‘realize’ is in present. So this too is incorrect.
In option (a), the third verb ‘left’ is in simple past and so are the first two verbs ‘boarded’ and ‘realized’. This seems to suggest that all these actions happened at the same time. However, the act of leaving the wallet must have happened in the earlier past, so we must use the past perfect tense ‘had left’.
In option (b), this is in reverse i.e. the first verb ‘boarded’ is in past tense, while the second verb ‘realize’ is in present. So this too is incorrect.
In option (a), the third verb ‘left’ is in simple past and so are the first two verbs ‘boarded’ and ‘realized’. This seems to suggest that all these actions happened at the same time. However, the act of leaving the wallet must have happened in the earlier past, so we must use the past perfect tense ‘had left’.
Question 7
Directions: From each set of sentences given below in question 1 to 10, choose the sentence that is grammatically correct.
D We can take either the morning flight or the one in the afternoon.
In options (a) and (b), the conjunction pairs (‘either-nor’ and ‘neither-or’)are incorrect.
In option (c), the singular countable nouns ‘flight’ and ‘afternoon’ are not accompanied by articles, so this construction is incorrect.
In option (c), the singular countable nouns ‘flight’ and ‘afternoon’ are not accompanied by articles, so this construction is incorrect.
Question 8
Directions: From each set of sentences given below in question 1 to 10, choose the sentence that is grammatically correct.
B The management has promised that it will consider my appeal.
In option (a), while the noun ‘management’ is used as a singular (see the pronoun ‘it’), yet the verb ‘have promised’ is in plural.
In option (c), the verb form in present perfect ‘has promise’ is incorrect – it should be ‘has promised’.
In option (d), the verb form in simple future tense ‘will considered’ is incorrect – it should be ‘will consider’.
In option (c), the verb form in present perfect ‘has promise’ is incorrect – it should be ‘has promised’.
In option (d), the verb form in simple future tense ‘will considered’ is incorrect – it should be ‘will consider’.
Question 9
Directions: From each set of sentences given below in question 1 to 10, choose the sentence that is grammatically correct.
C Tourists must follow the norms set by the country they visit.
In option (b), article ‘the’ is missing before the nouns ‘norms’ and ‘country’.
In option (a), the incorrect phrasal verb ‘set upon’ (which means “attack someone violently”) has been used.
In option (d) the last verb ‘visits’ is incorrect, as it does not agree with its singular subject ‘country’.
In option (a), the incorrect phrasal verb ‘set upon’ (which means “attack someone violently”) has been used.
In option (d) the last verb ‘visits’ is incorrect, as it does not agree with its singular subject ‘country’.
Question 10
Directions: From each set of sentences given below in question 1 to 10, choose the sentence that is grammatically correct.
D An important file, along with two uniforms, is missing from the police station.
In option (c), the article ‘An’ has been used along with the plural subject ‘files’, so this is clearly incorrect.
In option (b), the article ‘A’ has been used along with a noun-phrase (‘important file’) beginning with a vowel sound, so this too is incorrect.
In option (a), the verb ‘are missing’ does not agree with its singular subject ‘important file’. Note that the additive phrase ‘along with two uniforms’ does not affect the main subject in this sentence.
In option (b), the article ‘A’ has been used along with a noun-phrase (‘important file’) beginning with a vowel sound, so this too is incorrect.
In option (a), the verb ‘are missing’ does not agree with its singular subject ‘important file’. Note that the additive phrase ‘along with two uniforms’ does not affect the main subject in this sentence.
Question 11
Directions: In each of the questions given below in questions 11 to 15, each sentence is labelled with a letter. From the given choices, choose the most logical order of sentences that constructs a coherent paragraph.
a. One of them copied and pasted large portions of the required text from a website.
b. Before assigning the project to his students, the guide gave a presentation on plagiarism.
c. The expulsion order that followed was not alarming.
d. A few students did not pay much heed to the consequences of the illegal act.
a. One of them copied and pasted large portions of the required text from a website.
b. Before assigning the project to his students, the guide gave a presentation on plagiarism.
c. The expulsion order that followed was not alarming.
d. A few students did not pay much heed to the consequences of the illegal act.
D bdac
The pronoun ‘them’ in ‘a’ – One of them copied – refers to ‘a few students’ mentioned in‘ d’. So, ‘a’ must follow ‘d’ and this happens only in choice d. Hence, ‘d’ is the correct choice.
Question 12
Directions: In each of the questions given below in questions 11 to 15, each sentence is labelled with a letter. From the given choices, choose the most logical order of sentences that constructs a coherent paragraph.
a. Goals are set, and relevant data is collected and analyzed.
b. Strategies are made on the basis of the data and resources made available.
c. There are various stages in framing a management- strategy, and its implementation.
d. The strategies are implemented and monitored to ensure that the goals are achieved.
a. Goals are set, and relevant data is collected and analyzed.
b. Strategies are made on the basis of the data and resources made available.
c. There are various stages in framing a management- strategy, and its implementation.
d. The strategies are implemented and monitored to ensure that the goals are achieved.
C cabd
c- introduces the idea/scope of the paragraph – various stages in framing a management strategy ’b’ and ‘d’ are mandatory pair. This makes choice “c” the correct answer.
Question 13
Directions: In each of the questions given below in questions 11 to 15, each sentence is labelled with a letter. From the given choices, choose the most logical order of sentences that constructs a coherent paragraph.
a. Despite the awareness, some citizens fail to pay their taxes honestly.
b. One of the factors that impacts our country‘s economy is income- tax.
c. Awareness regarding this aspect of our economy is often made through the education system and media.
d. Most of these defaulters not only get into trouble, but they also create additional work for the income-tax department.
a. Despite the awareness, some citizens fail to pay their taxes honestly.
b. One of the factors that impacts our country‘s economy is income- tax.
c. Awareness regarding this aspect of our economy is often made through the education system and media.
d. Most of these defaulters not only get into trouble, but they also create additional work for the income-tax department.
C bcad
bc and ad are mandatory pairs with ‘b’ introducing the scope of the paragraph – ‘One of the factors that impacts our country’s economy is income – tax’. The order bcad is in choice “c” and is the correct answer.
Question 14
Directions: In each of the questions given below in questions 11 to 15, each sentence is labelled with a letter. From the given choices, choose the most logical order of sentences that constructs a coherent paragraph.
a. The responsible citizen helped to foil the plan of a hijack.
b. The deep pockets of his leather jacket contained what had been feared!
c. A person called up the airport and gave a message.
d. All the passengers were carefully frisked, and one of them was asked to step aside.
a. The responsible citizen helped to foil the plan of a hijack.
b. The deep pockets of his leather jacket contained what had been feared!
c. A person called up the airport and gave a message.
d. All the passengers were carefully frisked, and one of them was asked to step aside.
B cdba
The responsible citizen in ‘a’ refers to ‘a person called…’ in ‘c’. Hence a must be after c. This helps us to eliminate choices ‘a’ and ‘c’. db are mandatory pair as the pronoun ‘his’ in ‘d’ refers to ‘one of them was asked to step aside’ in ‘b’. db are together in choice “b” and hence choice “b” is the correct answer.
Question 15
Directions: In each of the questions given below in questions 11 to 15, each sentence is labelled with a letter. From the given choices, choose the most logical order of sentences that constructs a coherent paragraph.
a. In the following years, more layers of snow add up to the existing mass.
b. Consequently, the weight of the snow compresses and turns into solid ice.
c. Most glaciers are found near the Poles.
d. They begin to form when snow remains in the same area all year round.
a. In the following years, more layers of snow add up to the existing mass.
b. Consequently, the weight of the snow compresses and turns into solid ice.
c. Most glaciers are found near the Poles.
d. They begin to form when snow remains in the same area all year round.
D cdab
c introduces the scope of the paragraph ‘Most glaciers are..’ and so the paragraph must start with c. This helps us to eliminate choices “a” and “c”. b must follow a as it tells the final outcome after d and a. This order could be found in choice “d” which is the correct answer.
Question 16
Directions: Choose the correct meaning for each of the foreign language words and phrases given below in questions 16 to 20.
inter vivos
inter vivos
C a transaction made between living people
Question 17
Directions: Choose the correct meaning for each of the foreign language words and phrases given below in questions 16 to 20.
quantum ramifactus
quantum ramifactus
A the amount of damages suffered
Question 18
Directions: Choose the correct meaning for each of the foreign language words and phrases given below in questions 16 to 20.
malus
malus
C harmful
‘Malus’ refers to “a financial penalty incurred by a trader, investor, or banker when an investment or deal results in a loss”.
Question 19
Directions: Choose the correct meaning for each of the foreign language words and phrases given below in questions 16 to 20.
Volvo
Volvo
A I roll
‘Volvo’ means ‘I roll’ in Latin and is a conjugation of “volvere”.
Question 20
Directions: Choose the correct meaning for each of the foreign language words and phrases given below in questions 16 to 20.
Charade
Charade
C pretense
Question 21
Directions: Choose the correctly spelled words in questions 21 to 25 to fill in the blanks.
Malti Ahuja is making a sincere effort to pay off her ______.
Malti Ahuja is making a sincere effort to pay off her ______.
D creditor
Question 22
Directions: Choose the correctly spelled words in questions 21 to 25 to fill in the blanks.
It is our responsibility to leave a green and clean world for our ______.
It is our responsibility to leave a green and clean world for our ______.
C descendants
There are two right spellings here – “descendant” and “descendent” – that can be used interchangeably as either an adjective (meaning ‘moving downward’ or ‘descending from an ancestor’) or as a noun (simply someone who descends from someone else). While in traditional usage “descendent” is the adjective and “descendant” is the noun the two words are widely used interchangeably, and descendant is the preferred spelling.
In the exam options (a) and (c) we both awarded marks!
In the exam options (a) and (c) we both awarded marks!
Question 23
Directions: Choose the correctly spelled words in questions 21 to 25 to fill in the blanks.
The patient's death was the result of sheer ______ on the part of the surgeon.
The patient's death was the result of sheer ______ on the part of the surgeon.
B negligence
Question 24
Directions: Choose the correctly spelled words in questions 21 to 25 to fill in the blanks.
The scientist's biography is a blatant ______ of facts.
The scientist's biography is a blatant ______ of facts.
A misrepresentation
Question 25
Directions: Choose the correctly spelled words in questions 21 to 25 to fill in the blanks.
It was a ______ to work with these scientists.
It was a ______ to work with these scientists.
D privilege
Question 26
Directions for Questions 26 to 30: Fill in the blank with the correct options.
Son, ______! Research the company before you apply for the job.
Son, ______! Research the company before you apply for the job.
D hold your horses
To ‘hold your horses’ means to “wait a moment” and clearly will be appropriate in this sentence.
Question 27
Directions for Questions 26 to 30: Fill in the blank with the correct options.
Please, ______! This is not the time to get anxious.
Please, ______! This is not the time to get anxious.
A pull yourself together
To ‘pull yourself together’ means to “recover control of one's emotions”.
Question 28
Directions for Questions 26 to 30: Fill in the blank with the correct options.
In our company, we don‘t accept such carelessly done work. ______
In our company, we don‘t accept such carelessly done work. ______
B Get your act together.
To ‘get your act together’ means to “galvanize yourself into organizing your affairs effectively.
Question 29
Directions for Questions 26 to 30: Fill in the blank with the correct options.
I can‘t work on this assignment anymore! I think I have ______.
I can‘t work on this assignment anymore! I think I have ______.
D bitten off more than I can chew
To ‘bitten off more than you can chew’ means to “to try to do something that is too difficult for you”.
Question 30
Directions for Questions 26 to 30: Fill in the blank with the correct options.
I'm a historian. I‘m a ______ in this seminar on robots!
I'm a historian. I‘m a ______ in this seminar on robots!
B fish out of water
To be a ‘fish out of water’ means that the person “does not feel comfortable in a new environment”.
Question 31
The text in the passage can be best termed as
D expository
Expository means intended to explain or describe something. In the passage the author explains the difference between innovation and invention and also the challenges faced by innovators/inventors. Hence, choice “d” is the best answer.
Question 32
The main idea of the author is to
C compare innovators to inventors.
The author starts the passage by stating that though invention and innovation are closely linked, they are not interchangeable. He further discusses the similarities between them and also the challenges faced by innovators/inventors. This makes choice “c” the best answer.
Question 33
The author believes that
A innovators enhance the utility of inventions.
In first paragraph the author states “But this invention may or may not be of utility to the masses. It is the enterprising innovator who uses various resources, skills and time to make the invention available for use”. This makes choice “a” the correct answer.
Question 34
Benjamin Franklin and Steve Jobs, believe that
B making a mistake before finding success is not unusual.
From the last two sentences of second paragraph “b” becomes the best answer.
Question 35
Velcro can be best described as
D an accidental invention
The author uses the example of Velcro to elaborate the point – “Some inventions are the result of a keen observation or a simple discovery”. Hence “d” is the correct answer.
Question 36
It is believed that Graham Bell became the first patent holder of the telephone because of
A his ingenuity and good fortune.
Ingenuity means the quality of being clever, original, and inventive. It has been stated in the passage that he was a great inventor and innovator so we can assume these qualities in him. It is also mentioned that one of his peer/competitor – Antonio Meucci – was not able proceed with the patent of his invention for lack of resources. From this we can infer that Graham Bell may not have faced the problem of financial crunch. Choices “b” “c” and “d” are too extreme conclusions and cannot be inferred from the information given in the passage. Hence, “a” is the best answer.
Question 37
Which of the following is Untrue?
B Innovators are not expected to be enterprising.
Line 4 of the first paragraph states – “It is the enterprising innovator who uses various resources,…”. Hence, statement given in choice “b” is untrue which makes it the correct choice.
Question 38
Which of the following texts from the passage clearly indicates failure?
B Not every innovation sees the light of the day.
Not every innovation sees the light of the day means that not every innovation is successful and hence, b is the correct choice.
Question 39
Which of these words can replace the word intrepid?
C daring
Intrepid means fearless and so choice “c” is the correct answer.
Question 40
Which of these words is the antonym of laudable?
D disgraceful
Laudable means an action, idea, or aim deserving praise and commendation. Its antonym will be disgraceful – so choice “d” is the correct answer.
Section: General Knowledge
Question 1
The Chief Central Information Commissioner at present is:
A Sudhir Bhargava
Question 2
India has recently set up the latest ISRO's Satellite Tracking and Data Reception Centre in:
C Bhutan
Question 3
The number of complaints with the Banking Ombudsman registered during 2018 increased by:
D 25%
Question 4
Which of the following formally quit from UNESCO recently?
A U.S.A
Question 5
The maximum punishment for a cyber-stalker imposed by an anti-terrorism court in Pakistan is:
D 24 years
Question 6
In a major relief to micro, small and medium enterprises, the GST Council has recently increased the tax exemption limit per annum to:
C 40 lakhs
Question 7
Which of the following fruits got the Geographical Indication during October 2018?
A Shahi Litchi
Question 8
The richest person in the world as per the details revealed in March 2019 is:
B Jeff Bezos
Question 9
The number of EB – 5 visa applications, also known as 'cash for Green Card' visa to the U.S has increased in the last two years by about:
C 300%
Question 10
India purchased surveillance aircrafts (AWACS) during 2016 from:
D Israel
Question 11
The fastest train in India is:
C Vande Bharat Express
Question 12
The first humanoid police robot was introduced in the State of:
D Kerala
Question 13
The world's first Diesel to Electric locomotive twin engine of 10,000 horse power was flagged off in:
C India
Question 14
The Headquarters of International Solar Alliance consisting of more than 121 countries is located in:
A India
Question 15
The prestigious Seoul Peace Prize for 2018 was conferred on:
C Narendra Modi
Question 16
Which of the following countries during 2019 provided life time personal tax exemption to women with four children?
B Hungary
Question 17
In the 64th Film Fare Award, who won the best actress award?
D Alia Bhatt
Question 18
Recently, the Government of India relaxed the Angel Tax Norms for Start-ups and enhanced the investment limit to:
A Rs. 25 Crore
Question 19
India's first Chairperson of Lokpal is:
C Justice P.C. Ghose
Question 20
In how many phases the 17th Lok Sabha elections were held in 2019?
B Seven
Question 21
How many States went to polls along with the 2019 Lok Sabha elections?
B Four
Question 22
The National Common Mobility Card (NCMC), launched by the Central Government recently is also dubbed as:
A One Nation One Card
Question 23
Which of the following cities bagged the Cleanest City Award for three consecutive years?
D Indore
Question 24
Who is known as the 'Father of Local Government in India'?
D Lord Ripon
Question 25
Under which of the following missions, India has successfully tested its first-ever Anti-Satellite (A-SAT) Missile capability?
A Mission Shakti
Question 26
Which Indian personality is the recipient of the Oxford University's Bodley Medal 2019?
B Amartya Sen
Question 27
What is the name of the book containing English translation of the 100 year old classic Punjabi poem about Jallianwala Bagh massacre?
D Khooni Vaisakhi
Question 28
Which country has released a special stamp on Hindu epic Ramayana to commemorate the 70th anniversary of the diplomatic ties with India?
A Indonesia
Question 29
Which day is observed as International Mother Earth Day?
D April 22
Question 30
Which state's Kandhamal Haldi (turmeric) received Geographical Indications (GI) tag recently?
A Odisha
Question 31
Which country's Navy department has signed first reliable communication link with the Indian Navy and Pacific Naval Commands under the COMCASA pact?
D US
Question 32
Name the script writer, who won the Deenanath Mangeshkar Lifetime Award 2019 recently.
D Salim Khan
Question 33
Which space agency has recorded the first "marsquake," quake on the mars due to volcanic eruptions or land tides?
B NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration)
Question 34
Name the third edition of bilateral maritime exercise between Australia and India that was held in Visakhapatnam.
C Ausindex 19
Question 35
Holkhomang Haokip, who passed away recently, was a ______ ?
D Politician
Question 36
Name the Howitzers guns inducted into Indian Army recently.
A Dhanush
Question 37
Who was the first Indian President to visit Croatia?
D Ram Nath Kovind
Question 38
Which Island was notified as Island Protection Zone (IPZ) 2019 by Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change recently?
A Andaman and Nicobar Island
Question 39
Name the organization, which released the report on food crises titled 'Global Report on Food Crises' annually.
D Food Security Information Network (FSIN)
Question 40
Which is the happiest country as per the 2019 World Happiness Index?
A Finland
Question 41
The Headquarters of Asian Development Bank is situated in
A Manila, Philippines
Question 42
The 'Golden Peacock' Award is given for excellence in
D Corporate Governance
Question 43
Which planet is known as Red Planet?
C Mars
Question 44
What is Psephology?
A Statistical study of elections, voting, etc.
Question 45
The Global Teacher Award, 2019 was awarded to a teacher in:
D Kenya
Question 46
Which state in India is the first State to achieve 100 percent sanitation coverage?
C Sikkim
Question 47
The book titled 'God Save the Honourable Supreme Court' was authored by:
B Fali S. Nariman
Question 48
The book titled 'Anita Gets Bail' was authored by:
D Arun Shourie
Question 49
The first Indian Athlete to qualify for Olympics 2020 is:
A K.T. Irfan
Question 50
The South Asian nation that has won the SAFF Women's Championship for five times successively is:
B India
Section: Quantitative Aptitude
Question 1
The Municipality of a town increases water tax by 20% and water consumption decreased by 20%. Then the percentage of increase or decrease in the monthly expenditure is:
B 4% decrease
We should realize that: Expenditure = Tax x Consumption
Now, we are not given any values for either of the above three variables. So we can assume any convenient values for them.
Let Initial tax be 100 and Initial consumption be 100.
So Initial expenditure = 100 x 100 = 10000
Now New tax = 120 and New consumption = 80.
Then New Expenditure = 120 x 80 = 9600
Clearly consumption has reduced by 10000 – 9600 = 400
So % decrease = decrease/Initial Value x 100 = 400/10000 x 100 = 4%
Now, we are not given any values for either of the above three variables. So we can assume any convenient values for them.
Let Initial tax be 100 and Initial consumption be 100.
So Initial expenditure = 100 x 100 = 10000
Now New tax = 120 and New consumption = 80.
Then New Expenditure = 120 x 80 = 9600
Clearly consumption has reduced by 10000 – 9600 = 400
So % decrease = decrease/Initial Value x 100 = 400/10000 x 100 = 4%
Question 2
A child was born on 13th January 1976 which was a Tuesday. What day of the week will be the child's birth day in the year 1986?
D Monday
We want the number of odd days from 13th January 1976 to 13th January 1986.
Since the years 1976, 1980 and 1984 are leap years they will have 2 odd days while the rest will have only 1 odd day.
Hence total odd days = 3 x 2 + 7 x 1 = 13 days = 7 + 6 days
Hence her birthday will fall (after 6 days) on Monday.
Since the years 1976, 1980 and 1984 are leap years they will have 2 odd days while the rest will have only 1 odd day.
Hence total odd days = 3 x 2 + 7 x 1 = 13 days = 7 + 6 days
Hence her birthday will fall (after 6 days) on Monday.
Question 3
The perimeter of a rectangle is 60 cms. If its length is twice its breadth, then its area is:
A 200 cm<sup>2</sup>
Perimeter of a rectangle = 2(L + B) = 60
So L + B = 30 cms
Also we are given: L = 2B
So, 3B = 30 or B = 10. And L = 20 cms
Hence Area = 20 x 10 = 200 cm2
So L + B = 30 cms
Also we are given: L = 2B
So, 3B = 30 or B = 10. And L = 20 cms
Hence Area = 20 x 10 = 200 cm2
Question 4
A tree grows at the rate of 1/5th of its height annually. By how much height will it grow after 2 years, if its present height is 75 cms?
A 108 cms
Present height = 75 cms
After 1 year, Height = 75 + (1/5) of 75 = 90 cms
After 2nd year, Height = 90 + (1/5) of 90 = 108 cms
After 1 year, Height = 75 + (1/5) of 75 = 90 cms
After 2nd year, Height = 90 + (1/5) of 90 = 108 cms
Question 5
A train 600 meters long is running at a speed of 90 kms/hr. If it crosses a tunnel in one minute, then the length of the tunnel is:
D 900 meters
When a train crosses a tunnel, Distance needed to cross it will be the sum of lengths of the train and the tunnel. Say the tunnel’s length is L metres.
Then DC = (600 + L) metres
And, Speed of train = 90 km/hr = 90 x 5/18 m/s = 25 m/s
Also, Time to cross = 1 minute = 60 seconds
Now, DC = Speed x Time
i.e. 600 + L = 25 x 60 = 1500
So, L = 900 metres
Then DC = (600 + L) metres
And, Speed of train = 90 km/hr = 90 x 5/18 m/s = 25 m/s
Also, Time to cross = 1 minute = 60 seconds
Now, DC = Speed x Time
i.e. 600 + L = 25 x 60 = 1500
So, L = 900 metres
Question 6
A book seller sold a box of 10 pencils for Rs. 80 and incurred a loss. Had he sold it for Rs. 98, his gain would have been twice the loss he incurred earlier. The cost price of the box of pencils is:
B Rs. 86
Let the cost price of the box of pencils be Rs. C
Case-1: Sold for Rs. 80
Here, Loss = C – 80
Case-2: Sold for Rs. 98
Here, profit = 98 – C
Given, Profit = 2 x Loss
So, 98 – C = 2(C – 80) = 2C – 160
i.e. 98 + 160 = 2C + C
or C =258/3 = Rs. 86
Case-1: Sold for Rs. 80
Here, Loss = C – 80
Case-2: Sold for Rs. 98
Here, profit = 98 – C
Given, Profit = 2 x Loss
So, 98 – C = 2(C – 80) = 2C – 160
i.e. 98 + 160 = 2C + C
or C =258/3 = Rs. 86
Question 7
In a 100 meters race, A beats B by 20 meters B beats C by 5 meters. In the same race, A beats C by:
C 24 meters
Let the speeds of the three persons be A, B and C in m/s.
A beats B by 20 meters in a 100 m race
Clearly A runs 100 metres, while B runs only 80 metres in the same time!
So, 100 = A x T and 80 = B x T
On dividing: 100/80 = A/B
or A/B = 5/4 … (1)
B beats C by 5 meters in a 100 m race
Here too, B runs 100 metres, while C runs only 95 metres in the same time.
So, 100 = B x T’ and 95 = C x T’
Again on dividing we get: B/C = 100/95
Or B/C = 20/19 … (2)
From (1) and (2) we can equate the value of B:
B = 4A/5 = 20C/19
On rearranging, A/C = 20/19 x 5/4 = 25/19
Since A is faster, he will win. Now to find the margin (say X metres):
Clearly if A runs 100 m in time T, then C runs (100 – X) m in same time T.
i.e. 100 = A x T and (100 – X) = C x T
On dividing: 100/(100 – X) = A/C = 25/19
On cross multiplying: 1900 = 2500 – 25X
i.e. X = 600/25 = 24 metres
A beats B by 20 meters in a 100 m race
Clearly A runs 100 metres, while B runs only 80 metres in the same time!
So, 100 = A x T and 80 = B x T
On dividing: 100/80 = A/B
or A/B = 5/4 … (1)
B beats C by 5 meters in a 100 m race
Here too, B runs 100 metres, while C runs only 95 metres in the same time.
So, 100 = B x T’ and 95 = C x T’
Again on dividing we get: B/C = 100/95
Or B/C = 20/19 … (2)
From (1) and (2) we can equate the value of B:
B = 4A/5 = 20C/19
On rearranging, A/C = 20/19 x 5/4 = 25/19
Since A is faster, he will win. Now to find the margin (say X metres):
Clearly if A runs 100 m in time T, then C runs (100 – X) m in same time T.
i.e. 100 = A x T and (100 – X) = C x T
On dividing: 100/(100 – X) = A/C = 25/19
On cross multiplying: 1900 = 2500 – 25X
i.e. X = 600/25 = 24 metres
Question 8
Beena got married 8 years ago. Today, her age is 11/4 times her age at the time of marriage. If her daughter's age is 1/10 times her age, then her daughter's age is:
B 4 years
Note: In the actual exam, this problem was incorrect, and was in fact cancelled. Hence, we have made a minor correction in this question (“Today her age is 5/4 times her age at the time of marriage” instead of “Today her age is 11/4 times her age at the time of marriage”)
Let B be Beena’s age at the time of her marriage.
Then, her present age is (B + 8) years.
Given, (B + 8) = 5/4 x B
i.e. 4B + 32 = 5B or B = 32 years
Then her present age = 32 + 8 = 40 years
So her daughter’s age = 1/10 x 40 = 4 years
Let B be Beena’s age at the time of her marriage.
Then, her present age is (B + 8) years.
Given, (B + 8) = 5/4 x B
i.e. 4B + 32 = 5B or B = 32 years
Then her present age = 32 + 8 = 40 years
So her daughter’s age = 1/10 x 40 = 4 years
Question 9
A clock gains 2 minutes every hour. Then the angle traversed by the second hand in one minute is:
D 372°
This faulty clock gains 2 minutes every hour
i.e. in 60 minutes it runs 62 minutes.
i.e. in 1 minute it runs 62/60 = 31/30 minutes = 31/30 x 60 seconds = 62 seconds
Now, angle traversed by second hand in 60 seconds = 360°
So angle traversed in 62 seconds = 360°/60 x 62 = 372°
i.e. in 60 minutes it runs 62 minutes.
i.e. in 1 minute it runs 62/60 = 31/30 minutes = 31/30 x 60 seconds = 62 seconds
Now, angle traversed by second hand in 60 seconds = 360°
So angle traversed in 62 seconds = 360°/60 x 62 = 372°
Question 10
80% of students of a class took Statistics and 45% took Mathematics. If each student took Statistics or Mathematics and 40 took both, the total number of students in the class was:
A 160
Given: Each student took Statistics (S) or Mathematics (M)
i.e. n(S U M) = n(Universe) = 100%
So, n(S) + n(M) – n(S ∩ M) = 100%
i.e. 80% + 45% - n(S ∩ M) = 100%
i.e. n(S ∩ M) = 25%
If C be the total students in class, then:
n(S ∩ M) = 25% of C = 40
i.e. C = 40 x 100/25 = 160
i.e. n(S U M) = n(Universe) = 100%
So, n(S) + n(M) – n(S ∩ M) = 100%
i.e. 80% + 45% - n(S ∩ M) = 100%
i.e. n(S ∩ M) = 25%
If C be the total students in class, then:
n(S ∩ M) = 25% of C = 40
i.e. C = 40 x 100/25 = 160
Question 11
Kiran's brother is 5 years older to her. Her father was 30 years old when Kiran's sister was born, while her mother was 28 years old when Kiran was born. If Kiran's sister was 2 years old when her brother was born, what was the age of their father when Kiran's brother was born?
A 32
Let Kiran’s present age be K years.
Then, her brother’s age = (K + 5)
Kiran’s sister:
If Kiran’s sister was 2 years old when her brother was born, then her sister is 2 years older than her brother.
i.e. her sister’s age = (K + 5) + 2 = (K + 7) years
Kiran’s father:
Now Kiran’s sister was born (K + 7) years ago.
So (K + 7) years ago, her father was 30 years old.
Hence his present age will be 30 + (K + 7) = (K + 37) years
We want Kiran’s father’s age when her brother was born i.e. (K + 5) years ago
Her father’s age then would be (K + 37) – (K + 5) = 32 years
Then, her brother’s age = (K + 5)
Kiran’s sister:
If Kiran’s sister was 2 years old when her brother was born, then her sister is 2 years older than her brother.
i.e. her sister’s age = (K + 5) + 2 = (K + 7) years
Kiran’s father:
Now Kiran’s sister was born (K + 7) years ago.
So (K + 7) years ago, her father was 30 years old.
Hence his present age will be 30 + (K + 7) = (K + 37) years
We want Kiran’s father’s age when her brother was born i.e. (K + 5) years ago
Her father’s age then would be (K + 37) – (K + 5) = 32 years
Question 12
If Second Saturday and Sunday of every month is a holiday, then the total number of working days in a month of 31 days beginning with a Wednesday will be
D 26
Since the month begins on a Wednesday:
Clearly number of holidays = 4 + 1 = 5 days
So working days = 31 – 5 = 26
| Saturdays | Sundays |
| 4th | 5th |
| 11th | 12th |
| 18th | 19th |
| 25th | 26th |
So working days = 31 – 5 = 26
Question 13
A mess contractor can either serve 450 students with the meal that he prepares or can cater to 270 cops with the same meal. If 300 students have already eaten in the mess, how many cops can be fed with the remaining meal?
C 90
Let 1 student eat 1 unit of food.
The food prepared by the mess contractor = 450 units
Clearly this is the food eaten by 270 cops
So food eaten by 1 cop = 450/270 = 5/3 units
Now food eaten by the students = 300 x 1 = 300 units
So food left = 450 – 300 = 150 units
Say this food can be eaten by N cops
Then: N x 5/3 = 150 or N = 150 x 3/5 = 90 cops
The food prepared by the mess contractor = 450 units
Clearly this is the food eaten by 270 cops
So food eaten by 1 cop = 450/270 = 5/3 units
Now food eaten by the students = 300 x 1 = 300 units
So food left = 450 – 300 = 150 units
Say this food can be eaten by N cops
Then: N x 5/3 = 150 or N = 150 x 3/5 = 90 cops
Question 14
A car driver increases the average speed of his car by 3 km/hr every hour. The total distance travelled in 7 hours if the distance covered in first hour was 30 km, is
B 273 km
Distance travelled in 1st hour = 30 km
So initial speed = D/T = 30/1 = 30 km/hr
Now, Speed in 2nd hour = 33 km/hr
So distance covered in 2nd hour = 33 x 1 = 33 km
Similarly distance covered in 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th and 7th hours will be 36, 39, 42, 45 and 48 km.
i.e. distance travelled each hour is an AP with first term as 30 and common difference of 3.
So Total Distance = Sum of 7 terms = 7/2 x (60 + 6 x 3) = 7/2 x 78 = 7 x 39 = 273 km
So initial speed = D/T = 30/1 = 30 km/hr
Now, Speed in 2nd hour = 33 km/hr
So distance covered in 2nd hour = 33 x 1 = 33 km
Similarly distance covered in 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th and 7th hours will be 36, 39, 42, 45 and 48 km.
i.e. distance travelled each hour is an AP with first term as 30 and common difference of 3.
So Total Distance = Sum of 7 terms = 7/2 x (60 + 6 x 3) = 7/2 x 78 = 7 x 39 = 273 km
Question 15
A grocer mixes coffee powder of 2 types, one of which is priced at Rs. 60 and the other at Rs. 90. What should be the ratio of combining the two, to sell the blended mix coffee powder of the two types at Rs. 80?
C 1:2
Using the rule of allegation:
Rs. 60 Rs. 90
Rs. 80
So, (90 – 80)/(80 – 60) = W1 / W2
i.e. ratio of combining = 10:20 or 1:2
Rs. 60 Rs. 90
Rs. 80
So, (90 – 80)/(80 – 60) = W1 / W2
i.e. ratio of combining = 10:20 or 1:2
Question 16
The smallest number that should be subtracted from 2085, so that the new number is completely divisible by 23 is
B 15
By dividing 2085 by 23 we get quotient as 90 and remainder as 15.
So clearly 15 must be subtracted!
So clearly 15 must be subtracted!
Question 17
A tank is connected to three pipes – Pipe A, B and C. Pipe A can fill the tank in 6 hours, B can fill the tank in 8 hours and Pipe C can empty the full tank in 12 hours. How much time will it take to fill the tank completely if all three pipes are working together?
B 4 hours 48 minutes
Let the work be 24 units. Also let A, B and C be the rates of the three pipes (i.e. the amount of work done in 1 hour).
Using Rate = Work/Time we get:
A = 24/6 = 4 units/hr
B = 24/8 = 3 units/hr
C = -24/12 = -2 units/hr
Note that C has a negative rate since it empties the tank instead of filling it.
If all the pipes work together, then combined rate = 4 + 3 – 2 = 5 units/hr
Hence time taken by them = Work/Rate = 24/5 hours = 4 hrs and 4/5 x 60 min
i.e. 4 hrs and 48 min
Using Rate = Work/Time we get:
A = 24/6 = 4 units/hr
B = 24/8 = 3 units/hr
C = -24/12 = -2 units/hr
Note that C has a negative rate since it empties the tank instead of filling it.
If all the pipes work together, then combined rate = 4 + 3 – 2 = 5 units/hr
Hence time taken by them = Work/Rate = 24/5 hours = 4 hrs and 4/5 x 60 min
i.e. 4 hrs and 48 min
Question 18
Naresh bought a bicycle each for his two sons, each bicycle priced at Rs. 3500. If the first bicycle is sold at a profit of 5%, the how much should the other bicycle be sold for, to gain a total of 20% on both?
D 35%
Total CP = 3500 + 3500 = Rs. 7000
Profit needed = 20% of 7000 = Rs. 1400
Hence Total SP = 7000 + 1400 = Rs. 8400
Now, SP of 1st bicycle = 3500 + 5/100 x 3500 = Rs. 3675
Hence SP of 2nd bicycle = 8400 – 3675 = Rs. 4725
But CP of 2nd bicycle = Rs. 3500
So profit on 2nd bicycle = 4725 – 3500 = Rs. 1225
i.e. % profit on 2nd bicycle = 1225/3500 x 100 = 35%
Profit needed = 20% of 7000 = Rs. 1400
Hence Total SP = 7000 + 1400 = Rs. 8400
Now, SP of 1st bicycle = 3500 + 5/100 x 3500 = Rs. 3675
Hence SP of 2nd bicycle = 8400 – 3675 = Rs. 4725
But CP of 2nd bicycle = Rs. 3500
So profit on 2nd bicycle = 4725 – 3500 = Rs. 1225
i.e. % profit on 2nd bicycle = 1225/3500 x 100 = 35%
Question 19
An employee of an organization invests a total of Rs 25,400 in two different schemes X and Y at a simple interest rate of 18% per annum and 10% per annum respectively. If a total of Rs. 6460 has been earned as simple interest in 2 years, what amount was invested in Scheme Y?
B Rs. 16,775
Let amounts invested in X and Y be Rs. A and Rs. (25400 – A) respectively.
Then SI on 1st amount = A x 18 x 2/100 = 0.36P
And SI on 2nd amount = (25400 – A) x 10 x 2/100 = 5080 – 0.2A
So total SI = 0.36P + 5080 – 0.2A = 0.16P + 5080 = 6460
i.e. P = 1380/0.16 = Rs. 8625
Hence amount invested in Y = 25400 – 8625 = Rs. 16775
Then SI on 1st amount = A x 18 x 2/100 = 0.36P
And SI on 2nd amount = (25400 – A) x 10 x 2/100 = 5080 – 0.2A
So total SI = 0.36P + 5080 – 0.2A = 0.16P + 5080 = 6460
i.e. P = 1380/0.16 = Rs. 8625
Hence amount invested in Y = 25400 – 8625 = Rs. 16775
Question 20
The difference between Simple Interest and Compound Interest on Rs. 500 for 1 year at 10% per annum, reckoned half yearly is
B Rs. 1.25
SI in 1 year = (500 x 10 x 1)/100 = Rs. 50
For CI calculations we use CI = A – P = P(1 + r/100n)1 x n – P
Here n = 2 for half yearly compounding
So, CI in 1 year = 500 x (1 + 5/100)2 – 500 = 500 x (441/400 – 1) = 500 x 41/400 = 205/4 = 51.25
i.e. difference between CI and SI = 51.25 – 50 = Rs, 1.25
For CI calculations we use CI = A – P = P(1 + r/100n)1 x n – P
Here n = 2 for half yearly compounding
So, CI in 1 year = 500 x (1 + 5/100)2 – 500 = 500 x (441/400 – 1) = 500 x 41/400 = 205/4 = 51.25
i.e. difference between CI and SI = 51.25 – 50 = Rs, 1.25
Section: Legal Aptitude
Question 1
This section consists of fifty (50) questions. Each question consists of legal principle(s) (hereinafter referred to as 'principle') and facts. Such proposition may or may not be true in the real and legal sense, yet you have to conclusively assume them to be true for the purposes of this section. Principles have to be applied to the given facts to arrive at the most reasonable conclusion. Only one of the alternatives, i.e., (A), (B), (C), or (D) is the most reasonable conclusion. In other words, in answering the following questions, you must not rely on any principle except the principles that are given herein below for every question. Further you must not assume any facts other than those stated in the question. The objective of this section is to test your ability in legal aptitude, study of law, research aptitude and problem solving ability even if the 'most reasonable conclusion' arrived at may be absurd or unacceptable for any other reason.
Principle: Acceptance of proposal must be the exact mirror image of the proposal.
Facts: 'A' made a proposal to 'B' to sell a chair for Rs. 500. 'B' is desirous of buying the said chair for Rs. 400.
Principle: Acceptance of proposal must be the exact mirror image of the proposal.
Facts: 'A' made a proposal to 'B' to sell a chair for Rs. 500. 'B' is desirous of buying the said chair for Rs. 400.
B B has not accepted the proposal of A.
Option (b) is the correct answer because when A made a proposal to B to sell his chair for Rs. 500, then there was not any acceptance for the same from the side of B. Although it is written in the facts that B is desirous to buy chair for Rs. 400 but it was not communicated to A which eliminates Option (a), (c) and (d).
Question 2
Principle: An agreement with a boy below the age of eighteen years is not enforceable by law.
Facts: A man entered into an agreement with a girl of seventeen years of age.
Facts: A man entered into an agreement with a girl of seventeen years of age.
D No inference can be drawn.
A person is called as minor if he is under 18 years of age whether he is a boy or a girl. In the present case a man entered into an agreement with a girl of 17 years of age but the principle is talking about the enforcement of the agreement with a boy below the age of 18 years which makes option (d) as the relatable and the correct answer.
Question 3
Principle: Sale of liquor is illegal. All agreements relating to prohibited items do not exist in the eyes of law.
Facts: 'A' entered into an agreement with 'B' for the sale of liquor. 'A' failed to supply the agreed quantity of liquor to B.
Facts: 'A' entered into an agreement with 'B' for the sale of liquor. 'A' failed to supply the agreed quantity of liquor to B.
B B cannot bring any legal action against A.
As liquor is illegal and all the agreements relating to prohibited items are not enforceable in the court of law and when A failed to supply liquor to B, then B cannot bring him any legal action against A because he is purchasing that thing which is already banned. Thus option (b) is the correct answer.
Question 4
Principle: The communication of a proposal is complete when it comes to the knowledge of the person to whom it is made.
Facts: 'A' sent a letter making a proposal to 'B' to purchase the house of B.
Facts: 'A' sent a letter making a proposal to 'B' to purchase the house of B.
D The communication of proposal is complete when B reads the letter.
This is a very simple question which says that communication is complete when it comes to the knowledge of the person to whom it is made and in this case the proposal of letter is complete when B reads the letter of proposal.
Question 5
Principle: An agreement may be entered into orally, in writing, or by conduct.
Facts: 'A' went to the shop of 'B' and picked a tooth brush and gave a cheque of Rupees twenty to B and left the shop.
Facts: 'A' went to the shop of 'B' and picked a tooth brush and gave a cheque of Rupees twenty to B and left the shop.
A A entered into an agreement with B.
The agreement is complete when A gave a cheque of Rs. 20 to B after buying a tooth brush and A entered into an agreement with B at the same time. Thus, option A is the correct answer.
Question 6
Principle: Property consists of right to posses, right to use, right to alienate and right to exclude others. Sale is complete when property gets transferred from the seller to the buyer.
Facts: 'A' sold his car to 'B' B requested A to keep the car in his care on behalf B for one month. A agreed.
Facts: 'A' sold his car to 'B' B requested A to keep the car in his care on behalf B for one month. A agreed.
A Sale of car is complete.
When A agreed to keep his car with him for one month after selling it, at the same time the sale of the car is complete which makes option (a), the most appropriate answer because sale is complete when property gets transferred from the seller to the buyer.
Question 7
Principle: A person, who is usually mad, but occasionally not mad, may make a contract when he is not mad.
Facts: 'A' generally remains in the state of madness and rarely becomes capable of understanding anything.
Facts: 'A' generally remains in the state of madness and rarely becomes capable of understanding anything.
A A can make a contract.
Option (a) is the correct answer because A can make the contract when he is not mad.
Question 8
Principle: An agreement without free consent can be enforced only at the option of the party whose consent was not free.
Facts: A obtains the consent of B to enter into an agreement by putting a gun on the head of B‘s girl friend.
Facts: A obtains the consent of B to enter into an agreement by putting a gun on the head of B‘s girl friend.
A B can enforce the agreement.
Option (a) is the correct answer because when A obtains the consent by putting a gun on B's girlfriend, it can be enforced only at the option of the party whose consent is not free and here in this case the consent is given by B.
Question 9
Principle: Where one of the parties to a contract was in position to dominate the decision of the other party, the contract is enforceable only at the option of the party who was in a position to dominate decision of the other party.
Facts: A doctor asked his patient to make a payment of Rs. 10,00,000/- (Ten Lac Only) for treatment of his fever. The patient paid an amount of Rs. 5,00,000/- (Five Lac Only) and promised to pay the remaining amount after the treatment. After treatment the patient recovered from fever. The doctor demanded the remaining amount from the patient. The patient refused to pay.
Facts: A doctor asked his patient to make a payment of Rs. 10,00,000/- (Ten Lac Only) for treatment of his fever. The patient paid an amount of Rs. 5,00,000/- (Five Lac Only) and promised to pay the remaining amount after the treatment. After treatment the patient recovered from fever. The doctor demanded the remaining amount from the patient. The patient refused to pay.
B The contract is enforceable against the patient.
Option (b) is the correct option because in this case Doctor is in a dominating position and thus he can make the contract enforceable against the patient.
Question 10
Principle: When, at the desire one person, any other person has done or abstained from doing something, such act or abstinence or promise is called a consideration for the promise.
Facts: X, the uncle of Y, made a promise to pay him an amount of Rs. 1,00,000/- as reward if Y quits smoking and drinking within one year. Y quit smoking and drinking within six months.
Facts: X, the uncle of Y, made a promise to pay him an amount of Rs. 1,00,000/- as reward if Y quits smoking and drinking within one year. Y quit smoking and drinking within six months.
B Consideration has moved from the side of Y.
When X made a promise to pay him the amount on the condition that if Y will quit smoking and drinking then the consideration has moved from the side of X, making option (b) the correct choice.
Question 11
Principle: Law never enforces an impossible promise.
Facts: 'A' made a promise to 'B' to discover treasure by magic.
Facts: 'A' made a promise to 'B' to discover treasure by magic.
B Law will not enforce the promise.
As the principle says that Law never enforces an impossible promise, thus the promise given by A to discover treasure by magic is impossible, making (b) the correct option.
Question 12
Principle: When a person who has made a promise to another person to do something does not fulfill his promise, another person becomes entitled to receive, from the person who did not fulfill his promise, compensation in the form of money.
Facts: X made a promise to Y to repair his car engine. Y made the payment for repair.
Facts: X made a promise to Y to repair his car engine. Y made the payment for repair.
D Y will not be entitled to receive compensation from X
In this case X made a promise to Y to repair his car engine but the accident occurred due to bursting of tyre in which Y will not be entitled to receive any kind of compensation from X.
Question 13
Principle: Whoever takes away any moveable thing from the land of any person without that person's consent is said to commit theft.
Facts: During his visit to the home of C, A asks B, the son of C, to accompany A to a forest. Neither A nor B inform C in this regard. B accompanies A to the forest.
Facts: During his visit to the home of C, A asks B, the son of C, to accompany A to a forest. Neither A nor B inform C in this regard. B accompanies A to the forest.
B A has not committed theft.
In the eyes of law, a man is not a thing. Thus, the taking of B (C's son) by A is not said to be committed as theft which makes option (b) as the most appropriate answer.
Question 14
Principle: Nothing is an offence if it is done in good faith for the purpose of preventing or avoiding greater harm or damage to person or property.
Facts: A jumps into a swimming pool to save a boy from drowning. While pulling the boy from water A was hit by C. A left the boy in the water and attacked C. The boy died in the water.
Facts: A jumps into a swimming pool to save a boy from drowning. While pulling the boy from water A was hit by C. A left the boy in the water and attacked C. The boy died in the water.
A A has not committed the offence of killing the boy.
First of all, A was not duty bound to jump into the pool and to save the drowning boy and secondly if he jumped and then had a scuffle with C, then he is not liable for the death of the boy, when he died which makes option (a) as the most appropriate choice.
Question 15
Principle: Causing of an effect partly by an act and partly by an omission is an offence.
Facts: A did not provide any food to his daughter D. He also confined D in a room.
Consequently, D died.
Facts: A did not provide any food to his daughter D. He also confined D in a room.
Consequently, D died.
C A committed the offence of killing D.
The act of confining his daughter into a room and not giving any food to her will amount to cruelty and when D died due to all this, then A will be held liable for committing the offence of killing D. Thus option (c) is the correct option.
Question 16
Principle: Nothing is an offence which is done in the exercise of the right of private defence. Nothing is an offence which is done in madness.
Facts: A, under the influence of madness, attempts to kill B. B to save his life kills A.
Facts: A, under the influence of madness, attempts to kill B. B to save his life kills A.
D B has not committed an offence
In exercising the right of Private Defence, a person can even kill another person and same happened in this case where B killed A to save his life. Thus, option (d) is correct.
Question 17
Principle: A man is guilty of not only for what he actually does but also for the consequences of his doing.
Facts: A wanted to kill the animal of B. He saw B standing with his animal and fired a gun shot at the animal. The gun shot killed B.
Facts: A wanted to kill the animal of B. He saw B standing with his animal and fired a gun shot at the animal. The gun shot killed B.
A A is guilty of killing B.
According to the principle, A is guilty of killing B because a man is liable for his acts and also for the consequences of his act which he have done. No matter if his intention was to kill the animal of B and not B, but he is still liable for killing B.
Question 18
Principle: Mere silence as to facts likely to affect the decision of a person to enter into a contract is not fraud.
Facts: A sells to B (A‘s daughter who is a minor) a horse which A knows to be unsound.
A says nothing to B about the unsoundness of the horse.
Facts: A sells to B (A‘s daughter who is a minor) a horse which A knows to be unsound.
A says nothing to B about the unsoundness of the horse.
B A has committed no fraud
The rule of Caveat Emptor applies here which means let the buyer beware. In this case, it is the duty of B to know about the condition of horse before buying and thus there was no fault of A which makes option (b) as the correct answer.
Question 19
Principle: Whoever attempts to commit the offence of cheating, commits an offence.
Facts: A with an intention to defraud B, obtains from him an amount of Rs. 500. (A) A has committed no offence
Facts: A with an intention to defraud B, obtains from him an amount of Rs. 500. (A) A has committed no offence
B A has committed the offence of cheating
This a very simple question in which A's intention was to defraud B and then he obtains an amount of Rs. 500 which is a clear cut case of cheating.
Question 20
Principle: Whoever by words publishes any imputation concerning any person is said to defame that person.
Facts: During a marriage ceremony, A circulated a pamphlet saying sister of the bride 'S' is a thief, she has stolen the shoes of the bridegroom.
Facts: During a marriage ceremony, A circulated a pamphlet saying sister of the bride 'S' is a thief, she has stolen the shoes of the bridegroom.
A A defamed S
Although these are the rituals in the marriage ceremonies, but still if she is called as a thief for stealing the shoes of the bridegroom will amount to defamation which makes option (a) as the most appropriate choice.
Question 21
Principle: An employer is liable for an injury caused to an employee in the course of the employment.
Facts: 'A' and 'B' were working in a factory as unskilled laborers. A was carrying a basket of stones on his head. B was sitting on the ground. When A crossed B, all of a sudden a stone fell down from the basket and hit B on his head. B died instantaneously.
Facts: 'A' and 'B' were working in a factory as unskilled laborers. A was carrying a basket of stones on his head. B was sitting on the ground. When A crossed B, all of a sudden a stone fell down from the basket and hit B on his head. B died instantaneously.
A The employer will be liable
In this case the employer will be liable because A was carrying the basket of stones in due course of employment. Thus, option (a) is correct.
Question 22
Principle: Damages the money recompense, as far as money can do, for the loss suffered by a person.
Facts: A, an Indian citizen, having a right to vote, was not allowed to cast his vote on the polling booth, by the returning officer. Name of A was mentioned in the voter‘s list. A has also reported at the polling booth in time. However, the candidate in whose favor A would have cast his vote won the election. A filed a suit claiming damages.
Facts: A, an Indian citizen, having a right to vote, was not allowed to cast his vote on the polling booth, by the returning officer. Name of A was mentioned in the voter‘s list. A has also reported at the polling booth in time. However, the candidate in whose favor A would have cast his vote won the election. A filed a suit claiming damages.
B A will not be entitled to damages
The rule of ‘INJURIA SINE DAMNUM’ applies here which means Injury Without Damage. Although the legal right of A was violated because he couldn’t cast his vote but the candidate in whose favour A would have cast his vote won the election and as a result there was no damage to A in this case making option (b) as the correct choice.
Question 23
Principle: When a party to a contract has refused to perform, or disabled himself from performing, his promise in its entirety, the other party shall not put an end to the contract.
Facts: A engaged B on April 12 to enter his service on June 1, but on May 11, A wrote to B that his services would not be needed. On May 22, B joined C for employment.
Facts: A engaged B on April 12 to enter his service on June 1, but on May 11, A wrote to B that his services would not be needed. On May 22, B joined C for employment.
A B cannot put the contract to an end.
According to the principle B cannot put the contract to an end because when A has refused to perform or disabled himself from performing, in that case the other party (i.e. B) cannot put an end to the contract. Option (a) is the correct choice.
Question 24
Principle: Everyone shall be permitted to take advantage of his own wrong.
Facts: A legatee was heavily drunk and driving his car at a speed of 100 Km/per hour in a crowded market. All of a sudden his testator came on the road. There were other people on the road at that time. The car driven by legatee hit the testator and four other persons. All the five persons hit by the car died.
Facts: A legatee was heavily drunk and driving his car at a speed of 100 Km/per hour in a crowded market. All of a sudden his testator came on the road. There were other people on the road at that time. The car driven by legatee hit the testator and four other persons. All the five persons hit by the car died.
A The legatee can take the benefit under the will
According to the principle, everyone shall be permitted to take advantage of his own wrong and when legatee hits the testator then in this case, he can take the benefit under the will. Thus, the most appropriate answer is (a).
Question 25
Principle: Property can be transferred only by a living person to another living person.
Facts: A' transfers property of which he is the owner in favor of the unborn child of B.
Facts: A' transfers property of which he is the owner in favor of the unborn child of B.
C Property has not been transferred to the unborn child
According to the principle, property can be transferred only to living person and thus it cannot be transferred in favour of the unborn child of B making option (c) as the correct choice.
Question 26
Principle: An interest created, dependent upon a condition fails, if the fulfillment of the condition is impossible.
Facts: A promises to pay Rs. Ten Lakh to B on condition that he shall marry A‘s daughter C. At the date on which A gave Rs. Ten Lac to B, C was dead.
Facts: A promises to pay Rs. Ten Lakh to B on condition that he shall marry A‘s daughter C. At the date on which A gave Rs. Ten Lac to B, C was dead.
A B's interest fails
Due to the death of C, the fulfilment of the condition of marrying A's daughter fails, which makes option (a) as the correct answer.
Question 27
Principle: A condition must be complied with after the happening of the event to which such a condition is attached.
Facts: A promises to pay Rs. 5,000 to B on the condition that he shall marry with the consent of C, D and E. B marries without the consent of C, D and E, but obtains their consent after the marriage.
Facts: A promises to pay Rs. 5,000 to B on the condition that he shall marry with the consent of C, D and E. B marries without the consent of C, D and E, but obtains their consent after the marriage.
A B has fulfilled the condition
According to the principle, a condition must be complied with after the happening of the event and here B marries and obtains the consent afterwards, which makes option (a) as the most appropriate choice.
Question 28
Principle: A condition must be complied in order to claim the benefit of an agreement.
Facts: A agrees to transfer a farm to B, if B shall not go to England within three years after the date of the agreement, his interest in the farm shall cease. B does not go to England within the term prescribed.
Facts: A agrees to transfer a farm to B, if B shall not go to England within three years after the date of the agreement, his interest in the farm shall cease. B does not go to England within the term prescribed.
B B's interest in the farm does not continue
According to principle, a condition must be complied in order to claim the benefit of an agreement and B does not go to England for 3 years after the date of agreement. Thus option (b) is the correct answer.
Question 29
Principle: Existence of all the alleged facts is relevant whether they occurred at the same time and place or at different times and places.
Facts: A, a citizen of England, is accused of committing murder of B in India by taking part in a conspiracy hatched in England.
Facts: A, a citizen of England, is accused of committing murder of B in India by taking part in a conspiracy hatched in England.
A The facts that A accused of commission of murder and of conspiracy are relevant facts
All the relevant facts are considered when any crime is committed and here in this case the commission of murder and hatching conspiracy are relevant facts which makes option (a) as the correct choice.
Question 30
Principle: One who asserts must prove.
Facts: A desires a Court to give judgment that B, C and D shall be punished for a crime which A says B, C and D have committed.
Facts: A desires a Court to give judgment that B, C and D shall be punished for a crime which A says B, C and D have committed.
B A must prove that B, C and D have committed the crime
When A desires the court to give judgement for the punishment of B, C and D then it is his duty to prove that they have committed the crime. Thus, option (b) is the correct choice.
Question 31
Principle: Foreign judgment binds the parties and is conclusive unless it is obtained by fraud.
Facts: A obtains judgment from US court by producing fake documents. (A) New Suit can be filed in India on the same facts
Facts: A obtains judgment from US court by producing fake documents. (A) New Suit can be filed in India on the same facts
A New Suit can be filed in India on the same facts
New suit can be filed in India because the judgement obtained from US court was by producing fake documents.
Question 32
Principle: Decision of Court is Null and Void, if it is given by court which does not have jurisdiction over the subject matter.
Facts: A obtains decision from a court which did not have jurisdiction to deal with the subject matter.
Facts: A obtains decision from a court which did not have jurisdiction to deal with the subject matter.
B Decision cannot be enforced because decision is null and void
If the decision is given by that court which has no jurisdiction to pass that particular judgement, then the decision of the court is null and void. Thus, option (b) is the correct answer.
Question 33
Principle: Civil Suit can be filed where defendant resides or carries on business or where cause of action arises.
Facts: 'A' carries on business in Gurgaon, 'B' carries on Business in Mumbai. 'B' through his agent in Gurgaon purchases goods in Gurgaon and takes delivery through agent in Gurgaon. Where Civil Suit for payment of price can be filed by 'A'?
Facts: 'A' carries on business in Gurgaon, 'B' carries on Business in Mumbai. 'B' through his agent in Gurgaon purchases goods in Gurgaon and takes delivery through agent in Gurgaon. Where Civil Suit for payment of price can be filed by 'A'?
C At either of the places i.e. Mumbai or Gurgaon
In this kind of situation, suit can be filed at either of the places, where the defendant resides or carries on business or where cause of action arises i.e. either in Mumbai or in Gurgaon.
Question 34
Principle: Civil Suit can be filed where defendant resides or carries on business or where cause of action arises.
Facts: An agreement is signed and executed in New Delhi between A and B for supply of goods wherein B is to supply goods to be delivered at New Dehli to client of A. A carries on business at Haryana and B carries on Business in UP. Civil suit by 'B' for payment of consideration can be filed against 'A' at
Facts: An agreement is signed and executed in New Delhi between A and B for supply of goods wherein B is to supply goods to be delivered at New Dehli to client of A. A carries on business at Haryana and B carries on Business in UP. Civil suit by 'B' for payment of consideration can be filed against 'A' at
D At Haryana or at New Delhi
Suit can be instituted either in Haryana or in New Delhi because A (the defendant) resides in Haryana and cause of action arises in New Delhi.
Question 35
Principle: No court can execute the decisions unless it is having territorial jurisdiction over the property or the person against whom decision is to be executed. The Court which gave the decision can transfer the matter to the court which has the territorial jurisdiction over the person or property.
Facts: A decision is given by court at New Delhi on a contractual matter against X in a suit between X and Y. X is resident of Maharashtra and he has properties in Maharasthra and Gujarat.
Facts: A decision is given by court at New Delhi on a contractual matter against X in a suit between X and Y. X is resident of Maharashtra and he has properties in Maharasthra and Gujarat.
D New Delhi court can transfer the proceedings to either of the courts i.e. Maharasthra or Gujarat
In this case, New Delhi court can transfer the proceedings to either of the courts i.e. either in Maharashtra court or in Gujarat court.
Question 36
Principle: Nothing is an offence by reason of any harm it may cause to another person, if it is done in good faith and for the benefit of that person even without that person's consent.
Facts: A is attacked by a Lion and Lion drags him while he is crying for help. B, a passer by picks up A's gun in good faith and fires at Lion which injures A. B has never used the gun before.
Facts: A is attacked by a Lion and Lion drags him while he is crying for help. B, a passer by picks up A's gun in good faith and fires at Lion which injures A. B has never used the gun before.
B B is not liable as he has done the act in good faith
According to the principle, B fires in good faith and for the benefit of the person but unfortunately injured A, then also he cannot be held liable for injuring A because whatever he have done, he have done it in good faith. Thus, option (b) is the correct choice.
Question 37
Principle: Nothing is an offence if it is done under intoxication and the person commiting the offence was incapable to understand the nature of the Act. Intoxication should be without knowledge or against the will of the person.
Facts: A, B and C were having a party in Bar where A pursuaded B and C to take alcoholic drinks. On the persistent pursuation B and C also consumed alcohol along with A. B and C had never consumed alcohol before. After intoxiation, there was some argument between B and C where C pushed B with full force causing serious injury to B.
Facts: A, B and C were having a party in Bar where A pursuaded B and C to take alcoholic drinks. On the persistent pursuation B and C also consumed alcohol along with A. B and C had never consumed alcohol before. After intoxiation, there was some argument between B and C where C pushed B with full force causing serious injury to B.
C A is liable because A pursuaded them to consume alcohol whereas they had never consumed alcohol
C is liable in this case because he have voluntary consumed the alcohol with full knowledge and causing serious injury to B will make him liable making option (a) as the correct choice.
Question 38
Principle: Everyone has the right of private defence to defend his body and property by use of reasonable force unless that person had time to have recourse to protection of public authorities.
Facts: X receives information at 5.00 pm that Y along with few friends is planning to burn his crop at midnight which is ready to be harvested. He does not inform the village Police Station which was just one kilometer away. He gathers his family members and directs them to collect some weapons in the form of swords and lathis to protect his field/crop. At around 11.00 pm Y and his aides attack the crop and a severe fight ensues wherein Y is seriously injured.
Facts: X receives information at 5.00 pm that Y along with few friends is planning to burn his crop at midnight which is ready to be harvested. He does not inform the village Police Station which was just one kilometer away. He gathers his family members and directs them to collect some weapons in the form of swords and lathis to protect his field/crop. At around 11.00 pm Y and his aides attack the crop and a severe fight ensues wherein Y is seriously injured.
D X and his family is liable as they have not informed the police
X and his family is liable for injuring Y because firstly they would have informed the public authorities and secondly they would have applied reasonable force. Thus, option (d) is the correct answer.
Question 39
Principle: Anyone who induces or attempts to induce a voter to vote in a particular manner on the ground that the voter will face divine displeasure, shall be guilty of offence of interfering with free exercise of right to vote.
Facts: During election campaign period one candidate X told the voters that if they do not vote for her, voters will be cursed because the election candidate is the God‘s own child and those who do not vote for her, they will not be liked by God.
Facts: During election campaign period one candidate X told the voters that if they do not vote for her, voters will be cursed because the election candidate is the God‘s own child and those who do not vote for her, they will not be liked by God.
A X has committed an offence
The wrongful act of convincing of voters to vote for a particular man by representing him as a child of God makes X liable for an offence and hence option (a) is the most appropriate choice.
Question 40
Principle: Doing of an act which causes common injury, danger or annoyance to public or which is likely to cause such injury or annoyance is Public nuisance. A common nuisance is not excused because it causes some nuisance or advantage.
Facts: 'A' a farmer having large farmlands burns crop residue (stubble) on his fields after harvesting the crop to make the field ready for next crop as this is the easy, fast and convenient method of making the field ready for next crop. His farmlands are adjoining a densely inhabited residential area and people pass through the smoke while travelling on the road adjoining his farmlands. The smoke caused by fire also enters the houses in the colony
Facts: 'A' a farmer having large farmlands burns crop residue (stubble) on his fields after harvesting the crop to make the field ready for next crop as this is the easy, fast and convenient method of making the field ready for next crop. His farmlands are adjoining a densely inhabited residential area and people pass through the smoke while travelling on the road adjoining his farmlands. The smoke caused by fire also enters the houses in the colony
C A has committed public nuisance
The act of farmer of burning the crops residue is a clear cut example of Public Nuisance and hence, option (c) is the most appropriate choice.
Question 41
Principle: Death caused by rash or negligent act of a person is an offence.
Facts: X was driving his SUV car in a lonely road leading to a forest at 160 km per hour. Suddenly, someone appears from the forest on the road and in the resultant accident, the car hits the commuter causing his death.
Facts: X was driving his SUV car in a lonely road leading to a forest at 160 km per hour. Suddenly, someone appears from the forest on the road and in the resultant accident, the car hits the commuter causing his death.
C X is guilty of an offence death by rash or negligent act
X is liable for an offence as driving the car at a speed of 160 km/hr is very risky and death was caused due to rash and negligent driving making option (c) as the correct choice.
Question 42
Principle: Whoever causes death by rash or negligent act commits an offence.
Facts: X is having a house on the roadside which is also having a street on the back of the house. He has a lawn on the back of his house where he has built a toilet. To prevent the intruders from entering his house, he got the fence charged with a high voltage live electric wire. Z was passing through the street at the backyard of the house of X and sat down to take rest near the fence. While getting up, his hands came in contact with the fence which was connected to high voltage electric wire causing his death.
Facts: X is having a house on the roadside which is also having a street on the back of the house. He has a lawn on the back of his house where he has built a toilet. To prevent the intruders from entering his house, he got the fence charged with a high voltage live electric wire. Z was passing through the street at the backyard of the house of X and sat down to take rest near the fence. While getting up, his hands came in contact with the fence which was connected to high voltage electric wire causing his death.
B X has committed an offence of causing death by rash and negligent act
By not taking proper care and caution by X regarding the fence, he has committed the offence of causing death by rash and negligent act. Thus, option (b) is the correct choice.
Question 43
Principle: Killing is not murder, if it is committed in a sudden fight without pre-meditation in a heat of passion upon a sudden quarrel.
Facts: X and Y were buying liquor from a liquor shop at 7 pm. Y abused X and there was quarrel between them. X told Y that he will not spare him and Y shouted that his house is adjoining the shop only and if X had the guts, he can come anytime. X went back to his shop which was nearby, procured a knife and went to Y‘s residence at 9 pm and stabbed him to death.
Facts: X and Y were buying liquor from a liquor shop at 7 pm. Y abused X and there was quarrel between them. X told Y that he will not spare him and Y shouted that his house is adjoining the shop only and if X had the guts, he can come anytime. X went back to his shop which was nearby, procured a knife and went to Y‘s residence at 9 pm and stabbed him to death.
A X has committed murder
As there was a time gap of 2 hours which is sufficient enough to know that there is not any sudden fight and there was no grave and sudden provocation, so this is clearly a case of murder and hence option (a) is the correct choice.
Question 44
Principle: Use of criminal force intentionally knowing that it would cause or is likely to cause injury or annoyance to the person against whom force is used, is an offence.
Facts: X, a renowned social worker who had launched a movement for liberation of women, pulls up a Muslim women‘s veil in public in good faith without her consent causing annoyance to her.
Facts: X, a renowned social worker who had launched a movement for liberation of women, pulls up a Muslim women‘s veil in public in good faith without her consent causing annoyance to her.
D X has committed an offence by use of criminal force
Pulling up a Muslim women's veil in public without her consent causing annoyance to her will amount to use of criminal force against the person and thus option (d) is the correct choice.
Question 45
Principle: Inducing any animal to move or to change its motion and thereby intentionally causing fear of injury or annoyance to others by such act, is an offence of use of criminal force.
Facts: X incites his dog to chase and run after his neighbour Y, to teach Y to stay away from him. The act is done without neighbour’ consent and against his will
Facts: X incites his dog to chase and run after his neighbour Y, to teach Y to stay away from him. The act is done without neighbour’ consent and against his will
D X has committed an offence of use of criminal force
According to the principle, this is a clear cut case of using of criminal force by inciting his dog to chase and run after his neighbour.
Question 46
Principle: A spouse is not permitted to put in evidence in any court, any communication during marriage between the spouses without the consent of the person who made the communication.
Facts: X who is the wife of Y saw her husband (Y) coming out of the neighbour‘s house at 6.00 am in the morning. Y told his wife X that he has murdered the neighbour and handed over the jewellery of that neighbour to his wife.
Facts: X who is the wife of Y saw her husband (Y) coming out of the neighbour‘s house at 6.00 am in the morning. Y told his wife X that he has murdered the neighbour and handed over the jewellery of that neighbour to his wife.
C X is not allowed to appear as a witness to depose what was told by the husband to her, however, she can depose what she saw
According to the principle, a spouse is not permitted to put in evidence in any court and as a result she will not be allowed to appear as a witness to depose what was told by the husband. Hence, the correct option is (c).
Question 47
Principle: Oral evidence must always be direct i.e. of the person who says he saw the event and hearsay evidence is no evidence.
Facts: X was told by Y (whom X trusts) that Z has murdered A (A) Statement of X is admissible
Facts: X was told by Y (whom X trusts) that Z has murdered A (A) Statement of X is admissible
B Statement of X is not admissible because he has not seen Z murdering A
Hearsay evidence is no evidence in the eyes of law and in this case statement of X is not admissible because he has not seen Z murdering A.
Question 48
Principle: Terms of any written contract can be proved by producing the written contract only and oral evidence is excluded.
Facts: A gives B receipt for money paid by B. Oral evidence is offered to prove payment. (A) Oral evidence to prove payment is allowed
Facts: A gives B receipt for money paid by B. Oral evidence is offered to prove payment. (A) Oral evidence to prove payment is allowed
A Oral evidence to prove payment is allowed
According to principle, terms of any written contract can be proved by producing the written contract and in this case oral evidence to prove payment is allowed making option (a) as the most appropriate choice.
Question 49
Principle: Employer is liable for the injury caused to the employee in the course of his employment.
Facts: X organized a party and hired a caterer. During the party, generator set went out of order and he requested one employee of caterer i.e. Y to bring the mechanic on his vehicle and promised to pay 1000 for the same to Y. Y met with an accident while going to fetch the mechanic and he seeks compensation.
Facts: X organized a party and hired a caterer. During the party, generator set went out of order and he requested one employee of caterer i.e. Y to bring the mechanic on his vehicle and promised to pay 1000 for the same to Y. Y met with an accident while going to fetch the mechanic and he seeks compensation.
A X is liable as Y was working in the course of employment offered by X
As X is the employer here and liable for any injury caused to the employee in due course of employment, then in this case he is liable for the accident occurred because he promised to pay 1000 rupees to Y for doing the work which makes Y his employee. So, the correct choice is option (a).
Question 50
Principle: Master is liable for the acts of his servant done in the course of his duties.
Facts: X hired an employee Y in his construction business. Y was the property in-charge who received construction material and gave receipts for the material received by him. Z claimed payment for cement supplied to X which was duly received by Y. X denied the payment on the ground that he has only received half of the material and the balance was misutilized by the employee Y.
Facts: X hired an employee Y in his construction business. Y was the property in-charge who received construction material and gave receipts for the material received by him. Z claimed payment for cement supplied to X which was duly received by Y. X denied the payment on the ground that he has only received half of the material and the balance was misutilized by the employee Y.
A X is liable for the entire amount
As Y is the employee of X and he have done this in due course of employment which makes X liable for the entire amount. So, the correct option is (a).
Section: Logical Reasoning
Question 1
If in English Alphabet 'e' and every alternate letter from 'e' onwards is written in Capitals, then how will sixth month from March will be coded
B SEptEMbEr
As per the instructions – the letters starting from “e” onwards will be used as shown below:-
So September will be written as SEptEMbEr. So the correct answer is “b”.
| E | f | G | h | I | j | K | l | M | n | O | p | Q | r | S | t | U | v | W | x | Y | z |
Question 2
If in a certain code, 'Clever; is written as 'XOVEVI', then 'Smart' would written as
B HNZIG
If we look at “Clever” “e” features twice and if we compare it with “XOVEVI” – “V” also features twice and in the same place as is “e” in Clever. So this is a simple coding in which C is X, l is O and so forth. The only common letter between Clever and “Smart” is “r”. We know that “r” is “I”. Hence we know that correct choice is “b” as “I” replaces “r” only in choice “b”
Question 3
Fill in the blank :
Q4RT, ______ , QRT6, QR7T, Q8RT
Q4RT, ______ , QRT6, QR7T, Q8RT
B QR5T
The simplest way to solve it is using numbers – the four numbers given to us are – 4, 6, 7 and 8. The missing number most likely is 5 which appears only is choice “b”.
The overall logic is number starts with 4, increases with +1 and it position shifts one place to the right till it reaches the extreme right and then its position shifts one place to the left.
Q4RT, QR5T, QRT6, QR7T, Q8RT
The overall logic is number starts with 4, increases with +1 and it position shifts one place to the right till it reaches the extreme right and then its position shifts one place to the left.
Q4RT, QR5T, QRT6, QR7T, Q8RT
Question 4
Fill in the blank :
257, 291, ______, 365, 405
257, 291, ______, 365, 405
C 327
The logic is 257 + 34 = 291, 291 + 36 = 327, 327 + 38 = 365, and 365 + 40 = 405. Hence, the answer is “c”.
Question 5
Manoj walks a distance of 5 meters towards North, then he turns to east and walks a distance of 10 meters. Then he turns to his right and covers a distance of 15 meters. He then turns to his left and covers a distance of 15 meters. Which direction is he facing now?
B East
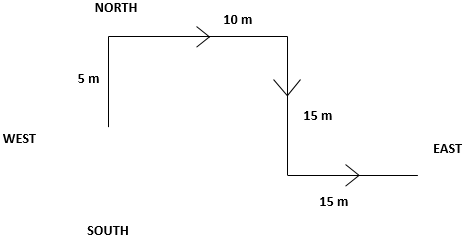
Question 6
A man introduces a girl as the daughter of the sister of his father. How the girl is related to the man
D Cousin
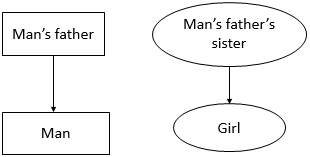
Question 7
Who is good in driving motorcycle, lorry and tempo?
C T
Using the information given we get the table as shown below:-
| Motor Cycle | Jeep | Lorry | Bus | Tempo | |
| P | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Q | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| R | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| S | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| T | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Question 8
Who is good in driving motor Cycle, Jeep and Lorry but not bus?
C P
Using the information given we get the table as shown below:-
As could be seen from the table, P is good at driving Motor Cycle, Jeep and Lorry but not bus.
| Motor Cycle | Jeep | Lorry | Bus | Tempo | |
| P | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Q | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| R | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| S | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| T | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Question 9
Who is good in driving Tempo, Motor Cycle, Lorry but not Jeep?
B T
Using the information given we get the table as shown below:-
As could be seen from the table, T is good at driving Tempo, Motor Cycle, Lorry but not Jeep.
| Motor Cycle | Jeep | Lorry | Bus | Tempo | |
| P | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Q | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| R | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| S | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| T | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Question 10
Who is good in driving all the vehicles?
A R
Using the information given we get the table as shown below:-
As could be seen from the table, R is good at driving all the vehicles.
| Motor Cycle | Jeep | Lorry | Bus | Tempo | |
| P | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Q | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| R | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| S | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| T | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Question 11
In a bag there are some gold coins. In another bag there are 1/3rd extra gold coins as compared to first bag. If the difference in the number of gold coins in first and second bag is 5, then how many coins are there in the first bag?
D 15
In such questions it is best to work from options. The correct choice has to be a multiple of 5. Choice “d” is the correct answer – one third of 15 is 5. This means the second bag as 5 more than the first bag which is what the information is also given.
Question 12
Examine the following numbers and identify the next number:
53, 50, 45, 38, 29, ______
53, 50, 45, 38, 29, ______
C 18
The logic is 53 – 3 = 50, 50 – 5 = 45, 45 – 7 = 38, 38 – 9 = 29. The final value will be 29 – 11 = 18.
Question 13
Examine the following numbers and identify the next number:
20, 30, 42, 56, 72, ______
20, 30, 42, 56, 72, ______
B 90
The logic is 20 + 10 = 30, 30 + 12 = 42, 42 + 14 = 56, and 56 + 16 = 72. The final value will be 72 + 18 = 90.
Question 14
The words in the bottom row are related in the same way as the words in the top row. Fill in the blank.
Rose, Flower, Plant
Flat, House, ______
Rose, Flower, Plant
Flat, House, ______
C Building
Rose is a flower and flower is a part of a plant. Similarly, flat is a house and house is a part of a building.
Question 15
The words in the bottom row are related in the same way as the words in the top row. Fill in the blank.
If Ocean: Waves, then Desert : ______
If Ocean: Waves, then Desert : ______
D Sand dunes
Just likes waves are formed in an ocean sand dunes are formed in a desert.
Question 16
If 1 × 7 = 8, 2 × 7 = 16, 3 × 7 = 24, 4 × 7 = 32, then what is value of 9 × 7?
B 72
The logic is 1 x 7(then +1) = 8, 2 x 7(then +2) = 16, 3 x 7(then +3) = 24, 4 x 7(then +4) = 32. The final value will be 9 x 7(then +9) = 72.
Question 17
Find the odd one out :
Onlookers, Theatre goers, Queue, Spectators
Onlookers, Theatre goers, Queue, Spectators
C Queue
Queue is the odd one out as the other three refer to people while queue refer to line of people.
Question 18
Find the odd one out :
Heart, Lungs, Kidney, Skin, Liver
Heart, Lungs, Kidney, Skin, Liver
A Skin
Other than Skin all organs are inside the body.
Question 19
Find the odd-man out:
A http://www.scholar.google.com
Only http://www.scholar.google.com has two words between www and .com.
Question 20
Find the odd one out:
C Mob
Other than mob all other are musical instruments.
Question 21
Which of the following day is the play day?
B Tuesday
Question 22
Physics day and Biology day have a gap of how many days between them?
D Four
Question 23
Which day is Social Science day?
C Wednesday
Question 24
Which day is Mathematics day?
D Thursday
Question 25
Which of the following is the correct statement?
A Biology day is after Chemistry day
Question 26
Which of the following is wrong?
C E will be to the immediate right of A
The given interpretation could be used in two ways:-
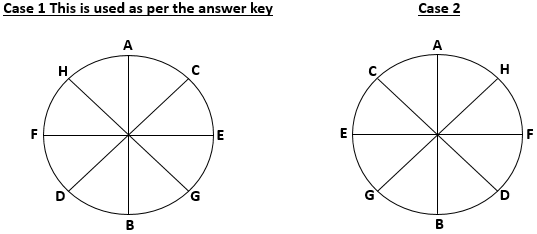
Because of this we will get two answers for two questions in this set:-
E is not the neighbor of A, hence choice “c” is incorrect.

Because of this we will get two answers for two questions in this set:-
E is not the neighbor of A, hence choice “c” is incorrect.
Question 27
Which of the following is correct?
B H will be to the immediate right of A
The given interpretation could be used in two ways:-

Correct choice as per the key is “b”. However even “d” could be correct as per case 2.

Correct choice as per the key is “b”. However even “d” could be correct as per case 2.
Question 28
A and F will become neighbours if:
D H agrees to change her sitting position
The given interpretation could be used in two ways:-

Correct choice as per the key is “d”. However even “b” could be correct as per case 2.

Correct choice as per the key is “d”. However even “b” could be correct as per case 2.
Question 29
During sitting:
C A will be directly facing B
The given interpretation could be used in two ways:-

In both the cases A will be facing B so choice “c” is correct.

In both the cases A will be facing B so choice “c” is correct.
Question 30
H will be sitting between:
B A and F
The given interpretation could be used in two ways:-

In both the cases H will be sitting between A and F, so choice “b” is correct.

In both the cases H will be sitting between A and F, so choice “b” is correct.
Question 31
Choose the set of three statements where the third statement can be logically derived from the preceding two.
Statements:
1. Some students love reading.
2. Some adults do not love reading.
3. Some students are not adult.
4. Some students are adult.
5. No reading lover is an adult.
6. Some men do not love reading.
The set of statements is:
Statements:
1. Some students love reading.
2. Some adults do not love reading.
3. Some students are not adult.
4. Some students are adult.
5. No reading lover is an adult.
6. Some men do not love reading.
The set of statements is:
B 1, 5, 3
Choice a - Conclusion 4 is Some students are adult. The counter of this statement is No student is an adult. Statement 3 – ‘Some students are not adults’ could also be interpreted as No student is an adult and since the counter of the conclusion can be proved choice “a” is not correct. For concept clarity refer to Eptitude’s theory.
Choice b – The counter of conclusion in 3 ‘Some students are not adults’ is All students are adults. Using the two statements in 1 and 5 we cannot prove the counter and hence choice “b” is the correct answer.
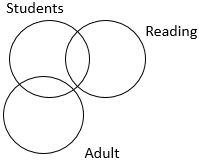
Choice b – The counter of conclusion in 3 ‘Some students are not adults’ is All students are adults. Using the two statements in 1 and 5 we cannot prove the counter and hence choice “b” is the correct answer.

Question 32
Choose the set of three statements where the third statement can be logically derived from the preceding two.
Statements:
1. All boys need books.
2. All girls need books.
3. Punjabis are girls.
4. Some Punjabis need book.
5. All boys are girls.
6. Some boys are Punjabis.
The set of statements is:
Statements:
1. All boys need books.
2. All girls need books.
3. Punjabis are girls.
4. Some Punjabis need book.
5. All boys are girls.
6. Some boys are Punjabis.
The set of statements is:
D 5, 2, 1
Choice a – The counter of conclusion in 1 ‘All boys need books’ is ‘Some boys do not need books’. This counter can be proved as is shown below by using the statements 5 and 4.
Hence choice “a” is not correct. Similarly we can prove the counter of choices “b” and “c”.
Choice d – The counter of conclusion in 1 ‘All boys need books’ is ‘Some boys do not need books’. We cannot prove this counter using 5 and 2.
Hence, choice “d” is correct.

Hence choice “a” is not correct. Similarly we can prove the counter of choices “b” and “c”.
Choice d – The counter of conclusion in 1 ‘All boys need books’ is ‘Some boys do not need books’. We cannot prove this counter using 5 and 2.

Hence, choice “d” is correct.
Question 33
Choose the set of three statements where the third statement can be logically derived from the preceding two.
Statements:
1. All human beings need education.
2. All teachers need training.
3. Education is provided by the teachers.
4. X is a teacher.
5. X needs training.
6. Students are future of a nation.
The set of statements is:
Statements:
1. All human beings need education.
2. All teachers need training.
3. Education is provided by the teachers.
4. X is a teacher.
5. X needs training.
6. Students are future of a nation.
The set of statements is:
C 2, 4, 5
Choice a -From 1 and 2 we don’t know whether X is a teacher or not and hence we cannot conclude 5 – ‘X needs training’.
Choice b -Same thing applies to choice “b” and hence this is also incorrect.
Choice c – The counter of conclusion in 5 ‘X needs training’ is ‘Some X does not need training’. Using 2 and 4 we cannot prove the counter.
Hence, choice “c” is correct.
Choice b -Same thing applies to choice “b” and hence this is also incorrect.
Choice c – The counter of conclusion in 5 ‘X needs training’ is ‘Some X does not need training’. Using 2 and 4 we cannot prove the counter.

Hence, choice “c” is correct.
Question 34
Each of the following questions has a main statement followed by four statements: 1, 2, 3, 4. Choose the ordered pair of statements where the first statement implies the second, and the two statements are logically consistent with the main statement.
Main statement: Only if the teaching standard is destroyed, will examination result be poor.
1. Examination result is poor.
2. Teaching standard is not destroyed.
3. Examination result is not poor.
4. Teaching standard is destroyed.
The ordered pair of statements is:
Main statement: Only if the teaching standard is destroyed, will examination result be poor.
1. Examination result is poor.
2. Teaching standard is not destroyed.
3. Examination result is not poor.
4. Teaching standard is destroyed.
The ordered pair of statements is:
A 2, 3
In Only A then B construct only two definite conclusion can be made.
Conclusion 1 – If A did not happen B will not happen.
Conclusion 2 - If B happened that means A would have happened.
In this question A is ‘if teaching standard is destroyed’ and B is ‘examination result will be poor’.
Choice “a”, that is, 2, 3 refers to Conclusion 1 and is the correct answer.
Conclusion 1 – If A did not happen B will not happen.
Conclusion 2 - If B happened that means A would have happened.
In this question A is ‘if teaching standard is destroyed’ and B is ‘examination result will be poor’.
Choice “a”, that is, 2, 3 refers to Conclusion 1 and is the correct answer.
Question 35
Each of the following questions has a main statement followed by four statements: 1, 2, 3, 4. Choose the ordered pair of statements where the first statement implies the second, and the two statements are logically consistent with the main statement.
Main statement: The computer will not work if operating system fails.
1. Operating system fails.
2. Operating system does not fail.
3. The computer does not work.
4. The computer works.
The ordered pair of statements is:
Main statement: The computer will not work if operating system fails.
1. Operating system fails.
2. Operating system does not fail.
3. The computer does not work.
4. The computer works.
The ordered pair of statements is:
D 4, 2
In If A then B construct only two definite conclusion can be made.
Conclusion 1 – If A happens B will happen.
Conclusion 2 - If B did not happen that means A would not have happened.
In this question A is ‘if operating system fails’ and B is ‘the computer will not work’.
Choice “d”, that is, 4, 2 refers to Conclusion 2 and is the correct answer.
Conclusion 1 – If A happens B will happen.
Conclusion 2 - If B did not happen that means A would not have happened.
In this question A is ‘if operating system fails’ and B is ‘the computer will not work’.
Choice “d”, that is, 4, 2 refers to Conclusion 2 and is the correct answer.
Question 36
Each of the following questions has a main statement followed by four statements: 1, 2, 3, 4. Choose the ordered pair of statements where the first statement implies the second, and the two statements are logically consistent with the main statement.
Main statement: Either X or Y will take the only computer in the room.
1. X took the computer.
2. Y did not take the computer.
3. X did not take the computer.
4. Y took the computer.
The ordered pair of statements is:
Main statement: Either X or Y will take the only computer in the room.
1. X took the computer.
2. Y did not take the computer.
3. X did not take the computer.
4. Y took the computer.
The ordered pair of statements is:
D 1, 2
As per this construct exactly one person will take the only computer in room.
Choice a – This is out as if 3 is true (X did not take the computer) then 4 (Y took the computer) should follow, instead 1 follows and so “a” is not the correct choice.
Correct choice given is “d”. However even “c” is correct.
Choice a – This is out as if 3 is true (X did not take the computer) then 4 (Y took the computer) should follow, instead 1 follows and so “a” is not the correct choice.
Correct choice given is “d”. However even “c” is correct.
Question 37
'All men are mortal and Victoria is a woman and hence Victoria is mortal'. This statement is:
B Logically Invalid
From the information given we can only make conclusion about men and their being mortal. Since Victoria is a woman we cannot make any conclusion about her being mortal or not and hence it is logically invalid. Due to lack of information we don’t know whether it is true or false.
Question 38
All men are chairs. John Doe is a man. In logical language, therefore:
A John Doe is a chair
Question 39
Identify the missing number:
1 and 3, 4 and 6, 7 and 9, …. and 12
1 and 3, 4 and 6, 7 and 9, …. and 12
A 10
The first number of the final term is missing. The relationship between first number (1) of the first term (1 and 3) and the first number (4) of the second term (4 and 6) is of +3. With the same logic the first term becomes 4 + 3 = 7. Applying the same logic to the final term the missing value becomes 7 + 3 = 10. Hence, choice “a” is the correct answer.
Question 40
Cobra: Snake :: Greyhound : ______
D Dog
Just like cobra is a type of various snakes, similarly greyhound is a type of various dogs.

